

 Vol. 39 (Nº31) Year 2018. Page 18
Vol. 39 (Nº31) Year 2018. Page 18
Mikhail B. SCHEPAKIN 1; Eva F. KHANDAMOVA 2; Ekaterina V. KRIVOSHEEVA 3; Oksana А. KUZNETSOVA 4; Dariya G. KURENOVA 5
Received: 18/03/2018 • Approved: 27/04/2018
ABSTRACT: Topicality of the studied issue is determined by the fact that, under conditions of competition aggravation and exacerbation of crisis events in economy, enterprises are forced to activate those internal reserves endowed with ability to adapt to new market environment. The goal of the presented article is elaboration of theoretical and methodical model of rational marketing behavior choice by a manufacturing enterprise acting as a tool for business economic advance control and its competitiveness. |
RESUMEN: La actualidad del tema estudiado está determinada por el hecho de que, bajo las condiciones de competencia, agravamiento y exacerbación de los eventos de crisis en la economía, las empresas se ven obligadas a activarse. El objetivo del artículo presentado es la elaboración del modelo teórico y metódico del comportamiento de marketing racional. |
The Russian economy is going through difficult times due to the unfavorable geopolitical situation and the continuing economic sanctions of the West. Certain spheres and sectors of the economy are experiencing difficulties due to the current crisis. The problem is that business resource potential is not being used effectively. We are talking about the opportunities that must be created within the business and in the society itself in the volume and with the quality that are demanded by the state and societies. They must be motivated by the co-workers’ collectives and the business elite and can be implemented not only in the long run but also in the current period, in the name of gaining benefits by all members of society. The deterioration of the market position of the enterprise in consumer markets is associated with a decrease in consumer demand, the inability of businesses to offer products that would satisfy the consumer at prices, quality, assortment and the conditions for stimulating it. To stay on the market, businesses need to either reduce prices, or to offer substitute products that are in demand and do not cause outflow to the consumer audience and satisfy the desired requirements of target audiences. The retention of market positions by the enterprise is connected with the need to include rational adaptive mechanisms and activation of innovative, communication, marketing and other activities of the entities (Schepakin, Krivosheeva & Yeremeev, 2017).
In the emerging market situation, businesses need to adjust their marketing activities to rational marketing behavior, which should be adequate to the requirements of the market, the requests of consumers and business partners (Mashtakov & Schepakin, 2016). Marketing behavior should weaken the influence of negative external and internal influences on the functioning of business by the ability to build up its competitive advantages and to keep them profitable positions in an unstable economy. Competitive advantages here are the basis for building relations between communication participants in the marketing economic space. To manage marketing behavior, new tools are needed to create conditions for increasing the competitiveness of the business. Such tools can be a marketing protector (Schepakin, Krivosheeva & Yeremeev, 2017), a regional marketing implant (Mashtakov & Schepakin, 2016), marketing injections, a person-centric resource in the production component of the enterprise. All these tools will contribute to the increase of consumer value, which acquires the properties of a measure of consumer interest in the business efforts materialized in the form of a product or as a service. It acts as a condition under which a business can count on engaging in a competitive position. It is not durable, as its retention requires constant changes in the use of resources, organizational support, marketing behavior in the market when building relationships with other participants in the marketing field. Key cost factors are the result of employees' actions to implement changes in technology, production, and marketing. They act as a measure of the success or failure of the marketing adaptation of the business to the changing demands of the market.
Enterprises focused on marketing adaptation to market requirements are forced to consider themselves in the context of evaluating their resource capabilities, having a specific content in the content, information, technology, innovation, marketing and other aspects. The real success of business can be ensured if it is professionally competently based inside and outside the enterprise on the aggregate of the following components: a) on a common knowledge base; b) on the ability of the components of the enterprise, included to achieve the objectives of the enterprise; c) balanced elements of the marketing mix; d) the labor resource accumulating the properties and abilities of employees, their business initiative in the interests of the enterprise and in their own interests; e) organizational culture as a catalyst for business activity of personnel at different levels of management; f) the marketing and resource adapter as a tool for managing the changing needs of customers, different actors in the interaction (Khandamova, Schepakin & Haragan, 2012); g) trust in business (Shchepakin, Khandamova & Pyzhenko, 2017) as an integrator of social and moral capital of the subject and his organizational culture.
