

 Vol. 38 (Nº 50) Año 2017. Pág. 28
Vol. 38 (Nº 50) Año 2017. Pág. 28
Emilia P. KOMAROVA 1; Alexander S. FETISOV 2; Tatiana V. LARINA 3; Olga V. GALUSTYAN 4
Recibido: 24/07/2017 • Aprobado: 23/08/2017
ABSTRACT: The paper is devoted to the problem of working out a health saving environment. It describes the developed program for the elaboration of physical culture of the individual to preserve and to promote health. The advantages and disadvantages of this program are analyzed. An integrated health assessment system is proposed in the paper. |
RESUMEN: El documento está dedicado al problema de la elaboración de un entorno de ahorro de salud. Describe el programa desarrollado para la elaboración de la cultura física del individuo para preservar y promover la salud. Las ventajas y desventajas de este programa son analizadas. En el documento se propone un sistema integrado de evaluación de la salud. |
Education in the modern world is undergoing significant changes (Galustyan, O.V., 2015, 2017; Fontoura F. B. B. et.al., 2016; Stošić, L. and Stošić, I., 2013; Uryadova T. et.al., 2017; Villarreal J.L. et al., 2016). Global changes in the social and economic structure, evident contradictions between the society and the educational system demand natural resources and sharp deterioration of environment due to their usage. It provides constant development, preservation and improvement of school children health support. The problem of school children health support becomes very urgent within the scope of the strategic goal. The problem of preventive work and health deflections of school children is extremely urgent due to the changes of the value system in education and its humanization, preserving health and workability in the system of health support technology of educational process of the school.
The paper is devoted to the changes dealing with globalization of education and its constant development. All these processes influence all spheres of personality's activity and it is especially important to develop strategic approaches to health saving technologies in the educational institutions. In this connection, there is a need to establish a system of education aimed at sustainable human development, providing the possibility of participation of everyone in solution and prevention of social, economic and environmental problems. A lot of scientists (Dowda M. et al., 2011; Pate R. R. and O’Neill J. R., 2011, 2012; Pate R. R. et al., 1990, 2006; Sallis J. F. and McKenzie T. L., 1991) who devoted their papers to the physical training education suggest that physical culture and physical training are closely connected with the health of school children. However, the problem of theoretical explanation and practical use of health support technologies in education, training and everyday life of school children has not been fully developed yet. This problem becomes especially important due to ecological situation deterioration in the world. That is why the creation of health saving educational environment of the school is urgent nowadays.
It is necessary to follow the conceptual ideas of different scientific approaches by integrating pedagogical theories for solving personality health support problem. The authors (Kakorina E.P and Rudiakova S.E., 2011; Stefanik R., 2014) suggest that there is a close interconnection of such tendencies in education as humanization, professionalization and fundamentalization. The prevailing point of different points of view of Russian scientists (Aghajanian N.A., 1983; Fetisov A.S., 2013; Kakorina E.P and Rudiakova S.E., 2011; Vinogradov P.A., 1996) is emphasis on systemic formative character of physical training education, developing of school children' personality and individuality based on physical culture.
The health saving educational environment of the school is considered as a combination of social, psychological and hygienic factors as well as psychological and pedagogical conditions based on realizing of personality's adaptive possibilities, preserving and strengthening health of school children (Katzmarzyk P.T. et al., 1998; Pate R. R. et al., 1990; Sallis J. F. and McKenzie T. L.,1991; Sallis J. F. et al., 1993; Taylor W. and Baranowski T., 2013). The analysis of the research works (Aghajanian N.A., 1983; Fetisov A.S., 2013; Vinogradov P.A., 1996; Kakorina E.P and Rudiakova S.E., 2011) revealed that in Russian school physical culture is a compulsory subject which is taught twice a week. The curriculum consists of two parts such as physical exercises and theoretical information. Exercises between the lessons are called "physical minutes" which are organized during the breaks. The improved program of physical culture included gymnastics, track and field athletics, skiing training, outdoor games, swimming. But the lessons organization was not well planned and the equipment used was outdated.
This paper examines the problem of the health saving educational environment and gives the description of the developed program of the formation of a personality's physical training culture. The main goal of the program is to preserve health which in its turn leads to the improvement of school children physical training culture which provides rational studies organization. There are six aspects of this program:
• prophylaxis and medical inspection, detection of early health deviations;
• physical education and culture; the goal of this aspect is realized by the measures leading to the improvement of school children' physical culture education;
• healthy lifestyle which includes rational nourishment and improvement of school children' leisure;
• complex value of the state of life which includes systematic testing at the beginning and at the end of academic year;
• school facilities; this aspect is developed with the purpose to provide sport gyms and necessary training equipment;
• education; the aspect includes measures for improving, organizing and introducing theoretical information.
