

 Vol. 39 (Nº 01) Year 2018. Page 22
Vol. 39 (Nº 01) Year 2018. Page 22
Lyubov I. VANCHUKHINA 1; Tatiana B. LEYBERT 2; Elvira A. KHALIKOVA 3; Artur R. KHALMETOV 4
Received: 28/08/2017 • Approved: 03/10/2017
1. Problem setting and its connection to important scientific and practical tasks
2. Analysis of recent publications on the topic
4. Main results of the research and their substantiation
ABSTRACT: The article is devoted to new approaches to formation of innovational human capital as an inseparable element of institutional environment, viewed from the position of professional characteristics of human resources, capable of generating ideas and creating innovations, and the level of technical equipment of a work place, characterized as high-technology. Special attention is paid to Russian and foreign approaches to evaluation of human capital, used by economic subjects. The authors characterize innovational human capital, systematize the criteria of assigning human capital to innovational capital, determine the main problems during creation of innovational human capital, and offer the organizational & economic mechanism for risk management during creation of innovational human capital in economic systems as an element of the institutional environment, which includes the algorithm of managerial actions aimed at reduction and neutralization of risks. |
RESUMEN: El artículo está dedicado a nuevos enfoques para la formación del capital humano innovador como un elemento inseparable del entorno institucional, visto desde la posición de las características profesionales de los recursos humanos, capaz de generar ideas y crear innovaciones, y el nivel de equipamiento técnico de un lugar de trabajo , caracterizado como alta tecnología. Se presta especial atención a los enfoques rusos y extranjeros para la evaluación del capital humano, utilizados por sujetos económicos. Los autores caracterizan el capital humano innovador, sistematizan los criterios de asignación de capital humano al capital innovador, determinan los principales problemas durante la creación de capital humano innovador y ofrecen el mecanismo organizativo y económico para la gestión del riesgo durante la creación de capital humano innovador en sistemas económicos como un elemento del entorno institucional, que incluye el algoritmo de acciones gerenciales dirigidas a la reducción y neutralización de riesgos. |
The institutional environment of economic system is determined by the general state institutes, among which the most important is the strategy of development of industrial spheres.
In the conditions of technological and institutional transformation, one of the state’s strategic courses is modeling the process of managing the innovational human capital, which is a component of innovational economy and is required by the character of the innovational process, motivated at implementing innovations into all spheres of activities. Innovational human capital is a so called basis for realization of innovational ideas and new technologies into production, sales, and management.
Formation of innovational human capital, which supposes creation of highly-effective work place, capable of ensuring manufacture of competitive products with minimal expenses of time and equipped with highly-technological equipment and highly-qualified personnel, is accompanied by large risks.
Diversity of risks, appearing in the process of formation of innovational human capital, supposes the necessity for the complex approach to their evaluation and minimization of the possibility of emergence of the problems, danger, and threats, as well as the necessity for formation of organizational & economic mechanism of risk management during creation of innovational human capital.
As the analysis shows, there’s a lot of discussion regarding the categorical apparatus, criteria of assigning human capital to innovational type, and risks management during creation of innovational human capital. In the conditions of integration of the national economy in the global economic system, studying new approaches to formation of innovational human capital, as an inseparable element of the institutional environment, becomes very topical.
There are a lot of works devoted to the problems of evaluation of human capital as an element of the institutional environment.
The foreign approach to evaluation of human capital was founded by American economists Gary Becker and Theodore Schultz.
T. Schultz proved that human capital is formed only when financial capital is invested into education, which stimulates the development of intellect with a person, who is then capable of providing the growth of added capital of companies [1].
Continuing the theory of human capital, G. Becker makes an analogy between human capital and physical capital, which can wear out and require certain expenses. According to him, human capital should take its cost through amortization, as the company realizes a long-term and expensive project, related to formation of intellectual human capital [2].
There’s also a concept of the theory of human capital at the corporate level - Human Resourсes Accounting, developed by Eric Flamholtz. In his studies, he used the cost method to evaluation of human capital and formulated the problem of keeping personnel at the company, which is a result of preservation and increase of human capital [3].
