

 Vol. 39 (# 20) Year 2018. Page 15
Vol. 39 (# 20) Year 2018. Page 15
Elikanida P. MUTAVCHI 1; Alexey I. PROKOPYEV 2; Galina V. KOSTYLEVA 3; Leonid V. BLINOV 4; Vladimir V. FEDOROV 5; Anatoly E. POLICHKA 6
Received: 02/03/2018 • Approved: 15/04/2018
ABSTRACT: The urgency of the research is due to the fact that the motivational sphere, values and meanings of professional activity are the condition determining the professionalism of the future specialist, giving direction to its content, orientation, and growth potential. The purpose of the paper is the development of a scientific and methodical resource for developing the motivation of university students as an adaptive mechanism for mastering the characteristics of professional activity. The basis of the scientific and methodical resource is the author's personality-oriented training for the development of the students' educational and professional motivation, the center of which is a unique integral personality, striving for maximum realization of its capabilities. A model of personality- oriented training was developed, reflecting methodological and didactic principles; units of personal-professional qualities of students; indicators of the effectiveness of their educational and professional motivation development. Presented in the paper, the scientific and methodical resource for the development of the student's learning and vocational motivation creates comfortable conditions for the formation of professional culture’s foundations in the process of learning and educational activities in the chosen direction and successful integration into the social and professional structure of society. |
RESUMEN: La actualidad de la investigación se deriva de la importancia de esfera motivacional, los valores y los significados de la actividad professional que son la condición determinante para formar la profesionalidad, contenido, dirección y potencial de crecimiento del futuro especialista. El propósito del artículo es elaborar recursos científicos y metodológicos para desarrollar la motivación de los estudiantes universitarios como un mecanismo para aprender las características de la actividad profesional. El artículo proponе un modelo deд entrenamiento centrado en la persona que se compatibiliza con los principios metodológicos y didácticos y con las cualidades personales y profesionales de los estudiantes; tiene indicadores de la efectividad del desarrollo de su motivación educativa y profesional. El presente recurso científico y metódologico para desollar de la motivación educativa y profesional del estudiante hace las condiciones cómodas para la formación de las bases de la cultura profesional en el proceso de actividades educativas en la dirección elegida y la integración acertada en la estructura social y profesional de la sociedad. |
The study of student motivation’s development, which acts as an integral personality formation, which combines the possession of educational and professional activity elements at the operational level with a motivational and value attitude to the profession, reflects the state and public order to increase the effectiveness of vocational education. The realities of modern life, the complication of a person's professional activity, the expansion of the subject's representation in the professional sphere make urgent the problems in the field of higher education, associated with the professional demotivation of the bulk of students.
Motivation is one of the fundamental problems of our time; its importance is connected with the analysis of human activity’s sources, the motivating forces of its activity, behavior. The complexity and multidimensionality of the problem of motivation determines the multiplicity of approaches to understanding its essence, nature, structure, and also to the methods of its study (Boldyreva, 2014; Zhokhov, 2011). Active development of the problem of motivation is connected with the study of such scientific aspects as: the system of human relations (Kolomiets, 2016; Furs, 2011; Masalimova et al., 2018); correlation of meaning and meaning (Shadrikov, 2012; Schuplenkov & Schuplenkov, 2013); the integration of incentives and their semantic context (Afanasenkova, 2011; Afanasenkova, 2017); personality orientation and dynamics of behavior (Ilyinsky, 2013; Pryazhnikova, 2010); professional-personal orientation in activity (Zagvyazinsky, 2012; Keldiyarova, 2014; Pakharenko & Zolnikova, 2012; Gluzman et al., 2018; Dorozhkin et al., 2018).
Productive in the study of motivation (Batarshev, 2014) is an idea of motivation as a complex system, which includes certain hierarchical structures. At the same time, the structure is understood as a relatively stable unity of the elements, their relations and the integrity of the object; as an invariant of the system. The concept given by S.L. Rubinstein (2017) was of great importance in the development of the theory of motivation, which considered the concept of the motive and purpose of the activity in terms of the development of the need. The key concept of personality is characteristic of the theory of S.L. Rubinstein’s (2017), through which the author reveals the system of various connections between consciousness and activity. The personality itself is defined as the triune of the motivational-need system; abilities and talents, as well as character traits.
