

Vol. 39 (Number 32) Year 2018 • Page 17
IVANOVA V.N. 1; YAZEV G.V. 2; KUDRYAVTSEV V.V. 3; SERYOGIN S.N. 4; SHLENOV Y.V. 5; RODINOVA N.P. 6
Received: 26/02/2018 • Approved: 11/04/2018
2. Objects and methods of research
3. Results and their discussion
ABSTRACT: Agricultural consumer cooperation plays an important role in strengthening the country's economic potential, competitiveness and social status of agricultural producers, improving farming conditions and creating incentives for the growth of commodity output. Currently, state incentive measures are being implemented in the form of grants for the development of the material and technical base of agricultural cooperatives, including the construction and modernization of industrial buildings, as well as the acquisition of specialized transport and equipment. This article presents an analysis of the current state of agricultural consumer cooperatives in the Tambov, Lipetsk and Smolensk regions, and the development of cooperation in Russia has been developed. A promising development of agricultural cooperatives is to unite them with processing enterprises, build an agrological chain and involve co-operatives in working with wholesale distribution centers, create and develop export-oriented cooperatives. |
RESUMEN: La cooperación de los consumidores agrícolas desempeña un papel importante en el fortalecimiento del potencial económico, la competitividad y la condición social de los productores agrícolas, mejorando las condiciones agrícolas y creando incentivos para el crecimiento de la producción de productos básicos. Actualmente, se están implementando incentivos estatales en forma de subvenciones para el desarrollo de la base material y técnica de las cooperativas agrícolas, incluida la construcción y modernización de edificios industriales, así como la adquisición de transporte y equipos especializados. Este artículo presenta un análisis del estado actual de las cooperativas de consumidores agrícolas en las regiones de Tambov, Lipetsk y Smolensk, y se ha desarrollado el desarrollo de la cooperación en Rusia. Un desarrollo prometedor de las cooperativas agrícolas es unirlas con las empresas procesadoras, construir una cadena agrológica e involucrar a las cooperativas en el trabajo con centros de distribución al por mayor, crear y desarrollar cooperativas orientadas a la exportación. |
World experience shows that the achievement of social stability in society is impossible without the democratization of property relations and the widespread dissemination of collective forms of management, the main of which are collective enterprises and cooperatives. The most common form is the cooperative movement. The unification of commodity producers on the terms of cooperation acquires particular urgency in modern conditions.
Agricultural cooperation is one of the main mechanisms of ensuring food security. Agricultural cooperation is one of priorities of agrarian policy of the Russian Federation. Agricultural consumer cooperation plays an important role in strengthening of economic capacity of the country, competitiveness and the social status of agricultural producers, improvement of conditions of managing and creation of incentives for growth of products. Cooperation promotes increase in production of different types of production, creation of new jobs, increase in profitability in agriculture, to conducting profitable production, uniting all subjects participating in production, processing and advance of production from production to the consumer.
Special attention is paid to development of agricultural consumer cooperation in Russia nowadays. Evidence of this is the holding of annual All-Russian congresses of rural cooperators. So, on November 16-17, 2017 under the slogan "Association in Cooperatives — a Way to Progress of Agrarian and Industrial Complex" in Moscow the V All-Russian congress of agricultural cooperatives was held. At the congress, the reports focused on the acute development of the soft loan institution and its accessibility to agricultural consumer cooperatives, the need for the use of agricultural consumer credit cooperatives by the rural cooperative system, the development of cooperative infrastructure, and the creation of wholesale distribution centers on the basis of supply and marketing cooperatives.
In 2017, Rosagroleasing, in fulfillment of the assignment of the President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin for the development of cooperation in the countryside, developed the Program for the Development of Agricultural Cooperatives using the Federal Leasing Instrument until 2020.
Within this Program Society carries out hardware of subjects of small and average business by creation of the machine and technological companies in various regions of the country thanks to which optimum loading of the park of agricultural machinery is provided, the cooperation principles are formed, and, above all, financial load of the landowner is reduced and profitability of production of agricultural products grows.
Measures of the state stimulation in the form of grants on development of material and technical resources of agricultural cooperatives, including on construction and modernization of production buildings, and also acquisition of specialized transport and the equipment are implemented. So, in 2017, 2 billion rubles have been allocated to this direction from the federal and regional budgets. Since 2017 grant support to agricultural cooperatives is given within the framework of a "uniform subsidy".