Development of approaches to evaluation of intellectual human capital in the conditions of innovational development of institutional экономики was studied by Russian scholars: V.P. Bagov, V.P. Barancheev, B.B. Leontyev, L.I. Lukicheva, O.V. Loseva, et al.
In the scientific works, devoted to development of the theory of human capital and its interconnection to innovational component at the meso-level, O.V. Loseva views the contents of human capital from the intellectual point of view as economic category that integrates two interconnected components - intellectual potential and results of intellectual and innovational activity [4].
She notes that a necessary condition for modernization of economic system is its capability to generate new knowledge, received by intellectual results, which is treated as human intellectual capital.
In the previous studies made by L.I. Vanchukhina, T.B. Leybert, and E.A. Khalikova [5], a problem of evaluating human resources of economic systems was determined, related to increase of labor efficiency and formation of highly-effective jobs at the micro-level.
The purpose of the research is to develop organizational & economic mechanism of risk management during creation of innovational human capital (IHC) in economic systems as an element of the institutional environment.
The issues of categorical apparatus of “innovational human capital” are viewed, specific types of risks peculiar for formation of innovational human capital are grouped, the exiting tools of determining the characteristics of human resources are evaluated, and the algorithm of managerial personnel’s actions for identification, minimization, and elimination of risks during formation of innovational human capital is determined.
Innovational human capital is a type of the resource of an economic system that can manufacture highly-effective product that provides the largest growth of added value with least expenses of labor and time. Provision of the set parameters requires two components – highly-qualified human resources (intellectual human capital, capable of generating ideas and innovations) and high-tech work place, equipped with leading (latest) technologies.
After studying extensive scientific and periodic materials in the sphere of assigning human capital, the criteria according to which human capital can be considered innovational are systematized (Table 1).
Table 1
Criteria of assigning human capital to innovational
Criterion |
Characteristic |
Efficiency |
Expressed in exceeding a certain indicator of labor efficiency, showing a special status of a work place, which allows for such efficiency, or in the volume of revenue that exceeds a certain average indicator |
Wages |
Expressed in high evaluation of labor cost of а specialist, who possesses the corresponding capabilities and competences for performing the work on the spot |
Decent conditions |
Expressed in providing a worker with proper comfort, created for the purpose of increasing his effectiveness, motivation, and maximum usage of existing resources |
Provision with resources |
Expressed in totality of characteristics of work place, which allow employee to achieve the results that are above the average for the sphere and are a combination of leading technologies and human management |
During creation of innovational human capital, economic system is open to certain risks that are multiple and can differ in specific spheres of activity. They could be divided into groups, within which a more detailed consideration and determination of ways for their reduction and neutralization will be performed.
Grouping of risks related to creation of innovational human capital in the sphere of oil and gas business, is presented in Table 2.
Table 2
Grouping of risks related to creation of innovational
human potential in the sphere of oil and gas business
Group title |
Short characteristic |
Risk of technological unpreparedness |
Very topical for high-technology spheres which include the oil & gas sector. IHC requires for employees to be provided by the newest technologies, which are not easy to learn for the workers with proper skills and who are not used to technological and program innovations. Also, a lot of unique technologies are not always accessible. |
Risk of moral unpreparedness |
IHC means increased expectations from worker. Despite the fact that professional worker has to be confident in his abilities, a lot of workers can experience stress, which leads to decrease of efficiency and failures in work |
Risk of inability of performing large volumes of work |
IHC often means that worker get a possibility to perform large volumes of work over lesser terms and with worse conditions, due to new technologies and methods; however, worker may see the situation only in the context of growth of the volume of his duties, which might complicate the adaptation |
Risk of desynchronization of departments |
It is obvious that any production is a complex system with a lot of stages. Highly-effective work place at one stage can disrupt the system’s balance, which neutralized the useful effect and requires organizational improvements for normalization of the system |
Risk of incapability for studying |
Despite the fact that specialists in the sphere of management are easy to teach, it is necessary to take into account that transfer of work place into the form of highly-effective and high-technology may be accompanied by large changes of the work process, which will require full preparation and feedback from the worker |
Viewing these risk groups, which are considered to be main, it should be noted that their neutralization requires the work with personnel, which means double expenditures for creation of IHC – creating all conditions and making sure that employees have adapted and use their potential and potential of provided additional resources in the best possible way.
