

Vol. 38 (Nº 33) Año 2017. Pág. 7
Zaur Namedinovich ISMIHANOV 1; Naida Omarovna OMAROVA 2; Patimat Gadzhievna ARIPOVA 3; Navrat Magomedsaidovna UMARGADZHIEVA 4; Magomed Sulajbangadzhievich MAGOMEDOV 5
Received: 30/05/2017 • Approved: 15/06/2017
ABSTRACT: The basic goal of the research was to study the interrelation of factors of the social and economic system of the region, to develop the cognitive map and to carry out the scenario forecasting of the situation development in the region on its basis. The work considers the methodology of cognitive modeling of social and economic systems. One of the approaches of cognitive modeling is the approach based on representing the modeled system as a signed-oriented graph (cognitive map) with the impulse distributed on it. The article structures the knowledge about the object (region) under research, reveals basic factors of the regional social and economic system, and forms a cognitive map of the region. The scenario forecasting of the situation development in the region is carried out on its basis. The scientific novelty lies in the development of the cognitive map for researching factors (social, economic and political) of the region in their interrelation that allows to carry out scenario forecasting of the situation development in the region depending on various managing impacts. Factors are revealed as a result of the conducted situational analysis. Basic conclusions of the research are related to revealing the factors that have the most positive and the most negative impacts on various indicators of the social and economic area development in the region. In particular, it is shown that when the negative impact of clannish and corrupted relations in the government and society decreases, and the labor potential is used efficiently, the revenues of the population increase. The article offers the recommendations on forming managing factors that have a positive impact on such indicators as region development, investment climate and revenues of the population. |
RESUMEN: El objetivo básico de la investigación fue estudiar la interrelación de factores del sistema social y económico de la región, desarrollar el mapa cognitivo y realizar el pronóstico de escenario del desarrollo de la situación en la región sobre su base. El trabajo considera la metodología del modelado cognitivo de los sistemas sociales y económicos. Uno de los enfoques del modelado cognitivo es el enfoque basado en representar el sistema modelado como un gráfico orientado a la señal (mapa cognitivo) con el impulso distribuido sobre él. El artículo estructura el conocimiento sobre el objeto (región) bajo investigación, revela los factores básicos del sistema social y económico regional y forma un mapa cognitivo de la región. El escenario de previsión del desarrollo de la situación en la región se lleva a cabo sobre la base de la misma. La novedad científica radica en el desarrollo del mapa cognitivo para la investigación de factores (sociales, económicos y políticos) de la región en su interrelación que permite llevar a cabo la predicción de escenarios del desarrollo de la situación en la región dependiendo de los diversos impactos de gestión. Los factores se revelan como resultado del análisis situacional llevado a cabo. Las conclusiones básicas de la investigación están relacionadas con la revelación de los factores que tienen los impactos más positivos y más negativos en varios indicadores del desarrollo del área social y económica en la región. En particular, se muestra que cuando el impacto negativo de las relaciones clanicas y corruptas en el gobierno y la sociedad disminuye, y el potencial de trabajo se utiliza de manera eficiente, los ingresos de la población aumentan. El artículo ofrece las recomendaciones sobre la formación de factores de gestión que tienen un impacto positivo en indicadores como el desarrollo de la región, el clima de inversión y los ingresos de la población. |
Over the recent years Russia has undergone considerable changes in all areas of the society development. The reforms that started in 1990s are going on now, too. However, many goals of these reforms did not lead to forming strong economy in the country and stabilization of the social and political situation.
As it is known, at the present time the Russian Federation (the RF) suffers certain pressure from the European Union and the USA. It is related to taking practical measures expressed as various sanctions. Such negative attitude affects the Russian economy and social area. Trading relations with the West were affected, investments decreased, the import of science-driven technologies and food to the country considerable fell. It is also possible to note great potential of threats from sanctions in the country banking. It is due to the considerable integration of this area in the global one that is actually controlled by the USA and its Western partners.
There are no doubts that the policy of foreign countries’ sanctions strengthens internal contradictions in the social and economic life of the country. The dependence on the foreign capital that ceased inflowing to the economy in the previous volumes causes a decrease in the production and reduction of food import. It causes an increase in demand and consequently the growth of prices for products. Low prices for petrol on the global market caused the increase in the budgetary deficit. It does not enable the government to fully fulfill its social obligations toward the population. There is a tendency related to decreasing real revenues of the population that intensifies the social tension in the society.
Russia was forced into various conflicts that take place beyond its borders. They include Syrian conflict, events in Ukraine, peace-support mission in the zone of the Nagorno Karabakh region, etc. One more peculiarity of the country development is also solving of some internal problems related to fighting against extremism and terrorism in some regions of the country. Anti-terrorist operations in such subjects of the Russian Federation as the Republic of Dagestan, Chechnya, Kabardino-Balkarian Republic, and Ingushetia have been taking place for above 20 years. All these peculiarities of the development and problems greatly affect the development of all areas of the society.
In such context of the country development, Russian regions, especially complicated regions with a low level of the economy development and high social instability become the most vulnerable pins.
Considerable attention must be paid to the management of the situation in regions and improvement of the population’s life quality. Welfare and progress of the country depend on the state of economy and social area of regions.
At the present time a lot of Russian regions are referred to depressive ones. There is an increasing tendency of the growth of the gap in the level of subjects of the Russian Federation. In this context it is necessary to focus efforts on developing and implementing an efficient model related to managing social and economic processes in regions. This model must take into account the whole diversity of economic, social, legal, ecological and other factors aiming at creating stable market economic and socially-focused space.
In the scientific literature there are many works devoted to the problem of analyzing, forecasting and managing regional social and economic processes. Researchers touch upon various areas related to analyzing regions development, revealing basic factors of managing the social and economic development of regions, implementing management solutions to eliminate negative tendencies of the region development (Kanischeva, 2014).
The works that offer how to solve issues related to the interrelation of the investment and innovational component of the region policy and estimation of the innovational potential are of great interest (Alklyichev 2014; Aliev, et. al. 2013; Ismihanov, et. al. 2014).