The purpose of the work is to assess the current state of agricultural consumer cooperatives in the Tambov, Lipetsk and Smolensk regions, in order to develop directions for the development of cooperation.
The survey was conducted in the form of individual, group interviews with experts. The survey period was August-December 2017. Experts from the regional departments of agriculture involved in supporting small businesses and cooperatives, managers of consumer cooperatives, informed members of cooperatives, and leaders of organizations promoting cooperation were involved as experts. The information base of the study was the interview materials, the data of the agricultural departments of the surveyed regions, the materials of Rosstat and the regional statistical bodies. For the survey, Lipetsk, Tambov and Smolensk regions were selected.
At present, there are problems of the development of agricultural cooperation in Russia, namely:
• psychological unpreparedness for independent co-operation and forging partnerships;
• imperfection of the legislative framework;
• low level of incomes of rural population, small business entities, which does not allow them to provide the necessary seed capital for creation and implementation of cooperative activities;
• limited access to investment resources, which does not allow updating and upgrading of the material and technical base;
• Inaccessibility of bank loans, due to a lack of collateral base and high rates for attracted financial resources;
• Insufficient level of legal culture, awareness of the population about the benefits of cooperation and the legislative conditions for its development and activities;
• Insufficient state support;
• Underdeveloped procurement network, storage system for agricultural products, commodity distribution infrastructure;
• The lack of an effective sales system as a key link in the commodity distribution chain, which hinders the development of cooperation and the entry of cooperatives into domestic and foreign markets, does not allow achieving the profitability required for extended reproduction;
• lack of an effective system of cooperation, a multi-level vertical management;
• Shortage of qualified personnel, lack of a mechanism for their preparation and consolidation.
Now small farms make a basis of agro-industrial complex of the country and are the potential of development of cooperation (tab. 1) [1].
Table 1
Number of agricultural producers by category
Categories of farms |
The Russian Federation |
Lipetsk region |
Tambov region |
Smolensk region |
Agricultural organizations, units. |
36400 |
440 |
508 |
435 |
Peasant (private) farms and individual entrepreneurs, units. |
174600 |
973 |
1839 |
1274 |
Personal subsidiary and other individual farms of citizens, units. |
18200000 |
232436 |
239593 |
186579 |
Non-profit associations of citizens, units. |
76300 |
144 |
586 |
996 |
According to expert assessments of the unions and associations of agricultural cooperatives, the structure of agricultural cooperatives includes about 1% of personal subsidiary plots and 12% of peasant (farmer) households.
Small farms in the Lipetsk, Tambov and Smolensk regions play a significant role in production of agricultural production, food supply, filling of the regional and local food markets. For many types of products, small forms of management in Russia provide about 50% of the total output in the industry (Table 2). So, in 2017 small forms of management produced: potatoes 86.5% of potato production in farms of all categories, 81.5% - vegetables, 51% - milk.
Table 2
The structure of production of certain types of agricultural products
by categories of farms in Russia and in the three study areas, 2017,%
Name of agricultural production |
The Russian Federation |
Smolensk region |
Lipetsk region |
Tambov region |
||||
Farm Enterprise (including self-employed entrepreneur) |
PSF |
Farm Enterprise (including self-employed entrepreneur) |
PSF |
Farm Enterprise (including self-employed entrepreneur) |
PSF |
Farm Enterprise (including self-employed entrepreneur) |
PSF |
|
Grain and leguminous crops |
28 |
- |
15 |
2 |
15 |
1 |
21 |
0,1 |
Potatoes |
8,5 |
78 |
9 |
83 |
2,3 |
77,8 |
3,0 |
75,4 |
Vegetables |
14,5 |
67 |
6 |
81 |
1,8 |
73,3 |
0,5 |
87,1 |
Fruits and berries |
|
|
- |
99,9 |
0,02 |
40 |
- |
70 |
Milk |
7 |
44 |
11,2 |
29 |
5,1 |
25 |
14,2 |
53,7 |
Meat |
4 |
25 |
2 |
18 |
1,0 |
9 |
0,009 |
10,6 |
Statistical data demonstrate that now personal subsidiary farms (PSF)make an essential contribution to development of agricultural production of the Smolensk, Lipetsk and Tambov regions. The contribution of small farms to agrarian economy of the Lipetsk region annually makes about 30%. In the Lipetsk region they produced 75% of vegetables, 80% - potatoes, in the Smolensk region - about 90% of potatoes and vegetables, milk – 40%, ; in the Tambov region - 25% of milk, and more than 70% of potatoes and vegetables. In the retail price of the product, up to 60% is the costs and profits of processors and traders. One of the most effective mechanisms to increase the producer's share in the price is the development of agricultural consumer cooperation in the processing and marketing of agricultural products.