Effective management of the manufacturing enterprise under conditions of market environment changing requirements cannot be achieved without methodological support providing for the selecting of the best variants of its marketing behavior and, assessing the level of its competitiveness at development of business processes with market participants involved in marketing communication space formed by enterprise.
The leading approach to studying this issue is marketing and integration lead-up to description of processes and events taking place during business processes reengineering, accumulating the components of marketing-eocnomic and motivation and communication approaches. Implementation of the specified approach enables to define resources and tools rating, which are involved by the business during formation of prerequisites for competitive advantages accretion in case of selection of certain variant of marketing behavior.
We carried out the review of literature on studied issue and revealed their aspects that allowed to integrate the scientific achievements previously obtained by the authors and other scientists into development of a new conceptual approach to management of entrepreneurship marketing behavior. The most significant works in this area belong to M. Porter, G.A. Bagiev, R.A. Fatkhutdinov, V.V. Zunde, M.B. Schepakin, E.F. Khandamova, M.S. Fitsurina.
Manufacturing enterprises, taking into account the state of the market, have to improve the marketing, organizational and functional processes (Zunde, 2009), and respond to the changes that occur during crisis periods in Russian economy. Such changes include the following: first, low level of enterprises competitiveness compared to Western companies; second, decline in purchase power under conditions of the Ruble unstable exchange rate (Aganbegyan, 2016); third, impact of the changing environmental factors of the enterprise, and, in particular, the negative trends of political pressure of the West (Bodrunov & Porokhovskiy, 2015). Such changes force the manufacturing enterprises to adapt their marketing behavior to new conditions. At the same time, consideration and timely assessment of these conditions can provide competitive advantages to manufacturing enterprises, both in domestic and global markets, as well as the increase in competitiveness through the development of measures for the rational use of all available and attracted resources. In particular, those include labor, material, financial, and communication resources (Schepakin & Khandamova, 2015). Without the efficient resource management of manufacturing enterprise, it is not possible to solve the problem of its stable and successful functioning in the market (Schepakin, 2008; Schepakin, Mikhaylova & Krivosheeva, 2016).
Enterprise resource management is focused on the development of solutions to improve its competitiveness when forming the desired marketing behavior. Thus, it is possible to choose a rational variant of marketing behavior, in order to improve competitiveness of the manufacturing enterprise under the conditions of resource constraints, according to the proposed model (step-by-step diagram) that includes 6 stages (Figure 1).
During the study of bread baking production industry, the methods of comparative, structural and factor analysis, as well as field, desk and marketing studies and expert estimations were used. The application of tese methods ensured the representativeness of research results, reasonableness of evaluations and credibility of conclusions.
1. Conceptual stage - identification of the economic nature of enterprise competitiveness in various aspects of its display through human-centric resource that contributes to rational marketing behavior of the subject in the market.