New approaches to estimating the efficiency of functioning of the production infrastructure of the region in the context of developing the strategy of its development are offered (Feraru and Dolgov 2014).
The urgency of estimating the social attractiveness of the region is stipulated, and methods of this estimation are offered (Popov and Kats 2014). Areas of efficient management of regions on the basis of considerable differences in their development are offered (Zhulanov 2011).
Works devoted to the issues on developing the infrastructure potential to increase stability of regional social and economic systems (Vdovin 2014) and monitoring the competitive environment are of special interest. On the basis of the Michael Porter’s (Porter and Ketels, 2003) approach, they consider peculiarities of the Russian regional competitiveness, analysis of the sectoral and territorial structure of economy that allows to objectively define promising areas of the region development, especially in the period of expected crisis phenomena (Belskih 2014).
A region as a territorial part of the economic system of the country pre-determines the need in deep study of peculiarities of its functioning and development. Such research of the region includes revealing and structuring the aggregate of factors that characterize it in terms of various positions (economy, social component, political processes, and innovational element). In this case there is a need to reveal, diagnose and give an adequate estimation for these factors in the context of indefiniteness and controversy of the processes that take place in the region. On this basis it is possible to develop efficient management solutions on strategic development of the region.
In this context works that offer various models of the mechanism of the regional economic system, formation of the region development strategies on the basis of diagnosing its state and forecasting situations cause interest (Guseynov, n. d.; Ivanova 2014; Petrosyants 2014).
They reflect problems on estimating the current state of the region, revealing factors that characterize the region in the context of social and economic, and social and political development, applying system analysis to solve tasks of stable development of the regional social and economic system. Such problems were also solved in the works of authors who offered cognitive technologies in combination with modern computer aids.
Over the recent 10-15 years a lot of works devoted to applying cognitive technologies to model social and economic systems of the region and forming strategies of their development have appeared (Avdeeva, et. al. 2007; Avdeeva 2010; Gorelova, et. al. 2006; (Ismihanov 2015; Ismihanov, et. al. 2015; Maksimov 2001; Petrosyants 2014; Popov and Kats 2014).
Basic areas in these works include researches related to issues on structuring knowledge about the research object, forming cognitive maps (models) and carrying out scenario forecasting of the situation development (Avdeeva, et. al. 2007; Avdeeva 2010; Ismihanov 2015; Popov and Kats 2014; Kochkarov and Salpagarov 2007; Peña, Sossa and Gutiérrez, 2007).
To a great degree a wide spread use of cognitive technologies in the analysis and forecasting of the development of the situation in regions is related to the fact that this tool allows to quickly and qualitatively (Gorelova, et. al. 2006):
- Estimate the situation and analyze the mutual impact of basic factors that define possible scenarios of the situation development,
- Develop the strategy of using the revealed tendencies of the social and political situation in interests of the country,
- Define possible mechanisms of the interrelation of members of the situation to achieve the goal of its development,
- Develop and stipulate areas of the situation management, and
- Define possible scenarios of the situation development taking into account consequences of taking extremely important decisions, and compare the scenarios (Bell, Raiffa and Tversky, 1988).
At the modern stage the issues related to researching the interrelation of many factors (political, economic, social, etc.) that characterize the region, revealing negative processes and generating management decisions for their adequate management by using cognitive technologies are definitely actual and require further scientific researches (Neocleous, Schizas and Papaioannou, 2011).
In the work we researched the interrelation of various factors of the Republic of Dagestan. This region is referred to very much complicated subjects of the RF with a low level of the industry development, unfavorable investment climate and complicated social and political situation. At the present moment issues related to monitoring and estimating key problems of the development are extremely important for the region. It is necessary to form strategic areas of overcoming the crisis situation and increasing the economic, labor and resourceful potential of the republic. Unfortunately, the Strategy of Developing the Republic of Dagestan for the Period up t0 2025 implemented over the recent 10 years has not solved the defined problems of the region.
This strategy pays great attention to issues related to analyzing the social and economic situation in the region (macro-economic indicators, labor market, international relations, tourism potential, power energy, etc.) and scenarios of development. When developing the latter, it is necessary to define the basic economic priorities for the nearest, medium-term and long-term perspective, and to provide the use of various forms of state support. To our mind the mechanism of implementing the optimal scenario of the region development is important in this issue.
However, in the research environment specialists have a lot of questions to the Strategy and mechanism of its implementation. They note that as a whole it has disadvantages.
In particular, it is possible to specify the following (Ahmedova 2013):
Firstly, it lacks a detailed analysis of basic social and economic indicators that define priorities.
Secondly, it was developed under entirely different social and economic conditions of the development and social and political situation in the region, country and the world, as a whole. At the present time they differ.
Thirdly, there is no any analysis of the defined vectors of the development, and there are almost no mechanisms to implement top priority areas of the development of the Republic of Dagestan.
Fourthly, the statistical base in the Strategy has greatly gone out of date. That is why at the present moment there is not adequate idea about the real situation in the economy.
It is impossible to work out the strategic area of the development without deep analysis of the republic peculiarities related to its social, economic, cultural, geographic and social dimensions.
Dagestan is referred to the most multi-national subject of the Russian Federation where representatives of above 100 nationalities live.
The Republic is one of those regions where geopolitical interests of various countries (Russia, Turkey, Iran, and Azerbaijan) are turned to.
Besides, the republic is the territory with “West-East” and “North-South” international transportation corridors of the country.
One of the important objects that form specific social and economic interests of various governmental and business groups is the Makhachkala Sea Trading Port. It is the only Russian port in the Caspian Sea that does not freeze and has a strategic location in the zone of “North-South” and “East-West” international transportation corridors. Besides, the airport is also an important object of the transportation infrastructure. It has a strategic meaning in the region, including for economically efficient passenger and transit freight transportation.