In general, this triune determines the motivation as the core of the personality and combines dynamic characteristics - orientation, motives and stable qualities (character and abilities). Vocational motivation is an internal driving factor for the development of professionalism and personality of student youth, because only on the basis of a high level of its formation it is possible effectively to develop vocational education and culture. The beginning of student life is always accompanied by contradictions and the breaking of habitual life views. A large number of researchers (Kamyshev, 2012; Zayarnaya, 2015; Pashkevich, 2010; Shushara & Khuziakhmetov, 2017; Cherdymova et al., 2017; Gorbunova & Kalimullin, 2017; Kong, Kayumova & Zakirova, 2017; Wang et al., 2018) with a high degree of statistical confidence prove that a high level of adaptation to training in university and the successful mastering by the personality of the professional activity are relevant to internal professional motivation.
The professional motivation of students forming in the system of higher education is a set of needs, attitudes, and interests, satisfied through the fulfillment of educational tasks and encouraging the individual to study future vocational activity. Reflecting in the mind, actual needs (getting higher education, acquiring a basis for further self-development and professional development, increasing their social status in the future, etc.) encourage and direct the student to master the future vocational activity.
At the same time, our analysis of approaches to the problem of motivation and motives for mastering professional activity in psychological and pedagogical theory and practice testifies that at the present time there is a contradiction between the high degree of importance formed by the educational and vocational motivation in the process of vocational education that determines goal-directed mastery of professional and personal knowledge and skills, and insufficient level of its development among students; in the present when enrolling in an institution of higher education applicants do not pass the testing of personal characteristics, in particular, professional motivation, therefore, the possibility of enrolling entrants with personal problems and motivational immaturity is not always ruled out. An attempt to approach the solution of the above contradictions prompted us to develop a scientific and methodical resource based on the program of personality oriented training for the development of the students' educational and professional motivation, the focus of which is a unique integral personality, striving for maximum realization of its capabilities.
Theoretical and methodological prerequisites for studying the development of students' motivation as a factor in the formation of their professional and personal qualities were determined by the following approaches:
The activity-based approach, which sets the system nature in the study of the needed-motivational sphere of the individual. This approach views the motive as a holistic way of organizing the activity of the individual, being an integral motivator and regulator of activity. It is aimed at involving students in a variety of personality-forming activities that allow you to form certain qualities and behaviors that are in demand in the occupational sphere. Attention is paid to increasing motivation, gradual complication of vocational activities and the content of its components;
Personally oriented approach promotes the professional development of the individual; creates conditions for its individual implementation based on positive qualities; organizes a pedagogical process on the basis of cooperation. This approach determines the development of professional and moral consciousness and behavior, the formation of personality and professional attitudes, motives, attitudes, socio-value orientations of student youth, determines the subjective position of the student in the process of transformation of subjective experience;
The socio-pedagogical approach ensures sustainable motivation and successful professional realization of students not only in the educational environment of the university, but also in the open society, in accordance with their personal expectations and preferences.
The indicated approaches are implemented in the study in the following principles: the principle of determinism, which determines the need to take into account various factors that affect the development of the individual. One such factor is motivation; the principle of the active activity of the individual; the principle of subjectivity, which determines the transformative character of the personality's activity, directed at the development of its abilities; the principle of personality- developing educational environment, emphasizing the need to create a specially organized educational environment at all levels of interaction of its subjects.
To identify the effectiveness of the developed scientific and methodical resource, which is based on the program of personally oriented training for the development of educational and professional motivation of students, a pilot study was conducted.
In order to verify the solution of the tasks posed, the following methods were used: theoretical: problem analysis and the synthesis of ideas that help to comprehend the categories of educational and professional motivation and personal and professional qualities of university students; analogy, generalization, concretization, abstraction, idealization, modeling of the organizational and pedagogical conditions for the development of the educational and professional motivation of students as a factor in the formation of their personally professional qualities; extrapolation of the revealed tendencies and patterns of social orientation of the educational process in the university on the possibility of their use and application in practice of other educational institutions; Empirical: ascertaining, forming, control experiment; mathematical statistics: statistical processing of questionnaire data and experimental results.
