

Vol. 40 (Number 18) Year 2019. Page 7
REBROWA, Natalia P. 1; FRIK, Olga V. 2 & KOVALEV, Alexander I. 3
Received: 11/02/2019 • Approved: 15/05/2019 • Published 03/06/2019
ABSTRACT: At present, regions are starting to show themselves as independent subjects of competition. Constant maintenance of competitiveness is becoming a strategic task for the region. A comparative analysis of methods currently used in Russia for assessing the competitiveness of regions demonstrates limitations in methodological terms. The authors propose a comprehensive universal methodology for assessing the competitiveness of a region. It includes three key conditions that can be changed depending on the goals and objectives of a particular study. |
RESUMEN: En la actualidad, las regiones comienzan a mostrarse como sujetos independientes de la competencia. El mantenimiento constante de la competitividad se está convirtiendo en una tarea estratégica para la región. Un análisis comparativo de los métodos utilizados actualmente en Rusia para evaluar la competitividad de las regiones demuestra limitaciones en términos metodológicos. Los autores proponen una metodología universal integral para evaluar la competitividad de una región. Incluye tres condiciones clave que pueden modificarse según las metas y los objetivos de un estudio en particular. |
In general, the region produces the economic situation of the state, the state of its service, resource, commodity and money markets, the structure of expenditures, the levels of prices and welfare, costs and technological structure. As a result, the region adapts key development trends, structural changes in the national economic system, reflects with more or less lateness and approximation its fluctuations, positive and negative dynamic changes.
At the same time, the region is distinguished by a certain economic originality: in some, smoothing of the negative dynamics of the national economy can be traced, in others, it is significantly enhanced. In the regions, there is a significant difference in the speed of opportunistic and strategic changes, in the level of adaptive changes, the mechanism for finding ways out of economically difficult situations, and also in the degree of controllability. The formation of the regional economy is due, in addition, to the balance of elements, its internal proportionality, functional order, expediency and breadth of external and intrasystem relations. Sustainability implies the creation of a certain adaptive mechanism that allows you to respond in a timely manner to systemic and subsystem changes of factors, as well as to make adjustments to the movement of the established direction. The nationwide changes include: transformation of the sectoral structure, goals and priorities of economic activity, increasing the openness of the national economy, negative fluctuations of the emerging market, transformation of intrasystem relations, as well as changes in social relations and increasing social tension. Of all the areas of modern marketing theory, the least developed is the marketing of the region. In our country, the regional market is less studied and less developed. Today, it is hardly possible to speak about the current system of studying the regional market; it is rather the preparation of the region for work in new conditions than the real reality. It is important to find out the methods and methods of studying and measuring the market, the behavior of subjects in a competitive environment, risk, the struggle for survival. The contradiction of the market will inevitably escalate with the emergence of various forms of management and the development of market relations. As a result, special attention is paid to foreign experience of marketing research as an economic phenomenon. In addition, there is a need for regions to independently adapt to long-term strategic changes, as well as to quickly capture cyclical and opportunistic changes in their own market. In the formation of such a mechanism, which, in turn, shows the strategic development of the region, considerable difficulties arise for states with long-standing market traditions. In addition, this process acquires considerable difficulty in the Russian regions under the conditions of their radical changes, when most of the problems are combined into a single whole with tightly compressed contradictions as soon as possible.
In a broad sense, the study of the development of the region implies the study of it as a subsystem of the national economy with all the difficulties of the relationship of the part and the whole. The process of market research is divided into two levels. At the first level, the current situation is analyzed, which makes it possible to efficiently organize operational activities and the achievement of goals for the near term. At the second level, measurements of existing market opportunities are carried out, allowing us to create a strategy of survival and effective functioning for the long term.
In the context of the development of private and individual entrepreneurship, it is important to ascertain the distribution of market shares (in the region, city and region) between different market actors. It is necessary to study the nature of the market.
Different schools and directions interpret it differently. Some people underestimate the market, as it carries a lot of contradictions that need to be solved not by market methods; others overestimate it, seeing in it a way to automatically solve all economic and social problems, since it forms incentives and motives for social and economic activity. Significant in the formation of the author’s research concept were general approaches to the understanding of regional competition, competitiveness of economic actors, formed in the works of J. Sachs, J. A. Hart, J.E. Spero, S. Cohen, J.B. DeLong (SACHS, 2015; SPERO and HART, 2010; COHEN and DELONG, 2016). In general, the market is viewed as either a constantly self-regulating process, or as a result of interaction between different market actors, or as a system of multiple connections between consumers and producers, buyers and sellers, owners of money and goods.