In the Republic of Dagestan like in all regions of the North Caucasian Federal District, the level of the shadow economy and corruption is very high. It is much higher than on average in the Russian Federation. The activity of processes related to terrorism and mobstery remains as high.
And, finally, modern social and economic and political processes in the Republic of Dagestan require the study in the context of shadow clannish and corporate relations that become system-forming factors of these processes. Moreover, the problem of the clannish nature greatly affects the development of democratic and civil institutes that often become secondary in favor of private interests of business.
Taking into account such specificity of the region, complication and controversy of processes that take place in it, weak economy and the other mentioned above peculiarities of the development, it is necessary to develop scientific approaches related to analyzing and monitoring regional factors, solutions on their strategic management.
The goal of the research is to carry out conceptual structuring of knowledge of the management group about the development of the situation in the region, formation of the cognitive map of the interrelation of factors of the region and carrying out scenario forecasting to form strategies of the region management (Axelrod, 1976; Carvalho and Tome Jose, 2009).
The cognitive approach that is the basis of the scenario modeling of the situation in the region assumes the implementation of the following stages:
Cognitive structuring of the knowledge about the object under research and internal environment for it is based on the PEST analysis and SWOT analysis.
Basic factors are selected by applying the situational analysis.
The situational analysis of problems or SWOT analysis lies in revealing
1) Strengths of the region (Strengths),
2) Disadvantages, weaknesses of the region (Weaknesses),
3) Opportunities of the region (Opportunities), and
4) Threats of the region development (Threats).
SWOT structuring of the social and economic system of the region is carried out to select important processes, areas, tendencies that will be taken into account when forming top priority areas of the region development, decrease in the negative impact of its disadvantages and threats. In our work SWOT analysis of the social and economic system of the region is interpreted as the research aiming at revealing and estimating advantages and disadvantages of the internal environment of the object under research, estimation of opportunities and potential threats on the part of the external environment.
Experts were involved to make this research. They included scientists, specialists and top managers of enterprises, organizations, and governmental bodies of the republic of Dagestan.
Further analysis lies in forming management solutions on the basis of the SWOT analysis. These solutions are a basis for developing top priority areas, decreasing negative impact of weak points, and protecting the system from threats. Besides, on the basis of this analysis it is possible to define what strong and weak points are essential depending on what conditions are formed in the external environment, and to define the priority of threats and opportunities depending on the state of the internal environment. The final estimation of factors of the internal environment (strong and weak points), factors of the external environment (threats and opportunities) allows to range them taking into account priorities. Using them, it is possible to allocate the resources between management solutions (strategies).
The final stage of the SWOT analysis is to reveal factors that characterize the problem situation, development of the social and economic system (environment) of the region. They will become the basis for forming concepts (tops) of the developed cognitive model.
The development of the cognitive model starts since forming the cognitive map that generally looks like (Ismihanov 2015):

![]() – curves that reflect the interrelation between these peaks (Figure 1).
– curves that reflect the interrelation between these peaks (Figure 1).
In order to form the cognitive map and carry out the scenario forecasting on its basis, we used the program system of cognitive modeling (CM PS).
The formed cognitive map of the situation is represented as a sign-oriented graph (Figure 1). Every graph is a scheme represented as peaks and arrows that connect them. Every arrow means a relation of two factors (“cause-effect”). The arrows are of two types: positive and negative.
The positive relation (“+” in the sign orgraph) points at the fact that an increase in the value of one factor causes an increase in the value of another factor the arrow is directed to. In case of the negative relation (“-“) it is considered that an increase in the value of one factor causes a decrease in the value of another factor. Cause and effect relations between the factors are determined on the basis of expert estimations by using active individual methods such as polling, interviewing methods, and free dialogue with the expert. Besides, the expert analysis used textological methods, too. They included methods of extracting knowledge based on studying texts from manuals, special references that made researches on social and economic, and social and political analysis and forecasting of the regional development.
After defining all cause and effect relations between factors, the future researches apply the sign orgraph for the scenario analysis and forecasting possible changes of the region situation. The dynamics of the situation processes is described by the system of the “If …, then…” productions equations (Kulba, Kononov, Kovalevskiy, Kosyachenko, Nizhegorodtsev and Chernov, 2002).
Table 1 represents the results of the SWOT analysis of the region (the Republic of Dagestan). Various factors on the basis of expert estimations are revealed and assessed. In our research the experts involved the leading researchers of the region and the country as a whole, specialists and top managers of various business structures and representatives of governmental structures of the region.
Table 1: SWOT – Analysis of the Estimation and Perspectives of Developing the Republic of Dagestan
Strengths (S) |
Weaknesses (W) |
1. Availability of great labor potential. Positive dynamics of the size of the population. |
1. Excess of labor forces, high level of unemployment. Low level of the population’s revenues. High level of the gap in the level of the material provision.
|
2. Good production base of enterprises of the industry |
2. High level of physical and moral tear and wear of the production equipment, engineering and utility infrastructure |
3. Advantageous near-border geo-political and geo-economical position |
3. Low level of inter-regional exchange and international relations. High donation nature of the budget
|
4. Great potential for the development of small-sized entrepreneurship |
4. Strong administratively corrupted pressure on business. Clannish nature in the system of economic relations. High level of the shadow economy |
5. Favorable natural and climate conditions for the development of the agro-industrial complex |
5. Technological arrearage of the industrial and agricultural production, low provision of enterprises with modern equipment |
6. Rich primary natural resources |
6. Great gap in the level of the social and economic development of municipal formations |
7. Tourism and recreational potential of the territory (sun, sea, mountains) |
7. Low investment attractiveness of the republic. Under-development of the infrastructure of the tourism and recreational complex. |
Opportunities (O) |
Threats (T) |
|
1. High level of unemployment and outflow of the qualified labor forces, creative youth and entrepreneurs. Distribution of ideas related to the religious extremism. |
2. Efficient use of the production capacities potential. |
2. Low financing from the local and federal budgets for developing the production infrastructure. |
3. Efficient use of the geo-economic position and international transportation corridor North – South for developing external economic relations and integration in the global market. |
3. Arrearage of the transportation infrastructure development from needs and tempos of the regional economy development, as well as from other regions.