Let's consider dynamics of development of agricultural production and consumer cooperatives in Russia from 2011 for 2017 inclusive (fig. 1). So, for the beginning of 01.01.2017 the number of agricultural production cooperatives made 8854 units, what is 27,4% less, in comparison with 2011. Although compared to 2014, we can note a growth of 8.6%. The support of small farms given by the state is demanded on places. In the last two years 740 cooperatives are created in Russia. Nowadays 4 thousand cooperatives work in the country.
Fig. 1
Dynamics of the number of agricultural cooperatives in the Russian Federation
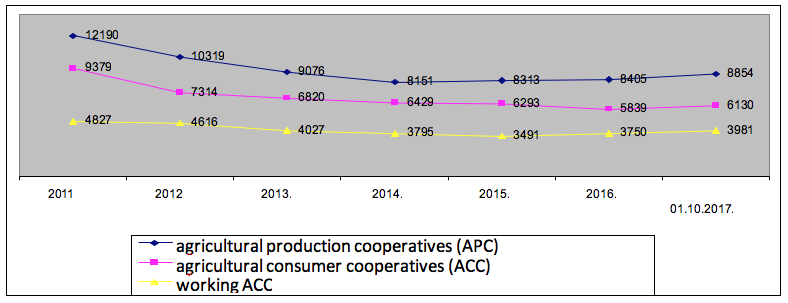
By type of activity, agricultural cooperatives for processing meat predominate - 36% and milk processing - 33%.
The development of agricultural cooperation in 2013-2017 is of a diverse nature. All forms of agricultural cooperatives function in rural areas in Russia as of January 1, 2017, (Table 3).
Table 3
Dynamics of number of agricultural consumer cooperatives
Forms of agricultural consumer cooperatives |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
Number of agricultural consumer cooperatives, including working, piece. |
6252
4027 |
5975
3795 |
5730
3491 |
6293
3491 |
6130
3981 |
- supplying and marketing |
1866 |
1595 |
1441 |
1474 |
1994 |
- credit |
1847 |
1846 |
1740 |
1578 |
1385 |
- processing |
1178 |
1043 |
1124
|
1013 |
1059 |
- serving |
932 |
799 |
750 |
709 |
850 |
others |
|
|
675 |
1519 |
846 |
According to the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation, the number of the registered agricultural consumer cooperatives for December 1, 2017 made 6130 units, and a share of actually working - 65%. In structure of cooperatives the prevailing share is occupied by supplying and marketing cooperatives (32,5%). In 2017 in Russia 740 cooperatives are created.
The considered regions significantly differ on the level and tendencies of development of the cooperative movement. If in the Lipetsk region the number of agricultural consumer cooperatives reached 895, then their quantity is respectively equal in the Tambov and Smolensk regions only 36 and 47 (tab. 1.3). From total number of educated cooperatives in the Lipetsk region really functioning 760 (85,0%), in Tambov – 10 (27,8%) and the Smolensk region – 6 (12,8%).
During 2013 - 2016 total number of cooperatives increased in the Lipetsk region on 414 units, or by 1,9 times, at the same time in the Tambov region their quantity was reduced by 21 units (more than by a third), and in the Smolensk region – by 14 units (almost by a quarter). In the explored regions 24% of all agricultural consumer cooperatives are concentrated, and the share of the working cooperatives in them makes 72% (tab. 4).
Table 4
Territorial educations |
Only, including working, piece. |
including |
|||
processing |
supplying and marketing |
credit |
Others |
||
Smolensk region |
47 6 |
5 |
22 |
1 |
19 |
Lipetsk region |
895 760 |
87 |
455 |
328 |
24 |
Tambov region |
36 10 |
8 |
23 |
3 |
2 |
At the same time the leader in development of agricultural cooperation in the Russian Federation is the Lipetsk region. In the Lipetsk region 895 cooperatives are registered, of which 760 operate. (table 5).