Experimental work was carried out on the basis of universities in Kazan (the sample of students was 281 people). Experimental work was built in the process of educational and extracurricular activities of students in the university in the framework of vocational education, using the possibilities of educational disciplines, in the forms of lectures, seminars, master classes, mini-trainings, role-playing, business games, in the course of training practice; resources of scientific activity (conferences, seminars, round tables); various forms of educational work (debates, reviews, competitions, festivals, thematic and festive events, club meetings, actions, adaptation meetings).
The questionnaire of terminal values (I.G. Senin) (Raigorodsky, 2011).
"Diagnosis of the motivational structure of the individual" (V.E.Milman) (Raigorodsky, 2011);
Test questionnaire 16 PF of R. Cattel (Raigorodsky, 2011)to determine the dominance of psychologists' propensities to theoretical or practical activities.
Method for studying the motives of educational activity (modification of A.A. Rean, V.A. Yakunin) (Raigorodsky, 2011).
"Motivation of study in high school" (test of T.I. Ilyina, modified by E.P. Ilyin (2014).
In accordance with the logic of the experimental study, several stages were identified.
I. Conducting the ascertaining stage.
Identification of the features of educational and professional motivation formation as a factor in the formation of students' personality-professional qualities, which does not imply the implementation of a special systemic realization of the totality of psychological and pedagogical conditions.
Preliminary testing for the purpose of revealing the initial data, the structure of the educational and professional motivation of the students in experimental and control groups. Identification of students 'orientation, motivation, individual qualities of students' personality at the educational and professional stage of education in the university.
Statistical processing and analysis of the results obtained.
II. Preparation and conduct of psychological and pedagogical experiment aimed at the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personal and professional qualities. Psychological and pedagogical experiment included a number of stages:
1. Theoretical, on which the problem, goal, object and subject of research, its tasks and hypotheses were determined.
2. Methodical (development of the research program, determination of the set of research methods and processing of the results). Taking into account the structure and content of the educational and professional activities of students and the selected conditions, a model of a person-centered training for the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personal and professional qualities was developed.
In the experiment, an intergroup scheme was used; the independent variable had two conditions: experimental (the realization in the course of practical classes of the conditions for the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personal and professional qualities) and the control (the absence of a purposeful implementation of the identified conditions of the indicated process in the educational process)
Dependent variable in the experiment was the level of development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personality-professional qualities, the indicators of which were: awareness of the significance and features of motivation; the formation of the orientation of students personality to study at a university; the expressed motives of the teaching; manifestations of personality traits that determine the success of educational and professional activities.
The study was carried out in three directions:
Studying the dynamics of the formation of students' personality orientation; the study of the formation dynamics of the students’ motives; the definition of the dynamics of students' personal and professional qualities’ formation;
-construction of the model of personally oriented training development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personality-professional qualities;
-revealing the link between changes in the structure of the educational and professional motivation of students before and after the training.
3.Analytic, including quantitative and qualitative analysis, interpretation of the data obtained, formulation of conclusions and practical recommendations.
III. Conducting repeated testing in order to identify the possible effect of the implementation of personally oriented training model on the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of personal and professional qualities of students in the university. Study of the peculiarities of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of personal and professional qualities of students after inclusion in practical (training) activities. Statistical processing, comparative analysis and interpretation of results obtained at different stages of training.
Summarizing the theoretical material accumulated in psycho-pedagogical science of studying the personal-professional qualities of the future specialist, we have identified the following structural units: reflexive, emotional, cognitive, behavioral, communicative, and value-semantic. Each of these units has its own substructure: reflexive (psychological observation, adequacy in perception of oneself and others, adequacy of the first impression, concentration on the client, etc., value-semantic (humanistic orientation, ethical principles, motivational and semantic attitudes, awareness of personality’s value, etc.), cognitive (professional knowledge, independence, criticality, the ability to predict human behavior, etc.), emotional (empathy, emotionality, the desire to help etc.), communicative (readiness for contacts, ability to listen and hear, willingness to accept the position of another, communicative qualities of speech, etc.), behavioral (flexibility and adequacy of behavior, self-control , tolerance to others, the ability quickly and adequately to navigate the situation, etc.) One of the effective tools for the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of personal and professional qualities of students is a personality centered training, which is being implemented within the framework of educational and vocational training.