|
4. Formation of the favorable entrepreneurial and investment climate, equaling the terms and conditions of the competition. Extending and strengthening the taxation base at the expense of legalizing the shadow economy. |
4. Extending the clannish nature in the economy. Presence of a narrow circle of people associated with the government, their impact on the greater part of the primary, financial, and budgetary opportunities of the republic. |
5. Development of areas related to processing agricultural product and extending the market of domestic products. |
5. Food dependence on Russian regions and import from foreign countries.
|
6. Equaling social and economic indicators of the development of the republic regions and cities. |
7. High tempos of the growth related to the tourism development in other regions. |
7. Use of the tourism and recreational potential and development of the cultural and leisure business. |
Source: Compiled by the authors
The strengths are considered as competitive advantages that can make up the basis of the perspective strategy of the region stable development. Weak points are efficient factors that decrease the efficiency of the economic and social policy pursued by state authorities of the republic.
The threats are negative factors that can really restrain tempos of the economic and social development of the region. Their correct estimation and taking proactive measures on the federal and regional level through the initiative and subject to efficient participation of bodies of the executive and legislative power of the republic can really reduce their negative effect.
Analyzing the results of the SWOT analysis, we offer basic factors of the region (Table 2) that made up the basis of the developed cognitive map (Figure 1).
Table 2: List of Basic Factors Characterizing the Region (Republic of Dagestan)
Development in Terms of Economy, Social Area, and Social and Political Situation
Factors |
Factors content |
V1 |
Labor potential |
V2 |
Level of unemployment |
V3 |
Geopolitical and geo-economical position |
V4 |
Inter-regional exchange and external economic relations |
V5 |
Level of technical provision of the industrial and agricultural production |
V6 |
Tourism and recreational potential |
V7 |
Investment attractiveness |
V8 |
Clannish and corrupted nature of the relations in the government and society |
V9 |
Nature and resource potential |
V10 |
Level of the population’s revenues |
V11 |
Resources and reserves for the development of small entrepreneurship |
Cognitive model of the region is a sign-oriented graph where
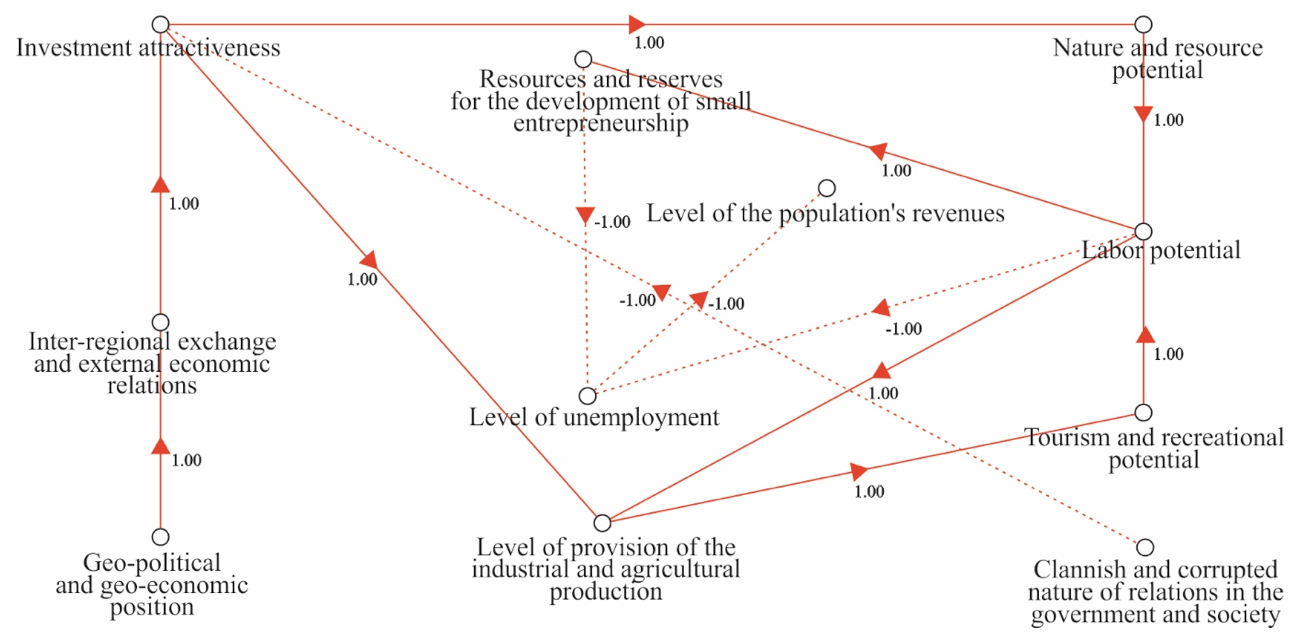
Figure 1: Cognitive Map of Interrelation of Factors of the Region
Solving the research tasks by using the results of cognitive modeling can be reduced to attempts to estimate (forecast) various scenarios of the situation development in the region (the Republic of Dagestan) on the basis of the analysis and modeling of mutual impacts of the determined factors (Table 3).
The scenario in the context of our research is an aggregate of tendencies that characterize the situation in the region at the present time, the desired goals of the development (improvement of the investment climate, the decrease in the corrupted pressure on business, the decrease in the shadow economy, etc.), a complex of measures that have an impact on the development of the situation, and a system of the apparent parameters (factors) that show the conduct of processes.
The scenario can be modeled according to three basic areas (Gorelova, et. al. 2006).
When analyzing the current state of such a complicated situation in the region, the researcher has inevitably to answer the following questions:
The model can be researched under various initial data (indicators of the high quality state of the system elements (factors) and parameters of the links resistance) about the state of the system and impulse impacts enclosed to various peaks (factors). It will allow to make the most veracious conclusions about the conduct of the researched system (region) under various conditions of external impacts (managing factors).