For substantiation of decision making in the process of creation of innovational human capital and minimization of the above risks, the authors offer the organizational & economic algorithm of risk management during creation of IHC.
The offered algorithm of risk management during creation of IHC consists of two stages – evaluation of general expedience of IHC creation and consideration of risks related to accessibility of the necessary technologies (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Supposed algorithm of managerial actions in the sphere of risk management during creation of IHC
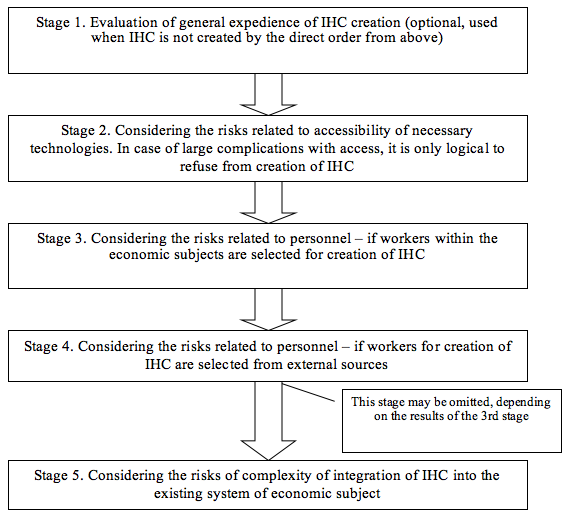
Schematically, algorithmization of the first stage of the managerial process for reducing the risks of IHC creation is shown in Figure 2.
The peculiarity of the first stage of the algorithm of managerial process for reducing the risks related to creation of IHC consists in the fact that any risks are to be temporarily ignored as it performs the task of additional verification of expedience of IHC creation. At that, before the managerial decision on creation of IHC, verification by the persons who make the decision should be made.
Figure 2
Algorithm of the first stage of the managerial process for reducing the risks of IHC creation
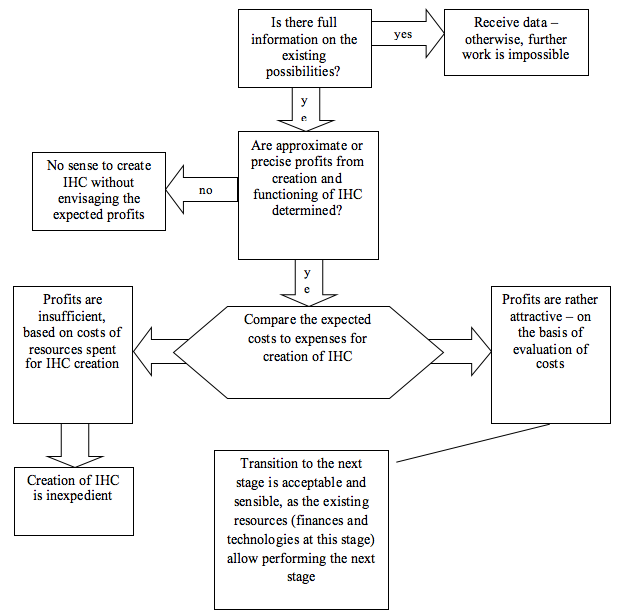
The advantage of the first stage of the algorithm is that it allows evaluating the general expedience of IHC creation, in order to avoid involvement of economic subjects into ineffective and doubtful project and forms the data base for the following stages of the algorithm.
Schematically, algorithmization of the second stage of the managerial process for reducing the risks related to IHC creation is presented in Figure 3.
At the second stage, the aspects related to accessibility for the economic systems of the technologies necessary for IHC creation and their further use are viewed.