Based on the results of the theoretical study, as well as the findings of the ascertaining stage, we developed a model of personally oriented training for the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personal and professional qualities. In general, the model is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Model of personally oriented training development of educational and professional
motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personal and professional qualities
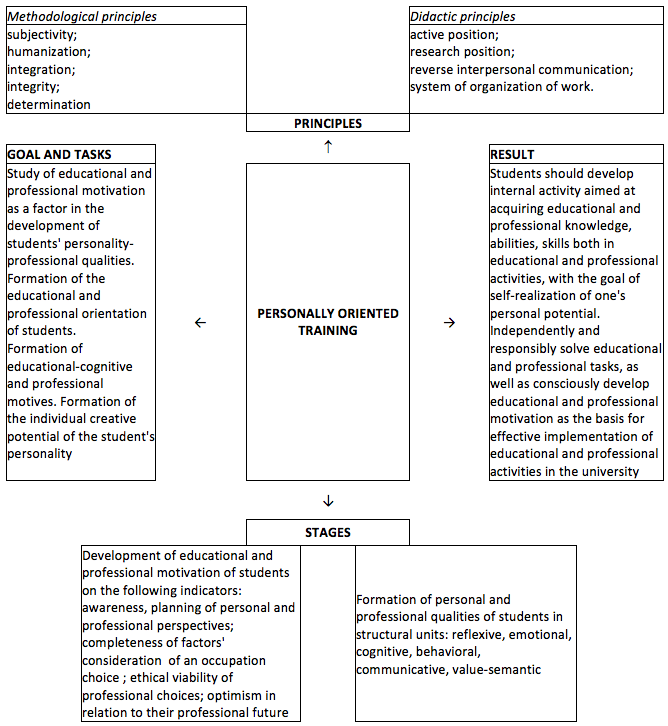
The theoretical basis for the training development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personal and professional qualities was the methodological principles:
humanization, involving the manifestation of increased attention to the personality of each participant as a value, as well as the use of an attitude to the formation of an individual with developed intellectual, moral, and professional qualities;
Integration aimed at systemic unification of participants and training structures with the common goal of organizing effective professional development of psychology students in educational and professional activities;
Individualization, where the leading orientation to the creative, personal and professional qualities of each student, with the aim of providing an individual creative approach to his professional development;
Subjectivity, acting as a factor of development of activity, initiative, responsibility of the personality of each student;
Integrity associated with the integration of leading principles into a single whole in the conditions of educational and professional activities of students in the university;
Determination as the interdependence of the educational process components at all levels for the purpose of forming students' personal and professional abilities.
During the training we observed the following didactic principles.
Active position of the participants. It is an obligatory principle that requires not passive participation, but the active work of self-cognition, self-discovery and self-acceptance;
Research position, which allows seeing the essence of a particular problem;
Inverse interpersonal connection in communication, increasing its adequacy and informative nature;
Systematic organization of work aimed at the effectiveness in achieving the goal.
Practical tasks of the training were: development of the educational and professional orientation of the students' personality; the formation of motives, in particular educational-cognitive and educational-professional; development of the individual creative potential of the student's personality.
At the heart of the stages of practical work lies the structure of motivation as a psychological and pedagogical phenomenon, which includes three components: the educational and occupational orientation of students; motives of educational and professional activity: educational and vocational; personal and professional qualities of the personality of students.
Consequently, the stages of the training work will be: the formation of educational and professional orientation; formation of educational and professional activity’s motives; the formation of personal and professional qualities of students.
As a result of the training work, students should develop internal activity aimed at acquiring educational and vocational knowledge, abilities and skills in educational and occupational activities with the goal of self-realization of one's personal potential. Independently and responsibly solve educational and vocational problems, as well as consciously develop educational and professional motivation as the basis for effective implementation of educational and professional activities in the university.