The purpose of the article is to study the factors and market conditions affecting the assessment of the competitiveness of a region.
The theoretical basis of the study is the provisions and conclusions contained in the works of Russian and foreign scientists in the field of methods for assessing the competitiveness of regions. The methodological basis of the research consists of such scientific methods as
system analysis, synthesis, deduction, induction, formalization, modeling and forecasting.
The results of the market research are used to analyze and assess the market opportunities of the region, while taking into account the goals and resources of the region itself. Survey and questioning are considered the easiest methods of such study.
Residents also act as an expert if they are surveyed and questioned. To carry out a wider coverage of aspects and in-depth analysis involved teams of specialists from the outside.
Expert evaluations of all groups are subjective in nature, so judgments can be very different. However, differences can be overcome on the basis of mutual correlation using additional information.
Statistical analysis methods are used in the analysis and processing of real data. As a rule, two adjacent periods are considered - the current and the base.
Analytical methods that unite broad classes of various research methods make it possible to find out the logic behind the development of any trends in the services market, and also make it possible to identify the interrelationships between various factors.
To consolidate in the market, the region must constantly improve its competitiveness. Continuing to maintain competitiveness and outrunning a competitor in the development and adoption of new technologies is becoming a key, strategic task for the region.
In a market economy, the problem of the strategic development of a region turns into a problem of dynamic equilibrium. The difference in the maturity of different social and economic processes, the multidirectional nature of their dynamics, the discrepancy in the duration and degree of their development under the influence of tools of direct and indirect regulation make it very difficult to ensure dynamic equilibrium. To make certain decisions, a detailed, adequate statistical basis is necessary, allowing immediate quantitative measurement of current processes, prediction of private and general development trends and the consequences of certain decisions. It is necessary to take into account the factor of uncertainty, unpredictability and risk. The problems of managing this process are now complicated by the reform of statehood, the painful process of separation of property rights and responsibilities of the center and regions, however, most of the national trends are barely visible.
The emergence of a new type of structure in the Russian Federation is inevitably combined with integration trends at the global and national levels, the globalization of trade, economic, informational and financial operations that objectively blur the boundaries of the region’s isolation and autonomization, are a strong constraint to the regionalization process, aggravate the problems of local regulation and increase uncertainty of strategic development. It is necessary to take into account that Western capitals are the most mobile and active, they can act strategically and quickly in a competitive struggle. The lack of such experience among Russian entrepreneurs in advance puts them in unequal conditions. The question of rational regional protectionism and the economic security of the regions is most pronounced in the case if you treat it with the necessary degree of responsibility. Difficult economic situation, complicated by the crisis, toughens competition among the regions for a limited number of investment projects, including foreign ones. In most cases, a significant increase and expansion of preferences is considered an instrument of this kind of struggle, and there is also a kind of competition between regions for providing investors with the most favorable conditions. This situation is beneficial for investors, but it means shifting the tax burden to the mass consumer, medium and small local producers, who inevitably are obliged to increase the reduction of the region’s aggregate demand, which is dangerous due to the imbalance in the development of the region. It is necessary to take into account the losses and benefits of investment policy in the short and long periods. The stability of the economic subsystem in terms of the market model is guaranteed by the equilibrium in the resource markets, including labor and financial ones.
The development of the region as a whole is ensured by the formation of the national economy system, the degree of interaction of its structural subsystems, besides this, the ability of the regions to independently set strategic and current goals, to form a mechanism for adapting to different changes, and also to search for reserves of self-development and self-organization.
The need to move from the “seller’s market” to the “consumer market” has caused a change in the marketing strategies of the region’s marketing, as well as significant transaction costs, market research, properties of services and products, and choice of partners. With the destruction of the monopolies, the countries of the organization remained in an “empty” environment and with a distorted organizational and cooperative structure that was not adapted to livelihoods in market conditions, which necessitated the formation of the newest paradigm of development of the region.
Today, the need for socio-economic strategic planning as a dynamic model of development has been recognized, starting with a single firm or enterprise to the region as a whole. The socio-economic policy of the region is designed to promote self-development and autonomy of business entities, the choice of rational allocation of resources, increase competitiveness, create specific, location-based programs with the involvement of regional expertise.
The term competitiveness is currently acquiring particular relevance at the regional level. This is primarily due to the fact that the regions are beginning to show themselves as independent subjects of competition.