This study presents the results of implementing the program of forming physical training culture of a personality aimed at saving health which leads to improvement of school children physical training culture. The participants of this study are the school children of the seventh and eighth grades (Voronezh, Russian Federation). Total amount of the participants was 173 (84 boys, 89 girls). This complex program of physical training culture of a personality on saving and strengthening the health developed by Fetisov A.S. (2013) includes health level rates which makes it possible to estimate physical level of the school children' health. This program allows to monitor blood pressure, vital capacity of the length. The results of the study are revealed in tables 1, 2, 3, 4.
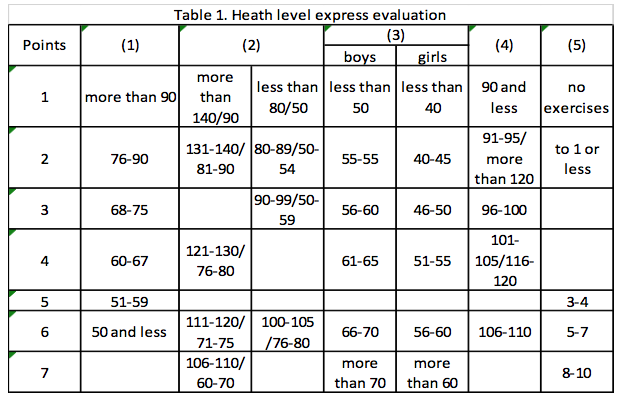
NOTE (I) - heart rate at rest, beats per minute (BPM); (2) - blood pressure at rest,
millimeter of mercury (mmHg), (3) - vital capacity of the lungs, ml/kg; (4) - height and
weight index. This characteristic can be used instead of (3); (5) - previous experience of
making up exercises is not less than twice a week during 20 min and more.
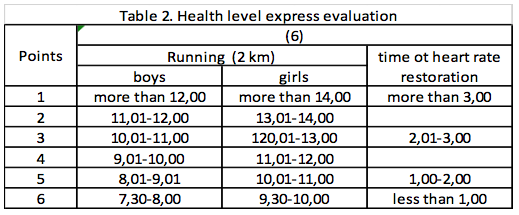
NOTE. (6) - general endurance
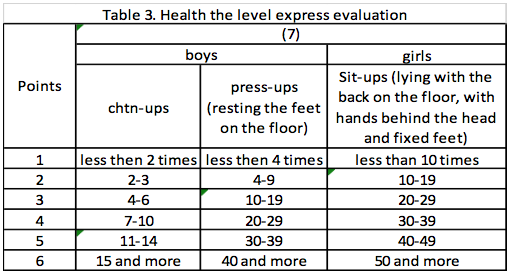
NOTE. (7) - power endurance
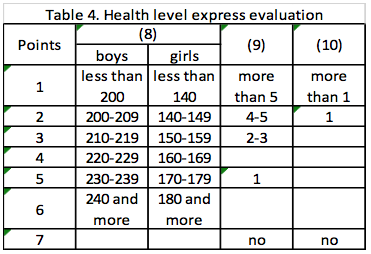
NOTE. (8) - jumps in length from the place; (9) - number of
colds per a year; (10)- number of chronical diseases.
Tables 1-4 contain the most informative and simple characteristics for quick determination of the health level. This level corresponds to the average of quantity of the following points: very high level - 5,0 and above; high level - 4,0-4,9; medium level - 3,0-3,9; low level - 2,0-2,9; very low level -1,0-1,9 points. Then each characteristic is considered in more details.
The analyzed data in this paper show that the development program of physical training culture in the sphere of educational environment of the school helps to preserve health of school children, its prophylactic leads to improvement of their physical state that provides rational organization of study.
The system of the health express includes level rates the complex evaluation of physical training culture of the personality helps to detect weak links in an organism for purposeful influence, to work out an individual program of improving exercises and estimate their efficiency, to prognosticate the risk of occurrence of hazardous to life diseases.
AGHAJANIAN N.A. (1983). Adaptation and Body Reserves. Physical Culture and Sport, 174.
DOWDA M., PFEIFFER K. A., BROWN W. H., MITCHELL J. A. (2011). Parental and Environmental Correlates of Physical Activity of Children Attending Preschool. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med., 165(10), 939-944.
FETISOV A.S. (2013). Health-saving Educational School Environment: History and Nowadays. AIST, 175.
