

 Vol. 39 (# 20) Year 2018. Page 18
Vol. 39 (# 20) Year 2018. Page 18
Anna A. MALTSEVA 1
Received: 27/03/2018 • Approved: 12/04/2018
ABSTRACT: The paper analyzes the mutual influence of intellectual capital of universities and regions of their location. As a basis the case study method of development programs of leading Russian universities was used. Strategic projects that made possible to establish the existence and significant mutual influence of the available intellectual capital of universities and regions were analyzed. The established qualitative interrelations can become a basis for their further quantitative analysis, and also can be implemented in the practice of management of universities and regions to enhance their use in the implementation of development programs. |
RESUMEN: El documento analiza la influencia mutua del capital intelectual de las universidades y regiones de su ubicación. Como base, se utilizó el método de estudio de casos de los programas de desarrollo de las principales universidades rusas. Se analizaron proyectos estratégicos que permitieron establecer la existencia y la influencia mutua significativa del capital intelectual disponible de universidades y regiones. Las interrelaciones cualitativas establecidas pueden convertirse en una base para su posterior análisis cuantitativo, y también pueden utilizarse en la práctica de la gestión de universidades y regiones para mejorar su uso en la implementación de programas de desarrollo. |
The identification of the mutual influence of the intellectual capital of the region and the universities located on its territory has a great importance for ensuring their development.
Higher education institutions within the framework of the "University 4.0" concept can ensure the creation and development of territories’ intellectual capital which in turn is the source and element of their own intellectual capital, taking into account created ties with other subjects of the regional economy. All this, with proper management, can create the synergy effect from the interaction of the parties, which strengthens the role of intellectual capital of territory’s individual subjects as well as the multiplier effect that arises during development of university’s intellectual capital which increases region’s intellectual capital, that can be ensured only with active participation and involvement territory’s intangible resources in the university’s activity.
The analysis of the literature made it possible to single out separate publications on the issues of mutual influence of the intellectual capital of territories and universities located within their boundaries, which for the most part has a framework nature.
So, Avilova (2013) concentrates more on universities’ role in the development of the human potential of the country and the region.
In the Serdyukova’s work (2011) the role of university education as a determining factor in the creation and development of region’s intellectual capital is also mainly considered. The author points out in this regard the need for the development of university’s intellectual capital which is broadcast to the region during staff training.
Bojayeva et al. (2015) considers the issue of the university’s role in the region and in the formation of its intellectual capital is much broader and argues that it should not be determined only by the training of specialists; it should be the basis of scientific, technical and socio-economic development of the territory, the foundation connecting generations, the custodian of historically accumulated ideas, developments, projects and their active generator at the new historical stage of society’s development.
Golubkin and Svetlov (2013) proves the importance of universities in the creation of intellectual capital at the regional level, by defragmenting it into separate components. Development of human capital of the regional economy’s subjects is ensured in the process of training personnel in universities; development of organizational capital is based on technologies created in universities. The authors propose to take a special attention to technological networks which represent a set of economic entities interacting with each other at all stages of the innovation process.
Thus, Kirshin et al. (2010) considers the role of federal universities in the development of the intellectual capital of the region and the country as a whole, which is expressed by the following key directions:
• training of competitive specialists on the basis of close integration of educational activities with fundamental and applied research;
• development of entrepreneurial activity on the university’s platform with the involvement of the external community and ensuring the satisfaction of its requests, which is ensured by the inclusion of teachers and students in joint practice-oriented activity;
• ensuring the possibility of implementing individual educational trajectories that can meet the educational needs of each person at his own relevant level.
The authors formalized the task of assessing the countries', regions' and universities’ intellectual capital on the basis of the intellectual potential index development. For this purpose the system of indicators of educational and scientific potentials was singled out.
The authors are developing a system of measures aimed at universities’ development contributing among other things to the active growth of the region's intellectual capital.
The formalization of university’s role in the development of primarily entrepreneurial activity in the region is represented in Trequattrini’s et al. work (2015). The authors primarily focus on the problem of territories' innovative development and view universities as a significant platform for the commercialization of research and development created on their platform. University of entrepreneurial type is able to create an entrepreneurial region’s culture which is characterized by such indicators as incubation of spin-off companies, provision of professional services, entrepreneurship training. The authors state the necessity of regional investments in universities’ development which can become the basis for outstripping growth of the intellectual capital of the territory as a whole.