Table 5
Dynamics of number of agricultural consumer cooperatives in the Lipetsk region
|
2014. |
2015. |
2016. |
at 01:01. 2017. |
at 01:12. 2017. |
Number of agricultural consumer cooperatives, including working, piece. |
516
|
613
|
733
|
830
|
895
760 |
- supplying and marketing |
131 |
149 |
189 |
228 |
455 |
- credit |
264 |
288 |
313 |
324 |
328 |
- processing |
36 |
52 |
67 |
76 |
87 |
others |
85 |
124 |
164 |
202 |
24 |
Constantly increasing growth of number of agricultural consumer cooperatives in the Lipetsk region is promoted by effectively operating three-level control system of cooperation development "area-area-settlement" and active work of institutes of development of cooperation (fig. 2).
Fig. 2
Three-level control system of cooperation development in Lipetsk
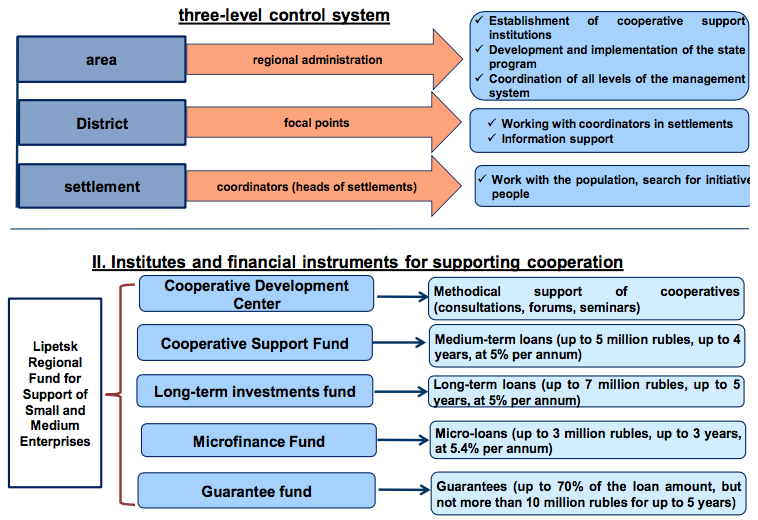
The complex system of development of cooperation created in the Lipetsk region is aimed at the development of rural territories and provides:
In each rural settlement responsible coordinators are defined, generally it is heads of settlements, and in municipal districts the coordination centers are organized. The institutes of development created under the auspices of the Noncommercial microcredit company of the Lipetsk regional fund of support of small and average business became a formula of success of development of cooperation in the field of also: Fund of support of cooperatives, Fund of microfinancing, Center of development of cooperatives. Realization of complex measures (the state support, a three-level control system, institutes of development) provide successful development of cooperation.
About 18 types of loans at the rate of 5% per annum on implementation of the investment projects directed to creation of livestock complexes and farms for cultivation of cattle, building of the cooperative wholesale or retail markets, acquisition of agricultural machinery, the equipment, cargo transport, farm animals, replenishment of current assets, replenishment of fund of financial mutual aid are provided to cooperatives.
Since 2014, the state program "Development of Cooperation and Collective Ownership in the Lipetsk Region" has been in effect until 2020. It is aimed at the development of cooperatives of various orientation, institutes of support of cooperation, creation of cooperative retail chain stores. Till 2020 the amount of financing of the state program makes more than 800 million rubles. For 2014-2016 354 million rubles, from the beginning of 2017 – 168 million rubles are directed to support of cooperatives within the State program of development of cooperation.
Measures of the state support cover all directions – from registration to the organization of sale. For cooperatives there are no restrictions, they can use at the same time all types of subsidies, including on:
- formation of multilevel system of cooperation (it is directed to involvement of new members in agricultural credit cooperatives, creation of cooperatives of the second level);
- maintenance of financial stability of cooperatives (compensation of costs of carrying out audits, on service of the settlement account of cooperative in banks);
- construction and reconstruction of production, warehouse buildings, rooms, constructions on production, processing and storage of agricultural production;
- acquisition of the equipment, vehicles, equipment and cars;
- acquisition of young growth of farm animals and bird, forages, seeds and landing material;
- building of the agricultural cooperative markets, installation of non-stationary shopping facilities for the organization of the agricultural fairs "Malls";
- branding of cooperative production.
Co-operatives are compensated from 30% to 60% of the costs incurred, adjusted for the amount of budgetary allocations provided for each individual subsidy.