FONTOURA F. B. B., WITTMANN M. L., FRIEDERICH L. R., SCARANO T. (2016). Educação contábil: Um ensaio sobre o ensino de contabilidade e o cotidiano da profissão. Revista Espacios, 37(33), 20. Retrieved from http://revistaespacios.com/a16v37n33/16373320.html
GALUSTYAN, O. V. (2015). Digital Campus as Electronic Image of the University. Rupkatha Journal on Interdisciplinary Studies in Humanities, 7(3), 263-270. Retrieved from http://rupkatha.com/V7/n3/28_digital-campus.pdf
GALUSTYAN, O. V. (2017). Some Methodological Aspects of the Evaluation of Students’ Educational Achievements at University. (IJCRSEE) International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education, 5(1), 43-48. Retrieved from http://www.ijcrsee.com/index.php/ijcrsee/article/view/278
KAKORINA E.P, RUDIAKOVA S.E. (2011). The Development of Mass Physical Culture and Sports in the Constituent Entities of the Russian Federation as a Factor of Formation of the Healthy Life Style. Vopr. Kurortol. Fizioter. Lech. Fiz .Kult., (6), 49-50.
KATZMARZYK P.T., MALINA R.M., SONG T.M, BOUCHARD C. (1998). Physical Activity and Health-related Fitness in Youth: a Multivariate Analysis. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 30(5), 709-714.
PATE R. R., DOWDA M., ROSS J. G. (1990). Associations Between Physical Activity and Physical Fitness in American Children. Am. J. Dis. Child., 144(10), 1123-1129.
PATE R. R., O’NEILL J. R. (2012). Physical Activity Guidelines for Young Children: An Emerging Consensus. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med., 166(12), 1095-1096.
PATE R. R., O’NEILL J. R. (2011). Youth Sports Programs: Contribution to Physical Activity. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med., 165(4), 369-370.
PATE R. R., STEVENS J., PRATT C., SALLIS J. F., SCHMITZ K. H., WEBBER L.S., WELK G., YOUNG D. R. (2006). Objectively Measured Physical Activity in Sixth-Grade Girls. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med., 160(12),1262-1268.
PATE R. R., WANG C., DOWDA M., FARRELL S. W., O’NEILL J. R. (2006). Cardiorespiratory Fitness Levels Among US Youth 12 to 19 Years of Age: Findings From the 1999-2002 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med., 160(10), 1005-1012.
SALLIS J. F., MCKENZIE T. L. (1991). Physical Education’s Role in Public Health. Physical Education, 62(2), 124-137.
SALLIS J. F., MCKENZIE T. L., ALCARAZ J. E. (1993). Habitual Physical Activity and Health-Related Physical Fitness in Fourth-Grade Children. Am. J. Dis. Child., 147(8):890-896.
STEFANIK R. (2014). Social and Political Aspects of Physical Culture in the Soviet Union in the Years 1917–1939. Central European Journal of Sport Sciences and Medicine, 8(4), 123–128.
STOSIC, L., STOSIC, I. (2013). Diffusion of Innovation in Modern School. (IJCRSEE) International Journal of Cognitive Research In Science, Engineering And Education, 1(1), 5-13. Retrieved from http://ijcrsee.com/index.php/ijcrsee/article/view/7
TAYLOR W., BARANOWSKI T. (2013). Physical Activity, Cardiovascular Fitness, and Adiposity in Children. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 62(2), 157-163.
URYADOVA T., NESHCHADIMOVA T., NESTERENKO A., BEZDOLNAYA T., SAFIULLAEVA R. (2017). Systematization of methods and ways of personnel analysis and evaluation in an educational organization. Revista Espacios, 38(20), 36. Retrieved from http://revistaespacios.com/a17v38n20/17382037.html
VILLARREAL J.L., CORDOBA J. X. M., CASTILLO C. M. (2016). De la educacion contable internacional al desarrollo de competencias. Revista Espacios, 37(33), 5. Retrieved from http://revistaespacios.com/a16v37n33/16373305.html
VINOGRADOV P.A. (1996). Fundamentals of Physical Culture and Healthy Lifestyle. Soviet Sport, 592.
1. Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Aerospace Engineering, Voronezh State Technical University, Voronezh. E-Mail: vivtkmk@mail.ru
2. Voronezh Institute for Educational Development, Voronezh. E-Mail: asfet-2011@mail.ru
3. The Military Educational and Scientific Center of the Air Force "The Air Force Academy named after Zhukovsky N.E. and Gagarin Y.A.", Voronezh. E-Mail: tanialar2008@yandex.ru
4. Institute of Mаnаgement in Economic, Ecological and Social Systems, Southern Federal University, Rostov-on-Don. E-Mail: ovgalustyan@sfedu.ru