Obviously, in some cases there is a substitution of concepts. The authors interpret intellectual capital from the positions of the achieved results, while it represents the potential, the possibilities of a university’s influence on the region and vice versa. Also the insufficient formalization and structuring of the directions of the mutual influence including in a majority generalizing formulations are noteworthy.
The goal within the framework of this research is to establish qualitative relationships between the intellectual capital of the university and the region, using the method of case studies of leading Russian universities.
The methodological basis for the study were publications on the issues of the definitions and structure of intellectual capital of the university and the region.
The general methodological framework of intellectual capital study is laid down in an early author's study (Maltseva and Monakhov, 2014), which summarized and systematized the classical and modern concepts of intellectual capital and was used as a basis for developing ideas about it in relation to the university and the region.
As the source for the theoretical study of university’s intellectual capital the works of Andreichikov and Isaenko (2010), Tsurikov (2010), Kramin and Kochetkova (2012), Zhukova and Chernyaev (2016), Sundukova (2012), Córcoles and Vanderdonckt (2013, Najim et al. (2012), Kok (2007) and others were used.
A theoretical study of the region's intellectual capital issues was based on the works of Chub and Makarov (2015), Khuzina (2016), Monakhov et al. (2016), Liu Chao et al. (2015), Bronisz et al. (2012), Lubacha-Sember (2016), Minasov (2012), Bontis (2004), Sánchez et al. (2007).
All these works made possible to distinguish the structure and essential features of the intellectual capital of the university and the region (Maltseva, 2017a, 2017b) which are used in this study as a basis.
The case study method was chosen as the key method of research because it allows to see various qualitative relationships between the intellectual capital of universities and the region.
Sources were development programs of flagship universities which implement directions of transformation of their own activities for the socio-economic development of the subjects of the Russian Federation.
Development programs and strategic projects of 33 universities which received the status of flagship were analyzed; the most striking examples of the mutual influence of the intellectual capital of universities and regions were marked out from this documents.
Strategic project "V.G. Shukhov BSTU is the integrator of system solutions within the framework of the Belgorod agglomeration’s development "
Brief description: Scientific, expert-consultative, organizational-economic, project-analytical assistance to the development of the innovation infrastructure of the Belgorod agglomeration, technological and social development; coordination of managerial decisions, creation of an effective personnel policy and the provision of regional-industrial manufacturing enterprises and municipal entities of the region with highly qualified personnel in order to achieve the multiplicative effect of municipalities.
Within the framework of the project additional image and brand capital of the university is being formed as a leading scientific, educational and innovation center because replicable solutions can become benchmarks for other agglomerations. This creates additional brand capital for the region itself which plans and implements its development on the basis of advanced scientifically grounded solutions.
The regional system of technological entrepreneurship is based on the capital of ideas and projects and on the capital of university’s intellectual property which is expanded and updated under the influence of similar types of capital of regional stakeholders.
The implementation of technological entrepreneurship development’s system at the university ensures the development of capital of competencies of university’s employees and students which contributes to the expansion of the capital of ideas and projects as a basis for potential start-ups and start-ups which are under creating as well as the regional environment where they participate.
The Innovation and Technology Park "Shukhov Innovation Valley" creates the basis for development of capital of regional environment and regional infrastructure, as it provides opportunities for the implementation of innovative projects.
The capital of university’s knowledge is actively influences on the capital of the regional management system in the process of organizing the system of additional education of the agglomeration’s managerial staff while forming the bases for its own increase during the process of expanding the development tasks that are being solved in the learning process.
The system of monitoring the staffing needs of regional industry manufacturing enterprises, as well as the system of corporate magistracies create the basis for the development of knowledge capital and capital of university’s competencies, since the training system have to be transformed in accordance with the requirements of customers.
Projects that increase the information culture of the population are the basis for expanding the knowledge capital, the capital of the regional environment of the territory at the expense of the university’s intellectual capital.
Strategic project "Interactive educational platform "Vladimir on Klyazma is the spiritual support of Russia"
Brief description: Integration of the region’s resources and the scientific and educational potential of the VlSU on the creation of an interactive educational space in Vladimir region "Vladimir on Klyazma is the spiritual support of Russia" with the aim of creating national self-awareness and educating the youth to respect the history, relics and traditions of Russia and the Vladimir land.