In the course of the training work, we assumed that motivation as a complex multicomponent phenomenon that combines the direction, motives and qualities of the student's personality is a system-forming factor, i.e. an integral phenomenon that organizes the above listed components into a single whole, in the formation of the student's personal and professional qualities. Indicators of development’s effectiveness of students’ educational and professional motivation are: awareness, planning of personal professional prospects; completeness of accounting for the main factors of profession’s choice; ethical viability of professional choices; optimism in relation to their professional future.
The results of experimental research have shown that the program of personally oriented training created and implemented in practice contributes to the effective study of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the development of students' personal and professional qualities. At the final stage of the study, the educational and professional values and spheres of life of the experimental groups’ students became statistically more significant than in the control groups.
1. After the training, the indicators for the following ratios of values and life spheres grew:
One’s own prestige in teaching and education (8,20);
Creativity in education and professional life (8,57);
Creativity in teaching and education (8,00);
Development of oneself in professional life (8,07);
Development of one- self in teaching and education (8,93);
Achievements in education and training (8,53);
Achievements in professional life (9);
Spiritual satisfaction in teaching and education (9,97).
2. Statistically has changed indicators of the individual’s motivational structure, namely, the indicators increased for factors of comfort: (13.22); social status (12.16); communication (21.16); total activity (13.66); creative activity (18.67); social utility (15, 91). Statistically, the indicators of motivation for learning in the university have changed; in particular, the indicators of motivation for obtaining knowledge (5.81), as well as the motivation for obtaining a profession (6.03) have increased. Slightly decreased the motivation for obtaining a diploma (6, 27).
In general, the indicators of the "working" motivational profile of the individual have grown, which speaks of the effective influence of a person-centered training on the educational and professional motivation of students. The purpose of interpreting the results of the experiment was to compare the changes in the structure of the educational and professional motivation of students before and after the training. The work was conducted with students of experimental groups of 4-5 courses.
At the final stage of the study, the indicators of multifactorial personality research were statistically changed. The data are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
Average values of factors of personality multifactorial research by R.Cattell before and after training
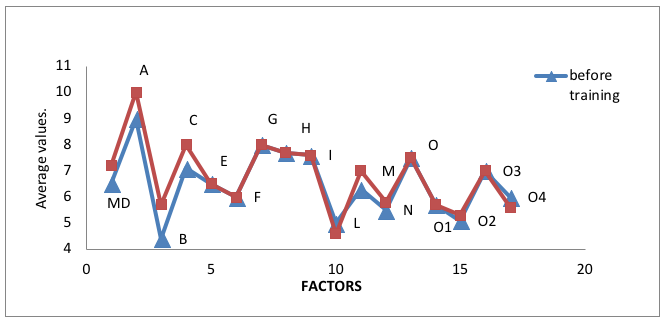
Students in the experimental groups began to evaluate themselves more adequately (MD); show cohesion and sociability in a small group, tolerance and empathy (A); verbal culture, ingenuity, abstract thinking increased (B); efficiency, emotional self-control, equanimity increased (C); creativity, imagination increased (M); there was frankness, benevolence towards other people, work efficiency increased. Thus, as a whole, the indicators of the "working" motivational profile of the individual have grown, which indicates the effective influence of the training on the educational and professional motivation of students.
Traditionally, in psychology, the following aspects of this problem are most thoroughly presented: the ratio of motive and need (Ilyin, 2014); the role of high positive motivation as a compensatory factor in case of low special abilities (Manzhos, Khazova & Khatit, 2015); motivation of certain types of activities, in particular, educational activities (Pushkaryov, 2011); the role of positive motivation for the effectiveness and success of training activities (Petrov, 2010; Chernaya, 2014). From the point of view of the authors (Belogurova, 2010; Dneprov, 2011, Kaplunenko, 2012, Kormiltseva, 2013), motivation is a set of motivating factors that determine the activity of the individual and determine the direction of its activities. We consider the educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of sustainable personal and professional qualities of student youth. In this context, students' personality-professional qualities are revealed as integral characteristics of activity’s subject, which include the following units: cognitive, emotional, motivational, value-semantic, reflexive, communicative-behavioral and which build the foundation for the professional success of the future specialist.