In a market economy, regions should, on the one hand, measure their competencies with resources from the federal center and find, if necessary, alternative sources of replenishment of the regional budget, on the other hand, take into account the role played by one or another region in the country's economy. Finally, the regional authorities are given the task of delegating authority to the regional and local community in order to obtain stable economic development.
But in the theory of competition, the importance of space, as well as the region, began to be taken into account relatively recently, since the region was previously regarded as a point on the map, whose position cannot be changed and improved. It should be noted that in a market economy, a region is considered to be a springboard for attracting investment, financial, labor and other types of resources and is fighting for its survival with other competing regions.
Therefore, we can conclude about the need to apply the theory of competitiveness in relation to the region. Due to this, it is possible to conduct a competent assessment of a region by its level of competitiveness, which will determine its strengths and weaknesses, external and internal threats, as well as the influence of certain economic, social, managerial and other factors on its economy. In the future, such an analysis will allow the region to assess its competitive potential, as well as use its competitive advantages in relation to other regions.
Evaluation of regional competitiveness is a complex multifactor task, which consists not only in the economically sound choice of economic and social factors for the analysis and calculation of their significance, but also in the practical use of the results obtained in regional planning and strategic development of the region.
A comparative analysis of methods currently used in Russia for assessing the competitiveness of regions demonstrates some limitations in methodological terms. In the study of integrated assessment, many scientists do not take into account the underlying factors affecting the level of competitiveness. This leads to a narrowing of the very concept of regional competitiveness. For example, many studies put regional attractiveness at the synonymous with competitiveness, especially in the area of finance and investment, but other important target groups such as tourists, regional producers, the population, potential residents and business may not be taken into account, therefore, the conclusion that they are complex The results will not be entirely true. To date, there is no one true and universal set of factors, each researcher forms a classification of indicators based on the goals and objectives that he has set in his work, therefore, the methodological aspects of regional competitiveness are not sufficiently developed.
In addition, in many works, you can see the approach, which is to study certain aspects of the competitiveness of the region and their predominance over the integrated integral assessments of the competitive position of the region (REBROWA, 2018).
Among such a variety of concepts and approaches to the analysis and assessment of the competitiveness of a region, the use of the rank method looks rather simple and yields reliable and accurate results, in our opinion. As a supplement to such a method, we can consider the method of expert assessments, which makes it possible at the highest level to establish weighting factors for indicators and indicators, which will reduce the subjectivity of the results obtained.
In our opinion, the assessment of regional competitiveness should be carried out on the basis of an algorithm containing eight consecutive stages (see Fig. 1).
The most important from the point of view of regional competitiveness assessment is the third stage, which implies the selection of such socio-economic indicators that most reflect the position and condition of one region in relation to another. In our opinion, it is rational to investigate the indicators and indicators that are in statistical collections, since, on the one hand, this will provide general accessibility for the study, and on the other hand, it will provide an opportunity to get objective and reliable results.
The results of the analysis of competitors and the degree of competition make it possible not only to create the right business strategy and policy of the region in the market, but also to clearly establish the shortcomings of the marketing activities of the region. Here, first of all, the main competitors of the region are established, and their strengths and weaknesses are analyzed. This is of particular importance when entering new markets, when developing a new area of economic activity. In this area, marketing research also affects the pricing policy of competitors, their financial situation, goals in a particular market, features of production, as well as the management process.
As competition develops, marketing activities develop to the most diverse and complex forms. Based on the conceptual understanding of the potential of the region and the possibility of its penetration and consolidation in this area, it is necessary to choose a market coverage strategy in order to implement a positioning system.
Having studied competitive positions, the organization seeks to fill the channel existing in the market and begin to plan in detail the marketing mix.
Forecasting sales is considered the basis of in-house planning. It begins with planning, sales forecast, the possible sales of a certain type of services for all departments of the organization. This forecast is based on uncontrolled, unspecified or random factors, the impact of which on the financial position of any industry is quite large.