As part of the project, the image capital of the Vladimir region is integrated and multiplied as a region which is rich in cultural heritage, traditions and spirituality. This is facilitated by the capital of knowledge, competencies, professional experience, image and brand of the university.
In addition the replication of the best practices systematized within the framework of the project will promote increasing the region’s image capital, that providing upon condition that the key types of university’s intellectual capital are actively used.
The small innovative enterprises that are planned to create within the framework of the project are a consequence of the concentration and development of the capital of ideas and projects and the capital of intellectual property.
In addition, this is the basis for development of capital of entrepreneurial competencies and experience in the university and in the region.
Within the framework of the project, new additional educational programs are expected to be created, which is ensured by the capital of knowledge, competencies and professional experience of the university’s staff and allows to distribute it in the region, thereby increasing the relevant types of intellectual capital of regional stakeholders in the project profile.
The umbrella-type scientific and educational project "Revived History" will help the university to increase its knowledge capital, which will ensure the growth of new knowledge and their broadcasting in the region, including in the format of master classes in folk arts.
Strategic project "Integrated adaptive technologies and methods of continuous education, support and assistance of citizens in need of social services".
Brief description: Creation on the basis of the university of a replicable inclusive system of people's support based on the unique experience of the Pskov region in the field of habilitation, people’s social adaptation, including children and adults with severe and multiple developmental disorders, and their inclusion in the society’s active life outside stationary institutions by creation of hospital-substituting medical care technologies for all age groups.
The project is aimed at solving region’s important social problems and accumulating the corresponding types of university’s intellectual capital to ensure their implementation, in particular, the capital of knowledge, competencies, and professional experience of scarce medical, pedagogical and socio-psychological personnel.
By creating an inclusive system, the university ensures the growth of image capital and brand capital of the region as a territory creating equal conditions and additional support for persons with health limitations.
In the process of system development, the university acquires additional image capital as a scientific and educational center of regional scope for involving people in need of social services into the region’s life.
The project implementation affects the capital of the regional environment, contributing to the growth of tolerance and social adaptation of persons with health limitations, as well as the capital of the regional health infrastructure. The project contributes to the growth of the health capital of individual citizens, thereby increasing its aggregate value in the region.
The role of the capital of knowledge and competences of university employees and attracted specialists in disseminating knowledge necessary for better social adaptation of persons with severe multiple developmental disabilities has been noted, as well as in the process of training of profile specialists.
Strategic project "Transfer of technologies as a platform for innovation activity of NovSU".
Brief description: Development of effective methodological approaches to mastering technologies from the initial stage to the promotion on the market. Commercialization of intellectual activity’s results through the establishment of targeted interaction of elements of university’s innovation infrastructure within the framework of the technology transfer algorithm.
As part of the creation of a technology transfer system the university consolidates the capital of knowledge, competencies, and the capital of intellectual property of research structures. An additional component of effective work in the field of technology transfer is the capital of knowledge, competencies, professional experience of innovative managers that can be supplemented by the corresponding types of intellectual capital of regional stakeholders which are the representatives of special innovation support structures and specialized experts both on innovation issues and on the issues of project itself.
The organization of the center and ensuring its network involvement in the regional innovation infrastructure contributes to the development of regional infrastructure capital, and also promotes a qualitative change in the capital of the regional environment which is becoming more susceptible to innovation.
The set of methodological documents developed for the dissemination of successful technology transfer experience in the Novgorod region is essentially a formalization of the capital of knowledge and competences that are integrated and formalized in the project.
The process of technologies' transfer to the region and beyond is essentially a system for transferring the university’s formalized knowledge, i.e. there is a movement of intellectual capital products.
Capital of ideas and projects of the university is the important component of the technology transfer system. This capital is actively involved in regional capital and creates the basis for its development and multiplication in the process of targeted promotion. This is possible if joint projects with other regional stakeholders are implemented, as well as when new technologies are introduced into the practice of regional companies, which is the basis for the development of employees’ new knowledge and competencies which are replenished also within the system of additional education organized by the university.
Particular importance in the implementation of the technology transfer center’s project is played by client capital, which provides opportunities for promoting the university's innovations. In the activity’s process it significantly expands and allows to involve all new stakeholders in the innovative ecosystem of the university and the region, which as a whole increases the client capital of the region as a whole.