Figure 3
Algorithm of the second stage of the managerial process
for reducing the risks that accompany IHC creation
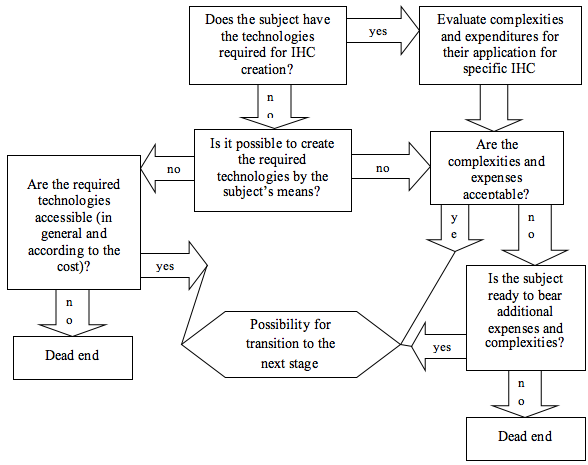
This stage is peculiar for its importance during transition to the following components of the algorithm. That is, at the first stage of the algorithm, unfavorable ratio of expenses and supposed profit from IHC creation can be ignored by the subject of management in favor of the fact that creation of IHC will serve some other purposes, which are invisible within a purely economic comparison, but at the second stage of the algorithm, the transition is possible only under clear conditions.
This stage of the algorithm is peculiar for the fact that it directly evaluates the possibility for creation of IHC according to the danger factor and allows for clear determination of the further position on the basis of the economic system’s possibilities.
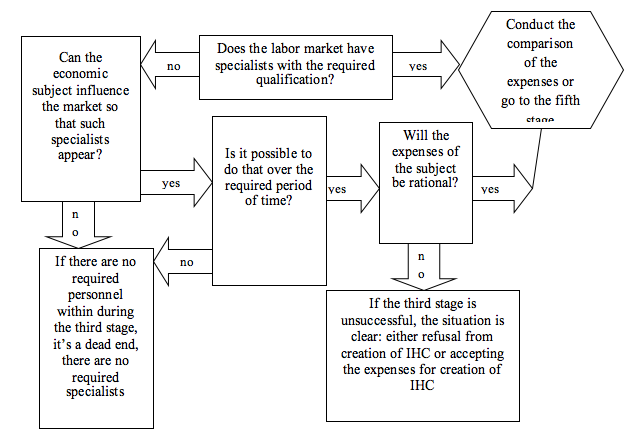
The third stage of the algorithm of risk management during IHC creation is devoted to the search for human resources for work at the created highly-effective work places at the economic subjects. While the presence or absence of technologies is very important (it is impossible to work without proper equipment), complexities with personnel are less important and could be solved in many ways, as any device or technology created by a human can be used by a human. The real issue is the one of knowledge and qualification, or the wish and possibilities to acquire the qualification. One way or another, the economic subject will be looking for workers at IHC – its own personnel. Schematically, algorithmization of the third stage of the managerial process for reducing the risks related to creation of IHC is presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4
Algorithm of the third stage of the managerial process
for reducing the risks related to creation of IHC
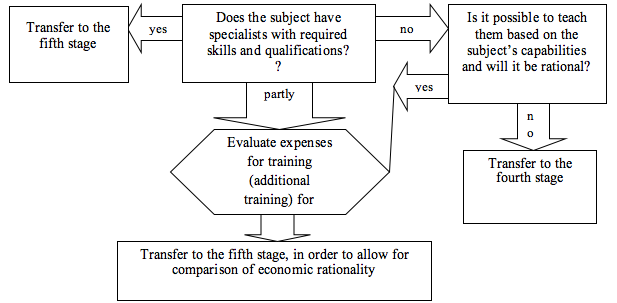
This stage of the algorithm is peculiar for dead end options and the largest number of further possible actions. If the required personnel are already within the economic subjects, the search for personnel at the external labor market is ignored. If personnel can be additional trained, it is possible to pass to evaluation of external labor market to compare the possible expenses or, by the management’s decision, to pass to the fifth stage (which is not recommended, as it is not correct). If the personnel within the economic subjects are absent and cannot be trained, a transfer to the external labor market is necessary.