Managing impacts are the basic tool to increase values of indicators of the high quality state of elements (factors) of the system.
Using the cognitive map that we developed will allow to see the methods to manage the situation in the region that seem to be not so obvious at the first glance.
Table 3: Plan of Scenario Modeling of the Regional System Conduct
Scenario |
Impulse |
V1 |
V2 |
V3 |
V4 |
V5 |
V6 |
V7 |
V8 |
V9 |
V10 |
V11 |
No. 1 |
QV3, QV8 |
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
|
No. 2 |
QV3, QV8 |
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
No. 3 |
QV3, QV8 |
|
|
-1 |
|
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
No. 3 |
QV3, QV8, QV1 |
+1 |
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
Figures 2-5 show the graphs of impulse processes.
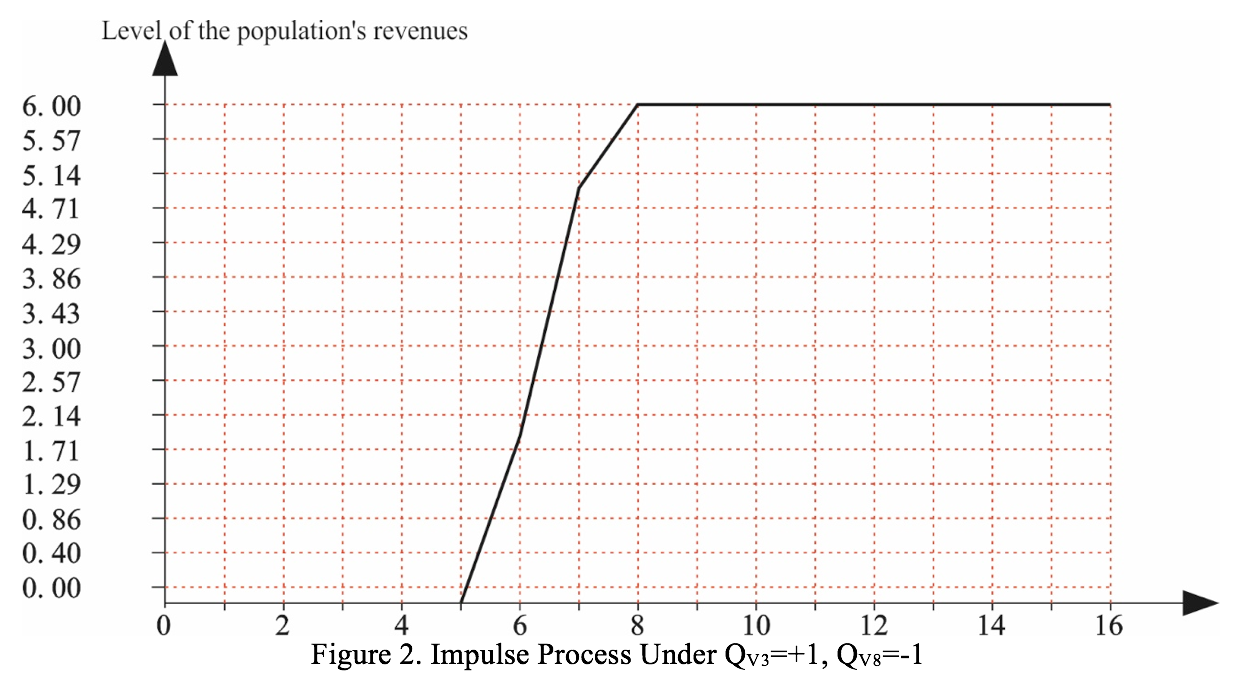
Scenario No. 1. The impulses come from peaks V3 and V8 (QV3=+1, QV8=-1). It means modeling of the situation when there is efficient use of the geo-economic position and North - South international transportation corridor for developing external economic relations and integrating in the global inter-regional markets. At the same time the negative impact of clannish and corrupted relations in the government and society decreases. It is necessary to note that the population’s revenues starting since the 5th to the 8th modeling step increase very quickly. Herewith, since the 8th step it is possible to observe the tendency of stable conduct without the growth and decrease.
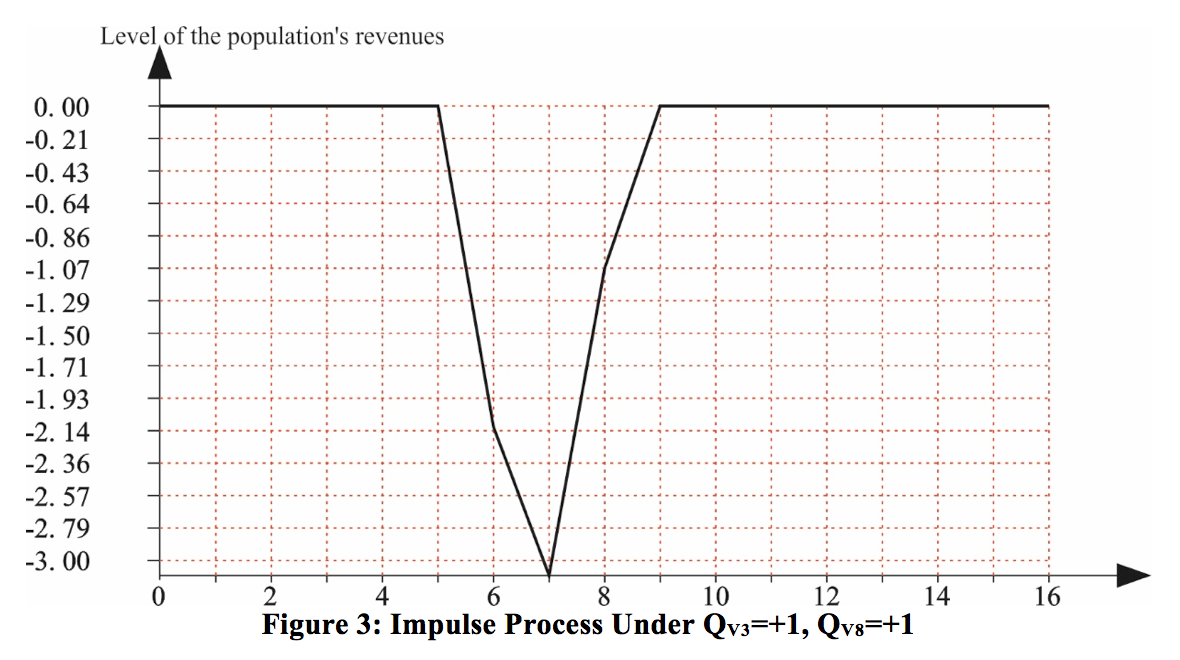
Scenario No. 2. The impulses come from peaks V3 and V8 (QV3=+1, QV8=+1). It means modeling of the situation when there is efficient use of the geo-economic position and North - South international transportation corridor for developing external economic relations and integrating in the global inter-regional markets. However, at the same time the negative impact of clannish and corrupted relations in the government and society is strengthened. It is necessary to note that the revenues of the population up to the 5th step neither increase nor decrease. Since the 5th to the 8th step they fall down very quickly. Herewith, since the 7th step it is possible to observe the tendency of their increase to the level of the 9th step. After that we again note stable conduct on the same level without increase and decrease.