Strategic project "Creation of the Siberian Center for the Export of Medical Services" on the basis of SibSMU clinics".
Brief description: creation of the "Siberian Center for the Export of Medical Services" with an extensive system of services for residents of the Russian Federation, countries of the far and near abroad, focused on providing high-quality high-tech medical services on the basis of SibSMU clinics.
In the framework of the project the positioning of territory as a center for high-quality medical services and tourism in the macroregion and beyond has a great important.
The university’s capital of knowledge, competencies and professional experience provides a symbiosis of advanced educational, scientific and clinical diagnostic technologies that are the basis of the center's functioning.
The development of the tourist and service component is also associated with the availability of university’s capital of knowledge and competencies.
The brand capital at an effective project implementation can create region’s additional positive image capital.
The region’s client capital is expanding due to attracting tourists from other territories which can be possible when university’s marketing policy is organized competently.
The system of tours and support of clients is formed with attraction of the university’s creative capital as well as innovative capital including not only university studies, but also the proposals of stakeholders - tour operators of the region, as well as regional infrastructure’s capital - tourist and medical. Hospitality infrastructure (restaurant and hotel business) and logistics are being developed under the influence of the university's intellectual capital in accordance with market requirements. All this provides additional region's brand capital.
The creation of a center for the standardization of medical services is another area of concentration of the university’s field-oriented capital of knowledge and competencies which is aimed at improving the quality of medical services, thereby providing the prerequisites for the growth and development of the relevant field-oriented regional intellectual capital.
Strategic Project "Project Office: University & Municipality +"
Brief description: Ensuring sustainable social and economic development of municipalities in the Ulyanovsk region through concentration of the educational, research and expert potential of the university.
The project implemented by the university has a special impact on the regional management system’s capital because it is aimed at its multiplication and transformation by the university.
At the same time, the capital of knowledge and competences of the university’s staff is concentrating including within the framework of advanced training by means of their "immersion" in the problems of socio-economic development of municipalities in the region which ensures its multiplication. The development of the intellectual capital of university’s employees is aimed at increasing its competitiveness and as a result the capital of the image and brand. An increase in similar types of intellectual capital in the region is possible when R&D improve the system of regional and municipal management, as well as certain measures ensuring territory’s development are carried out successfully.
The project is also aimed at increasing the intellectual capital of university’s graduates which ensures the modernization of educational activity. Graduates with advanced capital of competences in the sphere of state and municipal management become the carriers of the region’s capital of knowledge and competencies and in aggregate create the renewed capital of the regional management system and regional environment.
Within the framework of the project, the effective use and development of the university’s client capital in the process of researching the needs of the labor market and the demand on R&D are provided. This creates a basis for the development of the university's intellectual capital in the direction of the needs existing in the region. Collaborations created with regional stakeholders ensures the integration of their capital of knowledge, competencies and professional experience with the university’s one and creates the basis for the search of its further development.
The growth of the regional management system’s capital will be promoted by upgrading the skills of municipal employees which will be implemented on the basis of knowledge capital, university’s competencies.
The university's capital of the ideas and projects will be used to develop investment projects in the region.
In general, an effective management system in the region is the basis of its attractiveness in investment, educational and migration aspects, i.e. the outstripping growth of region’s image capital, as well as client capital is being provided.
As the data shows the most of the projects of regional flagship universities are aimed at concentrating and multiplying intellectual capital within their borders which at the same time ensures the renewal and growth of the region's intellectual capital. The mutual penetration of the intellectual capital of the university and the region in the framework of the implementation of complex projects demonstrates in the future the blurring of the borders between them ensuring their partial splicing to solve complex problems that support the development of both the university and the region.
The study of literature and the comparative analysis of the essential characteristics of intellectual capital of the university and the region made it possible to determine on a qualitative level the mutual influence of its key elements on each other (Table 1).