Figure 1
Model of choosing rational marketing behavior of manufacturing enterprise
on the factor “competitiveness” under the conditions of resource constraints
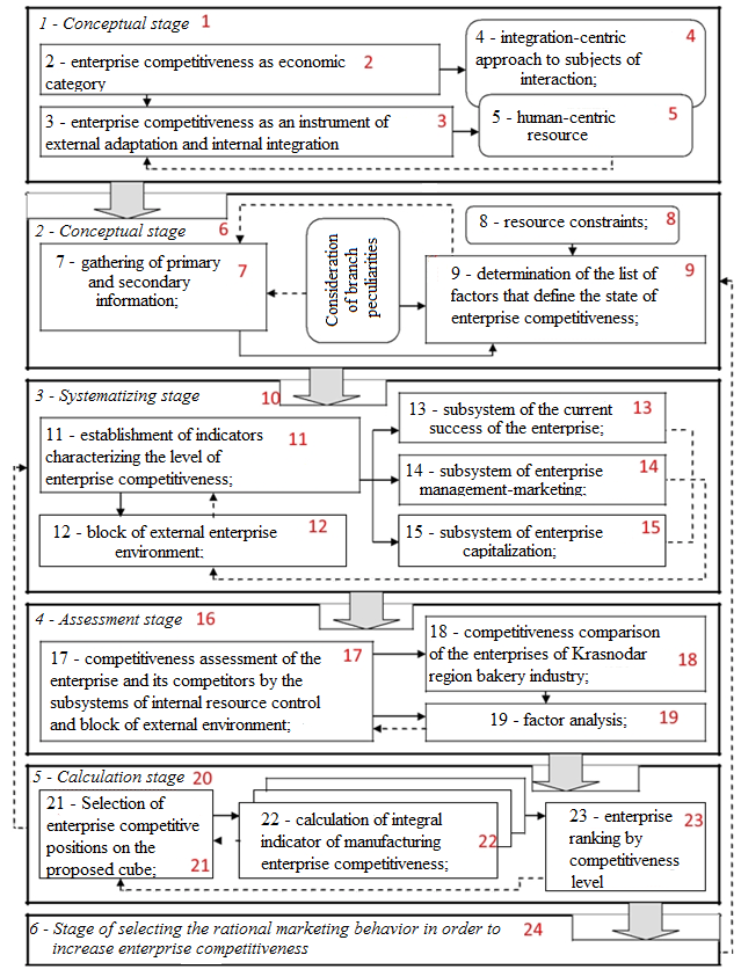
Source: Prepared by the authors.
At this stage, we carried out the comparative analysis of various visions of entrepreneurship competitiveness economic essence. The difference of researcher’s views, that deal with issue of entrepreneurship competitiveness, was revealed. The do not consider that as an instrument by which an economic entity (an entrepreneurship in this case) may adapt to competitive market requirements. Some scientists consider the economic nature of the concept as an “ability” of entrepreneurship to function successfully in the market, creating certain competitive advantages. Such position is presented in the works of the following scientists: A.G Bagiev (Bagiev, 2008), J.-J. Lambin (Lambin, 2008), Ye.P. Golubkov (Golubkov, 2008), Sh.Sh. Magomedov (Magomedov, 2007), T.S. Prakhova (Prakhova, 2005), M. McDonald and I. Dunbar (McDonald & Dunbar, 2012), V. Ye. Hrutskiy and I.V. Korneeva (Hrutskiy & Korneeva, 2005), M.L. Sher (Sher, 2005). Another group of scientists consider the entrepreneurship competitiveness as subject’s intrinsic “feature” that gives it the advantages in comparison with producers of similar goods and services (Beketov, 2007; Fatkhutdinov, 2002; Porter, 2016). Such views expose the essence of the “entrepreneurship competitiveness” concept incompletely, we offer, during disclosure of that concept, to single out two interconnected aspects of competitiveness economic nature: on the one hand, it is an ability of entrepreneurship to fulfill competitiveness reserves, and on the other hand, it is an intrinsic feature of the entrepreneurship, that is embodied in real practice during the building of business processes with various market participants. It is obvious that dichotomy in displays of competitiveness economic nature, that is obtaining, in real practice, a new systemic quality providing competitiveness with features of instrument for enterprise marketing behavior management.
The following interpretation of the enterprise competitiveness concept is proposed: “it is an economic entity instrument, marketing-adapting it to environmental changes due to full and effective use of human-centric resource created in the process of engagement, inclusion, acquisition of various resource types, and implementation of the existing and incremental innovative potential of employees in order to build effective business processes that define the prerequisites for sustainable growth and conquest of competitive position by the enterprise in industrial market in the context of forming its marketing behavior. Human-centric resource means an employee (person) or a group of employees having the innovation-motivational potential, which is aimed at achieving the general and specific organizational, economic and social objectives within the designated enterprise strategic development guideline (Schepakin & Krivosheeva, 2015). That is, the human-centric resource is an instrument with which the manufacturing enterprise defines its marketing behavior in the market. Based on this, we clarified the concept of “marketing behavior”.