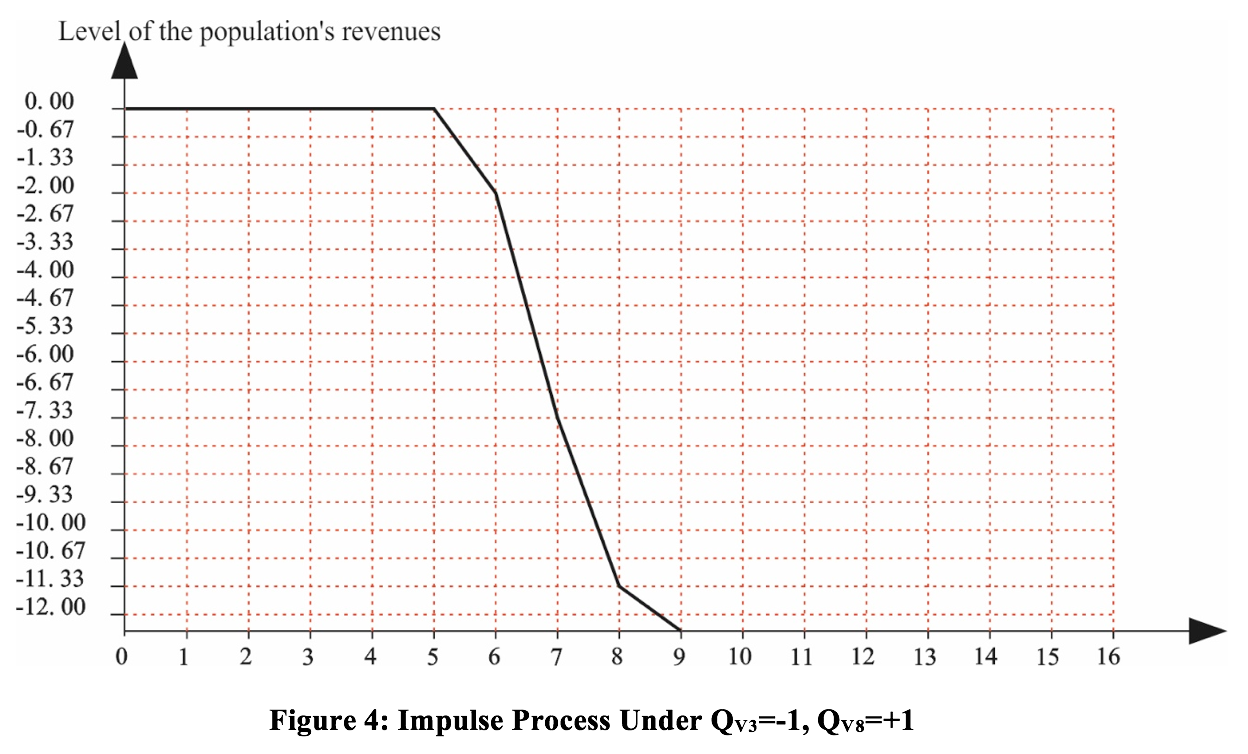
Scenario No. 3. The impulses come from peaks V3 and V8 (QV3=-1, QV8=+1). It means modeling of the situation when there is inefficient use of the geo-economic position and North - South international transportation corridor for developing external economic relations and integrating in the global inter-regional markets. Besides, at the same time the negative impact of clannish and corrupted relations in the government and society is strengthened. It is necessary to note that the population’s revenues up to the 5th step neither increase nor decrease. Starting from the 5th to the 9th step of modeling they fall down very quickly, and their further conduct tendency is not observed.
Scenario No. 1. The impulses come from peaks V3, V8, V1 (QV3=+1, QV8=-1, QV1=+1). It means modeling of the situation when there is efficient use of the geo-economic position and North - South international transportation corridor for developing external economic relations and integrating in the global inter-regional markets. At the same time the negative impact of clannish and corrupted relations in the government and society decreases, and the labor potential of the region is used the most efficiently. In this case the population’s revenues increase since the 2nd to the 6th step of modeling. Then they grow very quickly since the 6th to the 9th step. Herewith, since the 9th step it is possible to observe the tendency of stable conduct without the growth and decrease.