Table 1
Comparative analysis of the mutual influence of intellectual capital of the university and the region
Group of intellectual capital |
Influence of the intellectual capital on the region |
Influence of the intellectual capital on the university |
Indicators |
Human capital |
|||
Knowledge Capital |
-organization of knowledge’s translation in various areas within the basic and additional education of the region’s population, a system of open events, publications; - the generation of new knowledge as a result of R&D in the interests of the subjects of the regional economy |
- expansion of requirements for new knowledge, R&D in accordance with the development trends of regional systems |
Number of students enrolled in the undergraduate, specialist, master's programs per 10,000 population Number of higher-education teaching personnel engaged in educational activity in higher education programs per 1000 population Number of staff engaged in research and development per 10,000 population Number of researchers with academic degrees per 1000 population Graduation from the postgraduate training program per 1,000 population Graduation from post-doctoral programme per 100 population |
Capital of competencies |
- ensuring the transfer of competencies to the region’s inhabitants as an element of a system of practice-oriented education, events in the format of workshops, master classes, etc. |
- creation of an order for a system of competencies in accordance with the region’s needs |
Number of employees who received training in the form of short-term courses, professional trainings, mentoring from the number of workers in the payroll, in% The share of project-oriented programs in the total number of university educational programs Number of students of additional education who received training at the university |
Capital of professional experience |
- use of the accumulated professional experience of the university’s staff to ensure for educational, research, innovation process |
- filling up the lack of professional experience of the university’s staff in the process of interaction with the external environment |
Number of articles published in WoS per researcher Number of articles published in Scopus, per researcher |
Capital of professional and personal reputation |
- promotion of the region’s brand in the process of professional activity of the university’s staff |
- positioning of outstanding university’s staff in the region |
Number of university’s employees awarded with the President and Government bonuses, diplomas of federal executive bodies, winners of international and All-Russian competitions |
Health Capital |
- the system of health saving created in the framework of the university, educative activities |
- regional health care and environmental protection system that determines the health capital of the university’s staff |
Number of sports and recreation activities and educational campaigns conducted on the university’s platform |
Reputational capital |
|||
Image capital |
- university’s high image provides additional image characteristics to the region as a territory with high scientific and educational potential |
- region’s high image provides a positive attitude towards the university located on its territory |
University’s positions in world rankings Presence of 5-100 universities, regional flagship universities |
Client capital |
- university's established connections with the external environment which facilitate the involvement of stakeholders in regional projects |
- created client capital of the region as a whole and its individual subjects is able to provide additional effective links for the university’s development |
Number of organizations-customers of staff training in the region Number of organizations, customers of R&D Number of international events held by the university |
Brand capital |
- qualitative staff training, implementation of world-class R&D by the university is the basis for the development of the regional economy |
- development of products and services of the regional economy is largely determined by the level of human resources, technologies, etc. |
Number of grants, competitions which were won in the scientific and technical sphere Number of university’s graduates included in the Presidential Register of Management Personnel |
Infrastructure capital |
|||
The capital of the regional environment |
- the university’s internal environment is actively forms a regional environment within the framework of social and cultural initiatives, provides motivation for development |
- the regional environment creates a basis for university’s internal environment and regularly updates it in the process of interaction |
Number of socio-cultural activities conducted by the university Number of region’s residents involved in the social, cultural and educational activities of the university |
Capital of the regional management system |
- the university management system ensures interaction with regional government bodies in the framework of solving joint issues |
- regional management bodies in the framework of management decisions affect university’s management in terms of related tasks |
Presence of the University Development Strategy, coordinated with the region |
Capital of the regional infrastructure |
The university’s infrastructure is part of the regional infrastructure and participates in its functioning |
The regional infrastructure ensures the functioning of certain aspects of the university’s activity (health, logistics, etc.) |
Number of objects of innovative, medical, sports infrastructure of the university |
Innovative capital |
|||
Capital of Intellectual Property |
Technological solutions created on the university’s platform which form the basis for the region’s capital of intellectual property |
The capital of intellectual property of the region's economy subjects can be used in the process of university’s R&D |
Number of patents issued by the university Number of patents supported by the university |
Capital of ideas and projects |
ideas and projects are formed on the university’s platform within the framework of scientific and educational activities that are the part of regional pool of projects |
regional pool of projects is formed under the influence of the university's active activity in the field of science and education |
Number of patent applications lodged by the university Number of scientific, innovative, educational, social projects proposed and presented at the regional level by university’s staff |
In accordance with the allocated concepts of universities 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, it is possible to single out the most significant connections between the intellectual capital of the university and the region for each of them (Figure 1).
Thus, based on the systematization of sources and analysis of university development programs, the interrelations between the components of the intellectual capital of the university and the region were established which makes necessary to develop activities aimed at its audit and development.