This algorithm component’s advantage is the fact that it is possible to distinguish maximum possible variability that is to be open in the complicated form of the stage and to provide the economic subject with a lot of ways of solving the possible problem of human resources.
The difficulty may consist in insufficiently correct evaluation of the skills required during the initial formation of requirements to applicants for IHC and in the relative character of the notion of rationality during deciding which of the variants is the best for a specific subject.
Schematically, algorithmization of the fourth stage of the managerial process for reducing the risks related to creation of IHC is provided in Figure 5.
This stage is peculiar for the fact that is depends on the company’s plans for its further development – i.e., the largest companies may make a decision on the more expensive variant in the form of influencing universities for creation of the required new training programs, if this is a good contribution into the future of their own HR personnel, or decide that new specialties are not required and be satisfied with the existing human resources, with only additional training.
Figure 5
Algorithm of the fourth stage of the managerial process
for reducing the risks related to creation of IHC
This algorithm stage’s advantage is that it clearly shows the possibilities for the economic subject within the work with external labor market during search for personnel for IHC creation.
Difficulties may arise as well – despite the clarity of each specific end, in case of several possible alternatives the decision will have a character of a complex strategic decision, not a local project one.
The fifth stage of the algorithm of risk management during creation of innovational human capital consists in integrating IHC into the existing system of the economic subject. Certain difficulties are possible during conduct of this process, systematization of which is presented in Table 3.
Table 3
Main possible problems during integration of innovational human
capital into the existing system of an economic subject
Problem |
Probability of appearance |
Description |
IHC will work quicker/more effectively, which will cause discord in the whole system |
Almost 100% |
The sense of creation of IHC is to increase the effectiveness. The adjacent work places are to be corrected |
Special needs for equipment/resources will arise |
Depends on specifics of IHC |
Search for new suppliers |
Working schedule will change |
High |
Compilation of new plans and norms |
Based on the performed analysis of foreign and Russian approaches to formation of human capital, the authors substantiated the criteria of determinining innovational human capital as an inseparable element of the institutional environment. This notion is based on symbiosis of two economic categories – human capital as a resource and as a result of innovative activities. It is specified that creation of innovational human capital is related to specific forms of risks, for which there are no specialized mechanisms of reduction of risks.
The authors develop the organizational & economic mechanism of risk management during creation of innovational human capital (IHC) in economic systems, which includes the process of algorithmization of managerial decisions for reduction of risks related to creation of innovational human capital.
Schultz T. Investment in Human Capital: The Role of Education and of Research. N.Y., 1971.
Becker G.S. Human Capital: A Theoretical and Empirical Analysis. N.Y.: Columbia University Press for NBER, 1964.
Dobrynin А.I., Dyatlov S.А., Tsyrenova Е.D. Human capital in transitive economy: formation, evaluation, and effectiveness of use. – SPb.: Nauka, 1999.
Loseva О.V. Formation of the methodology of evaluating human capital in the innovational activity: doctoral thesis. – М., 2013. – 387 p.
Vanchukhina L.I., Leybert T.B., Khalikova E.A. Methodological Approaches to Evaluation and Analysis of Labor Efficiency in the Spheres of Fuel and Energy Complex // Journal of Environmental Management and Tourism. – 2016. – No. 1. – P. 585-594.
OECD, OECD Investment Policy Reviews: Botswana, 2014. – 26 p. - [E-source]. – URL:http://tinyurl.com/lenua3h (Accessed: 02.04.2016).
Highly-efficient work place in Russian regions (analytical note). – М.: TPP Inform LLC, 2013. – 28 p.
1. Ufa State Petroleum Technological University, Ufa, Russia. e-mail: BUA1996@yandex.ru
2. Ufa State Petroleum Technological University, Ufa, Russia. e-mail: lejjbert@mail.ru
3. Ufa State Petroleum Technological University, Ufa, Russia. e-mail: ydacha6@yandex.ru
4. Ufa State Petroleum Technological University, Ufa, Russia. e-mail: khalmetov@gmail.com