According to the author's judgment, the marketing behavior of the subject is a set of interrelated actions committed by the subject or his management and other units in relation to interaction participants, aimed at gaining competitive advantages in the marketing space that is being formed by optimizing the use of available and attracted resources, updating opportunities and reserves, building effective business processes (both inside and outside the subject), forming the image, as well as establishing communication environment balanced in motivations for the most complete satisfaction of consumer needs and social equity (Schepakin & Kuznetsova, 2015). Marketing behavior of an economic entity is integrating the capabilities of its elements, its inherent properties, as well as the resources at its disposal in such a way, that it can either seek mutual trust on the part of its consumers and partners, or contribute to the loss of interest in constructive cooperation (Schepakin, Vinogradova & Foygel, 1997). Thus, marketing behavior of the subject either strengthens its competitiveness, or weakens it.
Proceeding from this statement, it should be noted that marketing behavior actualizes the use of the so-called marketing tread to create the prerequisites for increasing the competitiveness of the business. The subject's marketing protector is an element of the marketing complex of the subject or a combination thereof that acquire such properties in the conditions of a particular market condition and a specific market position of the subject that allow this subject to maintain the retained competitive positions within the specified time period and carry out a marketing simulation to resolve marketing and resource contradictions of different nature in the commercialization of changes without causing significant harm to the state and society (Schepakin, Krivosheeva & Yeremeev, 2017).
The marketing protector acts as an instrument for managing the competitive position of the enterprise, which can create conditions for the adaptation of the economic entity to changes related to the weakening of the influence of the external economic and geopolitical environment. Adaptation of the subject to changes in the market can be conducted in the following directions:
Prerequisites for obtaining desired results of activity by market participants are initially formed within themselves and are created by the efforts of personnel and its person-centered resource. It assumes the role of a leading part in all innovative transformations and marketing initiatives accompanying the tactical behavior of the subjects, as well as their strategic development (through the expansion or rationalization of external communications, involvement in the reengineering of business processes of certain market players concerned, designation new market horizons and new product niches). Includes marketing mimicry as a form of marketing behavior in a particular market environment. Marketing mimicry is understood as marketing behavior of an economic entity that can:
Analytic stage - gathering marketing information to determine market participants, constructing a competitive market map (Krivosheeva, Kurenova & Mikhaylova, 2015; Kurenova, 2015), and defining the list of factors and sub-factors that determine the state of enterprise competitiveness under the conditions of resource constraints during their marketing behavior management. Gaining competitive stability for manufacturing enterprises is possible, if they take into account the variety of internal and external environmental factors of an economic entity on behalf of all participants in the market space. For that, there is a block of external environmental factors and block of controlling enterprise internal resources.
So, the block of management of internal resources is represented by three subsystems:
The block of external environment includes factors of the external environment (factors characterizing the macroeconomic state of the industry, investment, market, natural and climatic conditions, urbanization, risk occurrence and communication activities) that affect the subsystems: the current success of the enterprise; management-marketing; capitalization. It should be noted that environmental factors affect the state of the above subsystems in different ways.
Systematizing stage - establishing of indicators characterizing the level of enterprise competitiveness in specific industry in the context of managing their marketing activities; the formulas for the calculation of these indicators should be proven (Schepakin & Tsitsilina, 2017).
Assessment stage - competitiveness assessment of enterprise and its competitors by the subsystems of internal resource management and external environment block. Assessment of enterprise competitiveness can detect significant indicators that affect the enterprise competitiveness (Schepakin, Khandamova & Haradjan, 2013). Significance can be determined by applying factor analysis using the correlation method. Indicators with a smaller value of correlation coefficient should be excluded from the system of indicators that affect the manufacturing enterprise competitiveness.