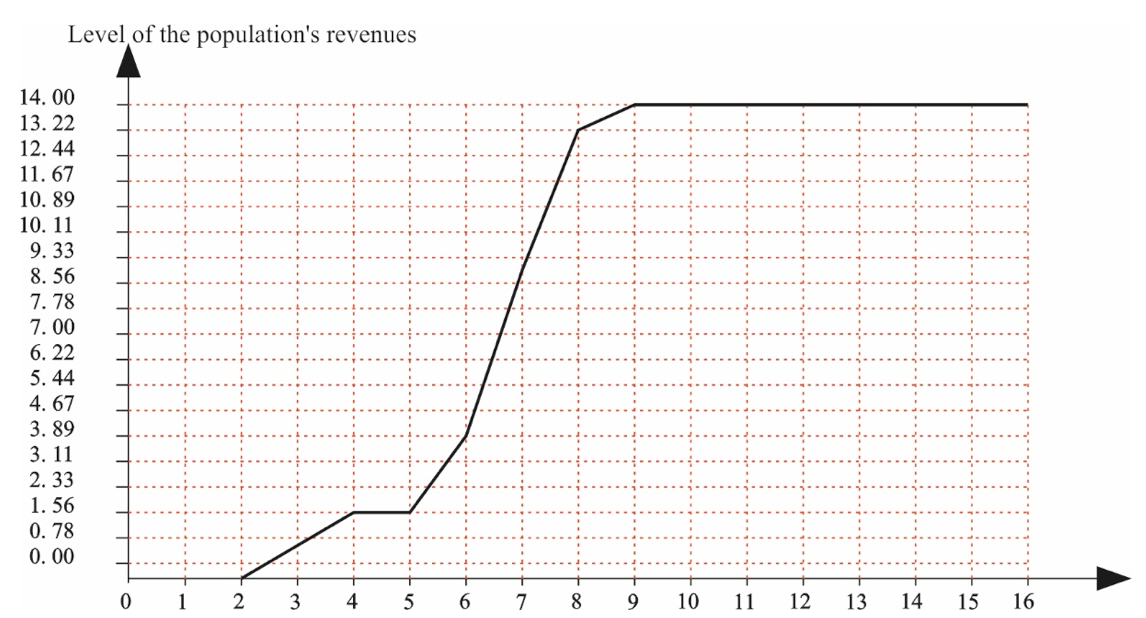
Figure 5: Impulse Process Under QV3=+1, QV8=+1, QV1=+1
In the nearest future the basic goal of the policy in regions of the Russian Federation must become the transfer to the stable level of social and economic position, renewal of the economic growth in every region, development of modern productions, increase in the population’s welfare and creation of conditions for the progress.
Herewith, it is necessary not to violate the principles of stable development when developing the economy and social area of the region.
The research of problems of such development of regions defines solving tasks of the strategic planning of their development and selecting practical approaches related to managing regions. Solving such tasks on the modern stage requires the use of such technologies that would allow to make the comprehensive analysis of the previous and current tendencies in the region, diagnose the state, develop strategies of developing and mechanisms of managing, and estimate possible consequences of the taken decisions.
It stipulates the urgency of the researches on the basis of applying cognitive technologies, methods of system analysis, and use of informational technologies.
In our research the cognitive approach offered by us through the example of diagnosing and estimating the most considerable factors of the region development factors allowed
Ahmedova, M.R., 2013. Regionalnaya politika Respubliki Dagestan kak chast natsionalnoy strategii sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya [Regional Policy of the Republic of Dagestan as a Part of National Strategy of the Social and Economic Development]. Basics of Economy, Management and Law, (10): 4-9.
Aliev, B.H., M.G. Alimirzoeva and Z.K. Dzhafarova, 2013. Investitsionnyiy protsess i ego vliyanie na konomiku Respubliki Dagestan Regionalnaya ekonomika: teoriya i praktika». [Investment Process and Its Impact on Economy of the Republic of Dagestan]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 5(284): 2-9.
Alklyichev, A.M., 2014. Innovatsionnaya politika regionov Rossiyskoy Federatsii v tselyah privlecheniya investitsiy i vozmozhnosti ee realizatsii [Innovational Policy of Russian Regions to Attract Investments and Opportunities of Its Pursuing]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 3(330): 2-10.
Avdeeva, Z.K., 2010. Evristicheskiy metod kontseptualnoy strukturizatsii znaniy pri formalizatsii slabostrukturirovannyih situatsiy na osnove kognitivnyih kar [Heuristic Method of Conceptual Structuring of Knowledge When Formalizing Slightly Structured Situations on the Basis of Cognitive Maps]. Managing Large Systems, 31 (3): 6-34.
Avdeeva, Z.K., S.V. Kovriga and D.I. Makarenko, 2007. Kognitivnoe modelirovanie dlya resheniya zadach upravleniya slabostrukturirovannyimi sistemami (situatsiyami) [Cognitive Modeling to Solve Tasks Related to Managing Slightly Strucutred Systems (Situaitons)]. Managing Large Systems, 16: 26-39.
Axelrod, R., 1976. The Cognitive Mapping Approach to Decision Making. Structure of Decision. The Cognitive Maps of Political Elites, Eds., Axelrod, R. Princeton: Princeton University Press, pp: 400.
Bell, D.E., H. Raiffa and A. Tversky, 1988. Decision Making: Descriptive, Normative and Prescriptive Interactions. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp: 9-33.
Belskih, I.E., 2014. Krizis regionalnoy ekonomiki 2015–2017 gg. v Rossii: poisk alternativ razvitiya [Crisis of Regional Economy in 2015-2017 in Russia: Searching for Development Alternatives]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 26(353): 2-10.
Carvalho, J. P. and A.B. Tome Jose, 2009. Rule Based Fuzzy Cognitive Maps in Socio-Economic Systems. In the 2009 Proceedings of IFSA-EUSFLAT: 1821–1826.
Feraru, G.S. and A.S. Dolgov, 2014. Metodicheskie podhodyi k otsenke effektivnosti funktsionirovaniya proizvodstvennoy infrastrukturyi regiona v kontekste razrabotki strategii ee razvitiya [Methodological Approaches to Estimating Efficiency of Functioning the Production Infrastructure of the Region in the Context of Developing Strategies of Its Development]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 17(344): 9-16.