To ensure the most effective use of the university's intellectual capital as one of the most important resources for its own development and active influence on the territory it is advisable to made a regular intellectual audit which can be carried out by one of the following methods (Maltseva et al., 2015):
Figure 1
Most significant connections between the intellectual capital of the university and the region
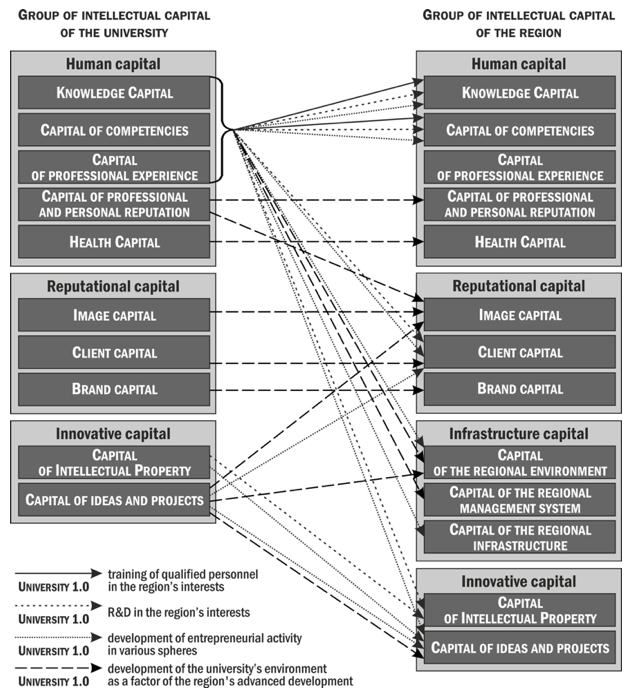
The intellectual capital which carriers are employees, university students, and the structure as a whole must be identified within the framework of the research. Identification can be carried out on the basis of documents, questionnaires, interviewing of employees, which will reveal the university’s potential to use intangible resources in current activity and development projects. It is advisable to establish special registers of intellectual capital on the basis of data on the experience of performing specific types of work by employees, participation in events, competitions, educational projects and programs that can be the basic information for the creation of interdisciplinary teams, R&D on a specific topic, and identify those types of intellectual capital, in which the organization most needs and determine the sources of their replenishment.
Complex information about the university’s intellectual capital can be the basis for the creation of competencies’ centers in priority areas of development.
The paper is the result of the research funded by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation within the research project «Scientific and methodological basis for the creation of competence centers on the platform of regional universities on the basis of the concept of intellectual capital» implemented by Tver State University.
Andreichikov, A.V., Isaenko, Y.S. (2010). The concept and structure of intellectual capital of a higher educational institution. Bulletin of Volgograd State University. Ser. 3. The economy. Ecology. Volume 3. 2(17), pp. 112-116.
Avilova, Z.N. (2013). Management of intellectual potential in the region’s innovative environment. Proceedings of the All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference with International Participation "Reproduction of Intellectual Capital in the System of Higher Professional Education", Belgorod, November 18-22, pp. 122-127. Retrieved from:
http://dspace.bsu.edu.ru/bitstream/123456789/20695/1/Vosproizvidstvo_Intellektualnogo_13.pdf
Bodjayeva, V.V., Slobodchikova, I.V., Nimgirov, A.G. (2015). The university as the center of creation and development of territory‘s intellectual capital. Business. Education. Right. Bulletin of the Volgograd Institute of Business. 4 (33), pp.63-66.
Bontis, N. (2004). National Intellectual Capital Index: a United Nations Initiative for the Arab Region, Journal of Intellectual Capital. 5(1), pp. 13-39. doi:10.1108/14691930410512905
Bronisz, U., Heijman, W. and van Ophem, J. (2012). The assessment of intellectual capital in Polish regions. Applied Studies in Agribusiness and Commerce. 6, pp.101-105.
Chub, A.A., Makarov, P.Y. (2015). Intellectual capital as a factor of russian regions’ sustainable development. Business Strategies. 6(14), pp.24-32. DOI:10.17747/2311-7184-2015-6-5
Córcoles, Y.R., Vanderdonckt, J. (2013). Empirical Evidence for the Increasing Importance of Intellectual Capital Reporting in Higher Education Institutions. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science. 3 (8)[Special Issue – April 2013], pp. 39-51.