Calculation stage - selecting enterprise competitive positions using the assessment cube of the enterprise competitive position, which is an instrument for forming its rational marketing behavior. The cube reflects different states of an enterprise in a real market environment and determines prospects and opportunities of achieving the desired competitive position in the industry market.
It is a system with three dimensions, each axis of which determines the state of the subsystems of management of internal resources of the enterprise, indicated above. The first dimension is the axis of the enterprise's management and marketing, the second is the axis of the company's current success (economic and financial activity) and the third dimension is the company's capitalization axis (innovation and investment activity). Each axis has set ranges of state changes (from low to high). For each axis, correction factors are introduced according to the factors determining them. Within the proposed cube, we can distinguish eight competitive positions reflecting the position of the enterprise in the conditions of a real market environment with different options for marketing behavior.
They are:
Having the characteristics of positions within the proposed cube, an economic entity has the opportunity to take a decision on occupying a certain position in the sectoral market and choose a competitive variant of functioning and development. So, achieving the desired competitive position is ensured by involving various market entities into interaction, as well as promoting organizational and functional behavior of the enterprise personnel through rationalizing the use of available and attracted resources.
After assessing competitiveness of the enterprise and its competitors, we calculate the integral indicator of manufacturing enterprise competitiveness, taking into account the weight and correction coefficients. Enterprises are ranked by the level of competitiveness. Integral indicator of manufacturing enterprise competitiveness as a tool of managing its marketing position in the market reflects the relationship of internal environmental factors and external environment, and formalizes them through the following indices: current success; management- marketing, and enterprise capitalization.
Result stage - the stage of selecting measures to improve the manufacturing enterprise competitiveness by rationalizing its marketing behavior in a real market environment through subsystems of internal resource management for a given period. Such measures may include the following (Schepakin, 2015):
Hereby, providing there is no marketing adaptation to customers’ demands and interests of market agents interacting with the entrepreneurship, no marketing injections into its activity constituents, no marketing mimicry mechanism actualization within unstable market environment, it seems to be impossible for an entity to arrange its reasonable marketing behavior and enforce its competitive positions in particular market (Schepakin, 2011; Schepakin & Khandamova, 2016; Schepakin & Krivosheyevа, 2015).
It should be clarified that by marketing injection the authors understand a kind of activity of the subject aimed at differentiated support of various links (elements) of the marketing chain by introducing into its economic turnover certain internal or external resources (material, financial, innovative, communication, organizational, industrial, technological, investment, psychological, etc.), they are involved in the economic turnover independently or attracted from the outside for stabilization and whether the fixation of their position in the system of relations of the economic entity (both inside and outside of it), as well as for the formation of prerequisites for the sustainable functioning and development of the subject in the socio-economic system.
Marketing injection is a form of management of a subject's condition by the factor “stage of the life cycle of its links and products (services)”. Marketing injection as a function of management in the activity of an economic entity, realizing the opportunities and available potential of its links (elements) to strengthen their positions in the system of relations within and outside the business entity, is a resource of tactical functioning and strategic development. It is a resource in the management of the business entity's activities on points of growth and obtaining mutual benefits by the interacting parties that are at different stages of their life cycles.
Marketing injection acquires the properties of a tool for managing the relations of an economic entity with various market agents (consumers, suppliers, partners, investors, intermediaries, authorities of various levels of authority, etc.) in its marketing communication field, which allows to adapt the subject to changes occurring within the subject and on developing competitive market.
Within the methodological approach to establishing of marketing communication field and on the basis of developing motivation and communication marketing concept (Khandamova, 2012; Khandamova & Schepakin, 2015), we suppose to emphasize integrationcentric approach to management subsystems formation within the subject and to building of mutually beneficial relationships with third-party subjects of interaction by means of resource potential rationalization (via actualization of its human-centered constituent).
The subsystems of internal resource management and external environmental factors supposed by us are interrelated in such a way that they allow to involve the unused reserves of enterprise marketing potential into economic circulation by integrating the resources of various participants of market exchanges for the benefit of the end-user, and gaining benefits by the actual interacting participants with the rational use of their combined resource potential. Thus, the following conclusions may be drawn.