In addition to state support for cooperatives, tax incentives are provided within the framework of the regulatory legal acts of the Lipetsk region, which ensure the financial stability of cooperatives, including:
- tax benefits to the agricultural cooperatives which are engaged in production of food products and applying a simplified tax system;
- tax benefits to the individual member businessmen of agricultural consumer cooperatives applying patent system of the taxation (regarding differentiation of the size of revenue, potentially possible to receiving, on kinds of activity, across territories of action of patents (for remote rural areas);
- tax benefits to cooperatives for the property tax of the organizations.
The Tambov region among regions of Central Federal District takes the 6th place on the volume of agricultural production. Regional associations of agricultural cooperatives, farms and personal subsidiary farms can promote ensuring stable development of the food sphere due to formation alternative to mass production and network trade of the market niche satisfying needs of the population for natural products and to development of rural territories on the basis of the increase in employment of the population involved in activity and served by cooperation.
The current state of agricultural consumer cooperation in the Tambov region is characterized by the following essential factors:
- only 9% of peasant (private) farms and 0,1% of personal subsidiary farms of the population are involved in system of consumer cooperation of the region;
- through system of consumer cooperation by small farms milk, and also the cattle and a bird in live weight is implemented generally;
- the operating agricultural consumer cooperatives carry out generally marketing activity, supplying activity is not developed;
- agricultural credit consumer cooperation actually does not function;
- agricultural consumer cooperatives of the second level are absent.
Despite the low level of development, agricultural consumer cooperation in the region at the due organization of the state support and regulation has favorable prospects owing to the following circumstances:
- high specific weight of small farms in structure of production of agricultural production;
- possibilities of expansion of activities of consumer cooperatives due to supplying activity, storage, processing and sale of vegetables and potatoes;
- security of small farms with necessary land resources, possibilities of its increase;
- high share of country people.
In order to create conditions for effective development of agricultural cooperation, it is necessary:
• The cooperative community needs to intensify activities to popularize the movement of agricultural cooperation, cooperative education and increase the cooperative literacy of the rural population; to strengthen work aimed at the exchange of experience between regions on the development of agricultural cooperation;
• Regional bodies of state power and local authorities to conduct regional events in 2018-2019 with the heads of municipalities on the development of agricultural cooperation;
• Regional bodies of state power and local self-government bodies to organize systematic work on training, informing and advising members of cooperatives, governing bodies, specialists in agricultural cooperatives and initiative groups of small forms of management on the development of cooperation in rural areas; create in the regions of the organization infrastructure for the development of agricultural cooperation: development centers, support funds, work to strengthen the audit unions of agricultural cooperatives, as well as strengthen and support agricultural second-level credit cooperatives;
• Regional government bodies and local authorities to promote the creation of logistics centers on the basis of cooperative associations of peasant farms of potato and vegetable growing, providing this process with grant support and preferential investment lending;
• The Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation to hold in 2018 an all-Russian seminar with young heads of rural settlements and young farmers on the creation of agricultural cooperatives. Establish a permanent school "Young Cooperator" in the regions;
• The Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation to make adjustments to the terms of grant support for agricultural cooperatives, in particular: to change the ratio of state support to own funds - 80% to 20%; inclusion in the program of grant support for agricultural consumer cooperatives agricultural consumer credit cooperatives;
• it is necessary to establish a zero tax rate for agricultural consumer cooperatives applying the general taxation system on transactions with products of cooperative members;
• Support the decision of the Congress of Co-operators to establish a structural unit in the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation for the development of agricultural cooperatives, including credit, with the transfer of the function of state regulation to it;
• The Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation, in conjunction with the regional agencies of the agrarian and industrial complex, to organize work on the establishment of regional centers for the development of agricultural cooperation, including on the basis of unions, cooperative associations and farmers' self-government;
• Introduction of best practices for the creation of first-level cooperatives presented by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation;
• It is necessary to implement integrated projects for the creation of storage cooperatives and the processing of agricultural raw materials and aquaculture developed by Razumovsky MSUTM.
A promising development of agricultural cooperatives is to unite them with processing enterprises, build an agrological chain and involve co-operatives in working with wholesale distribution centers, and create and develop export-oriented cooperatives.
Thus, the development of agricultural cooperation is a prerequisite for ensuring the profitability of agricultural production by small and medium-sized businesses, preserving rural employment, increasing purchasing power in rural settlements.