Golubkin, I.V., Svetlov, I.E. (2011). The role of intellectual capital of universities in the formation of innovative economy. Economics, statistics and informatics. Bulletin of UMO. 5, pp.9-13.
Khuzina, N.S. (2016). Structure of region’s intellectual capital. Intelligence. Innovation. Investments. 5, pp.52-57.
Kirschin, I.A., Vashurina, E.V., Ovchinnikov, M.N. (2010). The role of federal universities in developing and realizing the intellectual potential of the country and the region. International magazine "Educational Technology & Society". 13(3), pp. 456-470.
Kok, A. (2007). Intellectual Capital Management as Part of Knowledge Management Initiatives at Institutions of Higher Learning. The Electronic Journal of Knowledge Management. 5(2), pp. 181-192.
Kramin, T.V., Kochetkova, N.V. (2012). Management model of universities’s intellectual capital on the basis of the transaction approach. Actual problems of economy and law. 4, pp. 157-163.
Liu Chao, Li Xiao and Xu Lingyu (2015). The Influence of Regional Intellectual Capital on Regional Economic Development-Evidence from China. International Journal of u- and e- Service, Science and Technology. 8(6), pp.91-104 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2015.8.6.10
Lubacha-Sember, J. (2016). Intellectual Capital of the European Union Regions, on example of the Visegrad Countries regions. Building Bridges: Cities and Regions in a Transnational World RSA Annual Conference, Graz, Austria
Maltseva, A.A. (2017a). The essence and definition of the intellectual capital of the university. Bulletin of Tver State University. Series "Economics and Management", 4, pp. 164-170.
Maltseva, A.A. (2017b). The importance of intellectual capital for the development of modern universities: a review of domestic research. Bulletin of the Tver State University. Series "Economics and Management", 3, pp. 264-270.
Monakhov, I.A., Barsukova, N.E., Klyushnikova, E.V. (2016). Methodology and practice of development management of Russian Federation’s science cities at the present stage. Monograph. ed. by Maltseva A.A., Tver: Tver state University, 204 p.
Maltseva, A.A., Monakhov, I.A. (2014). Development of theoretical ideas about intellectual capital in conditions of dynamic transformation of the economy. Actual problems of the economy. 11, pp. 16-33.
Maltseva, A.A., Monakhov, I.A., Klyushnikova, E.V. (2015). Management of Intellectual Capital of Technology park Structures: Theoretical and Methodological Foundations. Ed. Maltseva A.A., Tver, Tver state university, 206 p.
Najim, N.A., Al-Naimi, M.A. & Alnaji, L. (2012). Impact of Intellectual Capital on Realizing University Goals in a Sample of Jordanian Universities. European Journal of Business and Management. 4(14), pp. 153-162.
Sánchez, A.J., Melián, A., García, J.M. (2007). Intellectual capital and sustainable development on islands: an application to the case of Gran Canaria. Regional Studies. 41(4), pp. 473-487.
Serdyukova, L.O. (2011). The role of universities in the management of intellectual capital in regional innovation systems. Innovative activity. 2 (15), pp. 65-71.
Sundukova, G.M. (2012). Management university’s intellectual capital. Author's abstract of dissertation of candidate of economic Sciences, Moscow, Retrieved from:
https://guu.ru/files / referate / sundukova.pdf
Trequattrini, R., Lombardi, R., Lardo, A., Cuozzo, B. (2015).The Impact of Entrepreneurial Universities on Regional Growth: a Local Intellectual Capital Perspective. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, pp.1-13.
Tsurikov, S.V. (2010). Evaluation of intellectual capital in the management of the organization's knowledge (on the example of the university). Author's abstract of dissertation of candidate of economic Sciences, Siberian Academy of Finance and Banking, Novosibirsk, 23 p.
Zhukova, Y.M., Chernyaev, S.I. (2016). Some Aspects of Knowledge Management and Management of Intellectual Capital in the University. Fundamental Research. 5(1), pp. 123-130. Retrieved from: http: //www.fundamental-re...rticle/view? Id = 40261
1. Associate Professor, Lurye Scientific and Methodological Center for Higher School Innovative Activity of Tver State University, Tver, Russia. E-mail: 80179@list.ru