1. Provision of the required competitiveness level of manufacturing enterprises is contributed by human-centric resource. The concept of “enterprise competitiveness” should be considered in the context of forming rational marketing behavior of the economic entity by activating human-centric resource that has properties of the tool for managing competitive position of the enterprise under the external pressure from market subjects and links of internal enterprise environment.
2. Effective management of manufacturing enterprise competitiveness at the contemporary stage of Russian economy development should provide the actualization of such an instrument, which allows to enable available capabilities and enterprise reserves to enhance its competitiveness under the conditions of resource constraints. Achieving the desired result is possible if we use the proposed theoretical and methodological model; it involves integration of resources and motivation elements (links, components) that form the internal structure of economic entity and define its marketing behavior in the market.
3. All stages of the theoretical and methodological model are connected by a single concept and allow to build a holistic view on the methodology of forming rational marketing behavior by a manufacturing enterprise. With the supposed model, the enterprise can take measures to enhance competitiveness under the conditions of real market environment through the subsystems of internal resource management by calculating the integral indicator, which takes into account the current state of external environment. Due to this, the competitive advantages are gained, which allow the manufacturing enterprises to build their marketing and commercial activity to achieve sustainable development and tangible economic growth in specific industry.
Socio-economic value of the supposed model is supported by the mentioned integrated index of manufacturing enterprise competitiveness which is used as an instrument allowing to select rational marketing decisions while building the relationships with market participants for the benefit of the enterprise in strengthening of its competitive positions.
4. Materials of the article may be of use for executives and top managers of manufacturing enterprises at the application of the proposed model as an instrument for selection of of reasonable marketing decisions by means of actuation of human-centered resource, for establishing mutually beneficial communicative relations with market participants, in order to assert competitive position of the enterprise.
Aganbegyan, A. (2016). Who suffered more during crisis - population or business? Arguments and facts: the business environment, 6, 13.
Bagiev, G. A. (2008). Marketing. Saint Petersburg: Piter.
Beketov, N.V. (2007). The concept of competitiveness and its evolution. Marketing in Russia and abroad, 6, 83-86.
Bodrunov, S.D. & Porokhovskiy, A.A. (eds.). (2015). The economic system of modern Russia: Anatomy of the present and future alternative. Мoscow: LENAND.
Fatkhutdinov R.A. (2002). Competitiveness of an entrepreneurship under crisis conditions. Moscow^ Marketing.
Golubkov, Y.P. (2008). Bases of marketing. Moscow: Finpress.
Hrutskiy, V.E. & Korneeva, I.V. (2005). Modern marketing. Handbook on market research. Moscow: Finance.
Khandamova, E.F. (2012). Enterprise communication field: establishing and management. Economics and business,6, 308-315.
Khandamova, E.F. & Schepakin, M.B. (2015). Development of motivation and communication concept of marketing. Economics and business,8(2,61S2), 968-973.
Khandamova, E.F., Schepakin, M.B. & Haragan, L.V. (2012). Marketing and resource adapter the organizational-economic mechanism of management safe functioning and development corporation, Polythematic network electronic scientific journal of the Kuban state agrarian University (the Scientific magazine of Kubsau), 4(78). Krasnodar: Kubgau.
Krivosheeva, E.V. & Kurenova, D.G. & Mikhaylova, V.M. (2015). Competitive environment in the market of the bakery industry in Krasnodar region: theory and practice. Economics and business, 8-1(61-1), 345-350.
Kurenova, D.G. (2015). Market competitiveness maps and their construction as a stage of studying enterprise competitiveness. Economics, Sociology and Law, 1, 88-92.
Lambin, J.-J. (2008). Market-Driven Management. Saint Petersburg: Piter.
Magomedov, S.S. (2007). Marketing researches of goods and services. Moscow: Dashkov & Co.