1. All-Russian agricultural census of 2016. Preliminary results: Statistical bulletin / Federal State Statistics Service. Мoscow: Information and publishing center "Statistics of Russia", 2016. 70 p. (in Russian)
2. Voronin B. V. Agricultural consumer cooperation in modern Russia: state, problems / B. A. Voronin, etc.//Agrarian bulletin of the Urals. – 2017. - No. 4, pp. 62-68. (in Russian)
3. Tkachyov A. V., Cherevko A. V. Tendencies and the prospects of development of agricultural cooperation in Russia//agrarian and industrial complex: economy, management. 2017. No. 1. 44 p. (in Russian)
4. Website AKKOP.URL: hpp://www.akkor.ru/
5. Bratanovic, S.B., Greuning, H. Analyzing and Managing Banking Risk: A Framework for Assessing Corporate Governance and Financial Risk / S.B. Bratanovic, H. Greuning.–2nd Edition .–Washington: D.C. ,The World Bank, 2003.– 367 с.
6. Bratanovic S. B., Greuning, H. Analyzing and Managing Banking Risk / S. B. Bratanovic, H.Greunin:A Framework for Assessing Corporate Governance and Financial Risk, 2003. – 245 с.
7. Europe INNOVA Gazelles Innovation Panel. the Evidence // Small Business Economics. Available at: http://www.europe-innova.org. (accessed 16.09. 2014)
8. Gumerov, А., Fast Multipole Methods for the Helmholtz Equation in Three Dimensions. – London, PRESS, 2010. – 426 с.
9. Batrak V.S. Methodology for assessing the level of regional competitiveness // Regional economy: theory and practice. 2016. No. 4, p. 89-103. (in Russian)
10. Buzdalov I.N. Structural distortions in Russia's agriculture: causes and consequences // AIC: economy, management. 2017. No. 2, p. 4-14. (in Russian)
11. Vershinin V.F. Organizational and legal foundations of agricultural cooperation. - M., 2016, - 199 p. (in Russian)
12. Volkov S.K., Orlova O.V. The system of state support of agricultural entrepreneurship as a factor of increasing the activity of the subjects of the industry // Regional economy: theory and practice. 2016. No. 4, p. 104-110. (in Russian)
13. All-Russian Agricultural Census of 2016. Preliminary results. Statistical Bulletin / Federal State Statistics Service. - Moscow: "Statistics of Russia", 2016. - 70 p.
14. Golubev A.V. Import substitution in the agro-food market of Russia: intentions and opportunities // Issues of economics. 2016. № 3, p.46-62. (in Russian)
15. Goncharova I.V., Haag A.V., Novik Ya.V. Agricultural cooperation - the basis for the development of personal subsidiary plots // Young scientist. 2016. No. 5.6, p. 112-115. (in Russian)
16. Devyatkina L.N. Farmers in Russia: results and problems of development // Economics of agriculture in Russia. 2015. № 6, p. 53-60. (in Russian)
17. Dementiev V.E., Kachalov R.M., Kleiner GB. Collective forms of management in the modern economy. Under. Ed. G.B. Kleiner. CEMI RAS. - Moscow: Publishing House "Scientific Library", 2017. - 356 p. (in Russian)
18. Ivanova V.N., Ivanov S.A. Import substitution of agricultural products. Factors of competitiveness. - Moscow: Finance and Statistics, 2014. - 216 p. (in Russian)
19. Rosemarie Buhlmann und Anneliese Tearns. Ainfuhrung in die Fachsprache der Betriebswirtschaft. – Band I-II. – Munchen, 1989. – 203 p.
20. Brehmen, B. The Psychology of Risk / B. Brehmen// Risk and Decisions Edited by W.T. Jingleton and J.Holden. Willy, 1987. – 345 p.
1. Federal State Budget Educational Institution of Higher Education «K.G. Razumovsky Moscow State University of technologies and management (the First Cossack University)»; Russia, Moscow, 73, Zemlyanoy Val
2. Federal State Budget Educational Institution of Higher Education «K.G. Razumovsky Moscow State University of technologies and management (the First Cossack University)»; Russia, Moscow, 73, Zemlyanoy Val
3. Federal State Budget Educational Institution of Higher Education «K.G. Razumovsky Moscow State University of technologies and management (the First Cossack University)»; Russia, Moscow, 73, Zemlyanoy Val
4. Federal State Budget Educational Institution of Higher Education «K.G. Razumovsky Moscow State University of technologies and management (the First Cossack University)»; Russia, Moscow, 73, Zemlyanoy Val
5. Federal State Budget Educational Institution of Higher Education «K.G. Razumovsky Moscow State University of technologies and management (the First Cossack University)»; Russia, Moscow, 73, Zemlyanoy Val