The results of the research give grounds for the following conclusions:
1. The structure of educational and vocational motivation has the following components: educational and vocational orientation, which includes vocational mission, needs for professional work, professional attitudes, value orientations; educational and cognitive and professional motives; stable qualities of students: personal and professional.
2. The student's personally and professional qualities are understood as the integral characteristics of the subject of activity, which affect the effectiveness of the educational and professional activity and the success of its development. At the same time, personality qualities form an important foundation for the professional success of a future specialist. Personality-professional qualities of students include the following units: cognitive, emotional, motivational, value-semantic, reflexive, communicative-behavioral.
3. The model of personality oriented training of educational and professional motivation development is the basis of the scientific and methodical resource for the formation of students' personality and professional qualities and includes methodological principles: humanization, integration, individualization, subjectivity, integrity, determination and didactic principles: active position, research position, feedback interpersonal communication, system; units of personality and professional qualities of students: cognitive, emotional, motivational, value-semantic, reflexive, communicative-behavioral; indicators of the development effectiveness of students’ educational and professional motivation: awareness, planning of personal vocational prospects; completeness of the main factors of occupation’s choice; ethical viability of occupational choices; optimism in relation to their occupational future. The results of experimental research have shown that the model of personality oriented training created and implemented in practice contributes to the effective development of educational and vocational motivation as a factor in the formation of students' personality and professional qualities.
Not all aspects of the problem in the development of educational and professional motivation as a factor in the formation of student personality and professional qualities were examined in this paper. In particular, individual studies in the future can be devoted to addressing such issues as the identification of mechanisms for the formation of educational and professional motivation for students, as well as the place and role of educational and professional motivation in the professional culture of the student's personality.
Afanasenkova, E. L. (2011). Dynamics of motivation teachings of students of the University. Psychology of learning, 12, 60-75.
Afanasenkova, E. L. (2017). Motivational sphere, motivation and motives of future specialists in the system of their professional training. Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk: Kano.
Batarshev, A. V. (2014). Educational and professional motivation of young people. Moscow: Academy.
Belogurova, V. A. (2010). Scientific organization of the educational process. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media.
Boldyreva, T. A. (2014). Personality deformities: an attempt to systematize modern psychological approaches in line with the concept of individuality. Bulletin of the Orenburg state University, 2, 195-198.
Cherdymova, E. I., Kuznetcov, V. A., Machnev, V. Y., Solovova, N. V., Sarbaeva, I. Yu. & Masalimova, A. R. (2017). Eco-Vocational Consciousness Formation Model of a Specialist in Modern Mega Polis. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 12(5b), 493-507.
Chernaya, Yu. A. (2014). Evaluation of the effectiveness of the university in connection with the implementation of criteria for assessing the quality of educational services. Fundamental research, 12(9), 1999-2002.
Dneprov, E. D. (2011). The latest political history of Russian education: experience and lessons. Moscow: Marios.
Dorozhkin, E. M., Kalimullin, A. M., Migacheva, G. N. & Sokolova, T. B. (2018). Optimization of the Subject Matter of Profile Training Disciplines for Bachelors’ Vocational Education on the Basis of Occupational Standards. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 14(3), 859-876.
Furs, M. V. (2011). Interactive forms of education are a means of increasing the level of professional training of students. Herald of Higher School, 10, 29-33.
Gluzman, N. A., Sibgatullina, T. V., Galushkin, A. A. & Sharonov, I. A. (2018). Forming the Basics of Future Mathematics Teachers’ Professionalism by Means of Multimedia Technologies. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 14(5), 1621-1633.
Gorbunova, N. V. & Kalimullin, A. M. (2017). Simulation of the Process of Training the Future Primary School Teachers for Organizing Extracurricular Activities. Elementary Education Online, 16(4), 1860-1872.
Ilyinsky, I. M. (2013). The effectiveness monitoring of higher education institutions. Knowledge. Understanding, 2, 3-9.