Mashtakov, A.I. & Schepakin, M.B. (2016). Regional marketing implant as a system-creating component of stable and secure development of the regional economics. Economics and business, 11-3(76-3), 1095-1104.
McDonald, M. & Dunbar, I. (2012). Market Segmentation. Moscow: Business and service.
Porter, M. (2016). Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Moscow: Alpina Publisher.
Prakhova, T.S. (2005). The concept and essence of the competitiveness. Collection of scientific papers of North-Caucasus State Technical University. Series Economics, 2, 17-20.
Schepakin, M.B. (2008). Manufacturing enterprise management under conditions of its adaptation to the market requirements: monograph. Rostov-on-Don: SFU Publishing.
Schepakin, M.B. (2015). Economic entity behavior management in conditions of changes of different nature. Economics and management of control systems, 3(2,17), 308-318.
Schepakin, M.B. (2016). Model of economic entity behavior management within changing marketing space. East European Scientific Journal. EKONOMIA, 6, 110-116.
Schepakin, M.B. & Khandamova, E.F. (2013). On developing the methodological approach of the corporate competitiveness evaluation in developing marketing communication conditions (part 3). Economics and business, 10(39), 304-311.
Schepakin, M.B., & Khandamova, E.F. (2015). Resource management of economic entities in the face of exacerbation of external and internal contradictions in the market space. Economics and business, 6-3(59-3), 1163-1168.
Schepakin, M.B. & Khandamova, E.F. (2016). Adaptive management of subject marketing behavior within an unstable market”. East European Scientific Journal, EKONOMIA, 6, 117-124.
Schepakin, M.B., Khandamova, E.F. & Pyzhenko, I. A. (2017). Increasing confidence to a business entity as a tool of economic growth management. Economics and business, 2-2(79-2), 599-612.
Schepakin, M.B. & Krivosheeva, E.V. (2011). Classification approach estimating factors that define the enterprise competitiveness (based on the example of bakery industry). Scientific and Technical Journal of SPbSPU. Economic Sciences, 2(119), 219-229.
Schepakin, M.B. & Krivosheeva, E.V. (2015). Management of increase of business enterprise’s competitiveness in the changing market environment”. International Research Journal, 9(40), 81-84.
Schepakin, M.B., Krivosheeva, E.V. & Yeremeev, A.V. (2017). Marketing protector as a business tool for keeping competitive position in the market. Vestnik of Astrakhan state technical University. Series: Economics, 3, 16-35.
Schepakin, M.B. & Kuznetsova, O.A. (2015). Concept formation of rational and socially equitable resource management in the developing socio-economic systems. Economics and business, 12-3(65-3), 238-245.
Schepakin, M.B. & Mikhaylova, V.M. and Krivosheeva, E.V. (2016). Resource approach to competitiveness in the production of bakery industry: monograph. Electronic educational scientific publication. Krasnodar.
Schepakin, M.B. & Tsitsilina, V.M. (2007). The methodological approach to assessing resource usage efficiency in enterprises of bread production sub-complex. Scientific and Technical Journal of Saint-Petersburg State Polytechnic University. Economic Sciences, 4(52), 36-44.
Schepakin, M.B. & Vinogradova, N.A. & Foygel, M.A. (1997). Enterprise adaptation to market influence in terms of industry heterogeneity. Bulletin of Higher Schools. Food technology, 2-3, 11-14.
Sher, M. L. (2005). Bases of competitiveness increase among Russian entrepreneurships of goods and services sector under the modern conditions. Stavropol.
Zunde, V.V. (2009). Concept and algorithmic model of forming the system of integrated marketing communications of Russian companies: dissertation thesis of the doctor of economic sciences, Rostov-on-Don.
1. Kuban state technological university, Russia, E-mail: shchepakin@mail.ru
2. Kuban state technological university, Russia
3. Kuban state technological university, Russia, E-mail: keselz@mail.ru
4. Kuban state technological university, Russia, E-mail: oksana.kuznecova.1974@bk.ru
5. Kuban state technological university, Russia, E-mail: ipatovadaria@yandex.ru