Gorelova, G.V., E.N. Zaharova and S.N., 2006. Issledovanie slabostrukturirovannyih problem sotsialno- ekonomicheskih sistem: kognitivnyiy podhod [Researching Slightly Structured Problems of Social and Economic Systems: Cognitive Approach]. Rostov-on-Don: Publishing House of the Rostov State University, pp: 332.
Guseynov A.G. Innovatsionnaya sostavlyayuschaya v razrabotke strategiy sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya regionov [Innovational Component in Developing Strategies Related to Social and Economic Development of Regions]. Strategy of Economic Development of the Republic of Dagestan up to 2020, Eds., Kamilov, I.K.. Makhachkala: Publishing House of GUP “Tipografiya DNC RAN”, pp: 941-956.
Ismihanov, Z.N., 2015. Modelirovanie sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya regiona na osnove kognitivnogo podhoda [Modeling Social and Economic Development of the Region on the Basis of the Cognitive Approach]. Business Informatics, 2 (32): 59-68.
Ismihanov, Z.N., G.U. Magomedbekov and M.A. Magomedova M.A., 2014. Kognitivnyiy podhod k issledovaniyu faktornogo kompleksa religioznogo ekstremizma (na primere Respubliki Dagestan) [Cognitive Approach to Researching Factorial Complex of the Religious Extremism (Through the Example of the Republic of Dagestan)]. Modern Problems of Science and Education, 6. Date Views: 30.09.2016 www.science-education.ru/ru/article/view?id=23701.
Ismihanov, Z.N., P.G. Aripova and S.A. Nazhmutdinova, 2015. Issledovanie vzaimosvyazi faktorov sotsialno-ekonomicheskoy sistemyi regiona na osnove kognitivnoy tehnologii [Researching Interrelation of Factors of the Social and Economic System of the Region on the Basis of Cognitive Technology]. Modern Problems of Science and Education, 2-3. Date Views 30.09.2016 www.science-education.ru/ru/article/view?id=23701.
Ivanova, I.A., 2014. Modelirovanie i prognozirovanie osnovnyih indikatorov innovatsionnoy deyatelnosti regionov Rossiyskoy Federatsii [Modeling and Forecasting Basic Indicators of Innovational Activity of Russian Regions]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 27(354): 9-14.
Kanischeva, M.A., 2014. Soglasovannost investitsionnoy i innovatsionnoy politik kak faktor razvitiya regiona [Coherence of Investment and Innovational Policies as a Factor of the Region Development]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 3(330): 12-16.
Kochkarov, A.A. and M.B. Salpagarov, 2007. Kognitivnoe modelirovanie regionalnyih sotsialno-ekonomicheskih sistem [Cognitive Modeling of Regional Social and Economic Systems]. Managing Large Systems, 16: 137-145.
Kulba, V.V., D.A. Kononov, S.S. Kovalevskiy, S.A. Kosyachenko, R.M. Nizhegorodtsev and I.V. Chernov, 2002. Stsenarnyiy analiz dinamiki povedeniya sotsialno-ekonomicheskih sistem [Scenario Analysis of Dynamics of the Social and Economic Systems Conduct]. Moscow: V.A. Trapeznikov Institute of Management, pp: 122.
Maksimov, V.I., 2001. Kognitivnyie tehnologii – ot neznaniya k ponimaniyu // Kognitivnyiy analiz I upravlenie razvitiem situatsiy (CASC'2001) [Cognitive Technologies – From Lack of Knowledge to Understanding (CASC'2001)]. Moscow: IPU RAN, pp: 4-41.
Neocleous, C., C. Schizas and M. Papaioannou, 2011. Fuzzy Cognitive Maps in Estimating the Repercussions of Oil/Gas Exploration on Politico-Economic Issues in Cyprus. In the Proceedings of 2011 IEEE 26.International Conference on Fuzzy Systems: 1119–1126. Date Views 07.09.2016 ieeexplore.ieee.org/ xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber=5976945.
Peña, A., H. Sossa and A. Gutiérrez, 2007. Cognitive Maps: an Overview and Their Application for Student Modeling. J. Comp. y Sist., 10 (3): 230-250. (Jan./Mar. 2007), (230-250), ISSN: 1405-5546.
Petrosyants, V.Z., 2014. Strategicheskoe regulirovanie razvitiya problemnyih regionov v sostave Severo-Kavkazskogo federalnogo okruga [Strategic Regulation of the Development of Problematic Regions within the North Caucasian Federal District]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 2(329): 2-12.
Popov, E.V. and I.S. Kats, 2014. Strategii povyisheniya sotsialnoy privlekatelnosti regionov [Strategies to Increase Social Attractiveness of Regions]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 21(348): 2-15.
Porter, M.E. and C.H.M. Ketels, 2003. UK Competitiveness: Moving to the Next Stage, DTI Economics. Paper 3, London: Department of Trade and Industry.
Vdovin, S.M., 2014. Razvitie infrastrukturnogo potentsiala v tselyah ustoychivogo razvitiya regiona [Development of Infrastructural Potential for the Purpose of Stable Development of the Region]. Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 25(352): 10-19.
Zhulanov, E.E., 2011. Upravlenie sotsialno-ekonomicheskoy asimmetriey regionov kak faktor ekonomicheskogo rosta [Managing Social and Economic Asymmetry of Regions as Factor of Economic Growth]. Managing Large Systems, 32: 131-154.
1. "Dagestan State University" Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education, 43 "a", Gadjiev St., Makhachkala, 367000, Republic of Dagestan, Russian Federation. Email: zaur_7979@mail.ru
2. "Dagestan State University" Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education, 43 "a", Gadjiev St., Makhachkala, 367000, Republic of Dagestan, Russian Federation
3. "Dagestan State University" Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education, 43 "a", Gadjiev St., Makhachkala, 367000, Republic of Dagestan, Russian Federation
4. "Dagestan State University" Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education, 43 "a", Gadjiev St., Makhachkala, 367000, Republic of Dagestan, Russian Federation
5. "Dagestan State University" Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education, 43 "a", Gadjiev St., Makhachkala, 367000, Republic of Dagestan, Russian Federation