Ilyin, E. P. (2014). Motivation and motives. Saint Petersburg: Piter.
Kamyshev, S. V. (2012). Globalization of education and" global education " in the modern world. Philosophy of education, 6, 124-131.
Kaplunenko, A. M. (2012). On the advantages of the system-activity approach to pedagogical discourse. Bulletin of Irkutsk state linguistic University, 4, 175-178.
Keldiyarova, G. N. (2014). The role of young people in modern conditions of society development. A young scientist, 15, 225-227.
Kolomiets, O. M. (2016). Organization of educational and professional activity of the student in teaching on the basis of competence-activity approach. Pedagogical journal, 5, 47-58.
Kong, Y., Kayumova, L.R. & Zakirova, V.G. (2017). Simulation Technologies in Preparing Teachers to Deal with Risks. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 13(8), 4753-4763.
Kormiltseva, M. I. (2013). Psychological determinants of professional mobility of a person. Innovative projects and programs in education, 2, 9-11.
Manzhos, L. V., Khazova, S. A. & Khatit, F. R. (2015). Features of professional self-realization of teachers in modern conditions. Bulletin of Adygea state University, 3, 83-89.
Masalimova, A. R., Sangadzhiev, B. V., Shagieva, R. V., Gurbanov, R. A. & Zhdanov, S. P. (2018). Philosophical and socio-psychological meaning of the concept of psycho violence in learning environment. XLinguae, 11(1), 126-135.
Pakharenko, N. O. & Zolnikova, I. N. (2012). Model of determining the level of formation of General cultural and professional competences. Modern problems of science and education, 6, 45-49.
Pashkevich, A. V. (2010). Technology of realization of competence approach in educational process of school. Tobolsk: thspa them.
Petrov, A. V. (2010). Value preferences of young people: diagnosis and trends of changes. Socis: Sociological research, 2, 83-90.
Pryazhnikova, E. Yu. & Pryazhnikov, N. S. (2010). Career guidance. Moscow: Academy.
Pushkaryov, Yu. V. (2011). Education in a modern University: new ideas and directions of development. Bulletin of Novosibirsk state pedagogical University, 1, 40-43.
Raigorodsky, D. Ya. (2011). Practical psychodiagnostics. Methods and tests. Moscow: Bakhrakh-M.
Rubinstein, S. L. (2017). Existence and consciousness. Saint Petersburg: Piter.
Schuplenkov, O. V. & Shchuplenkov, N. O. (2013). The problem of the formation of an innovative personality in modern society. Psychology and Psychotechnics, 8, 21-27.
Shadrikov, V. D. (2012). Quality of teacher education. Moscow: The Logos.
Shushara, T. V. & Khuziakhmetov, A. N. (2017). The Problem of Professional Orientation of Youth: Trends and Prospects. Man In India, 97(14), 197-205.
Wang, Z., Utemov, V. V., Krivonozhkina, E. G., Liu, G. & Galushkin, A. A. (2018). Pedagogical Readiness of Mathematics Teachers to Implement Innovative Forms of Educational Activities. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 14(1), 543-552.
Zagvyazinsky, V. I. (2012). Strategic guidelines for the development of national education and ways to implement them. Education and science. News of the Ural RAE, 4, 3-16.
Zayarnaya, I. A. (2015). Theory and methodology of formation of effective system of management of competitiveness of higher education institution. Tver: LLC "Tver printer»
Zhokhov, A. P. (2011). About professional culture as the main reference point of modernization of modern education. Education and science. News of the Ural RAE, 9, 42-52.
1. Department of Social and Cultural Services and Tourism, Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University, Kaliningrad, Russia. Contact e-mail: elikanida@mail.ru
2. Department of State and Legal Disciplines, Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Moscow, Russia
3. Economy Legislation Department, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia
4. Department of Theory and Methods of Pedagogical and Defectology Education, Pacific National University, Khabarovsk, Russia
5. Department of Theory and Methods of Combat Sports and Weightlifting, Far East State Academy of Physical Training, Khabarovsk, Russia
6. Department of Mathematical Methods and Information Technologies, Pacific National University, Khabarovsk, Russia