Figure 1
Algorithm for assessing the
competitiveness of a region
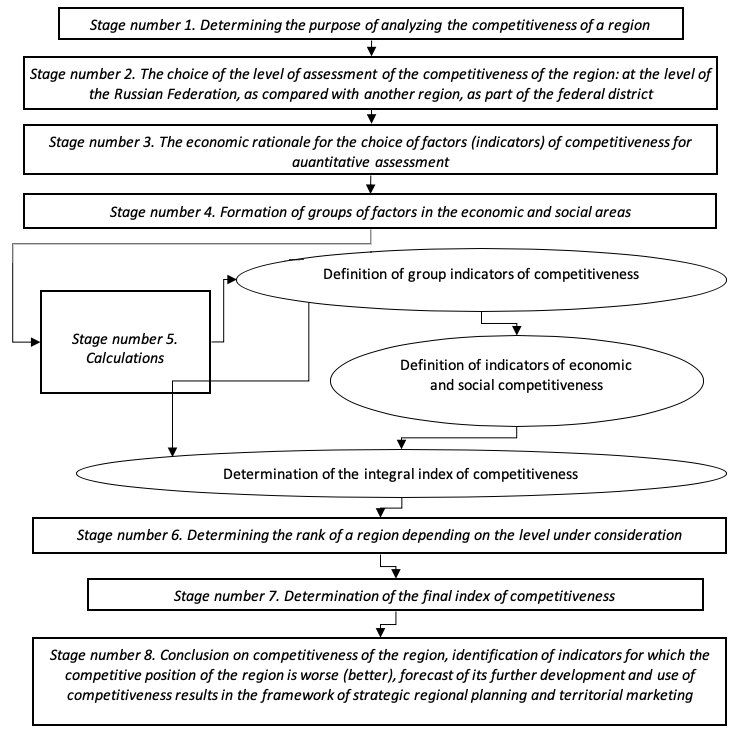
Source: REBROWA, SEDELNIKOV, 2014, p.94.
Today, there is no single point of view among the scientific community regarding the factors reflecting a greater degree of competitiveness of the region. Some scientists propose to consider as the main indicators and indicators of investment attractiveness, the second take into account innovative activity, the third - the level of infrastructure development, as well as the standard of living of society. In addition, there is also such a point of view, according to which, separately, it is necessary to single out the so-called managerial factors that determine the quality of management of state institutions.
Despite this diversity of approaches, in our opinion, it is rational and expedient to use more proven indicators and indicators, that is, those that are included in the statistical compilations, and this, as a rule, is socio-economic indicators and indicators (CHAYNIKOVA, 2008).
To analyze and assess the competitiveness of a region, we suggest using the following economic and social indicators (see Table 1).
Table 1
Economic and social indicators of regional competitiveness
Economic indicators |
Social indicators |
Per capita income of the population |
Economically active population |
Average consumer spending per capita |
Number of unemployed |
Revenues of consolidated budgets of subjects of the Russian Federation |
Number of enterprises and organizations |
Net financial result (profit minus loss) of organizations |
Average prices in the primary housing market |
The costs of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for the implementation of measures of social support for certain categories of citizens |
Average prices in the secondary housing market |
Fixed investment |
Air pollutant emissions from stationary sources |
Investments in fixed capital of organizations with foreign capital participation |
Discharge of polluted wastewater to surface water bodies |
Organizations performing research and development |
Graduation of students of state and municipal educational institutions |
Technological Innovation Costs |
Graduation of specialists with secondary vocational education |
Retail turnover |
Graduation of specialists with higher professional education |
Catering turnover |
Number of preschool educational institutions |
The volume of public utilities |
The number of doctors of all specialties |
The volume of transport services to the population |
Number of hospital beds |
The volume of communication services to the population |
Children's health institutions |
Therefore, it can be concluded that the complexity and universality of the proposed competitiveness assessment methodology is that it includes three key conditions that can be changed depending on the goals and objectives of this or that study. We note these conditions:
1. All information that is needed for calculations, and in particular, socio-economic indicators and indicators, which are taken from the statistical compendium - Regions of Russia. Socio-economic indicators;
2. All information is usually analyzed not in one year (static), but in dynamics - 3-5 years;
3. All data are disclosed as part of the analysis of the level chosen by the researcher (level of the Russian Federation, federal districts, neighboring regions, etc.)
All this makes it possible for other researchers to make the necessary corrections in the form of a time period, to take all possible indicators and indicators existing in statistical collections, and also to examine and analyze them at various levels in order to assess the competitiveness of a region.
Significant level of economic culture and flexibility of thinking, knowledge of economic psychology of various market subjects, in-depth development of functional, structural, strategic and system analysis skills, abilities to predict and catch changes in endogenous and exogenous conditions in time, ability to foresee their various consequences, conditions of high risk and implement appropriate operational and strategic decisions - not at all complete A list of specialist qualities identified by the stringent requirements of the modern market Preparation of such a specialist is a long and difficult process, but at the same time administrative structures and business circles are interested in this.
As part of the personnel policy, the training of specialists in the field of marketing for a market economy is part of a promising strategic regional programming. This training should be the most manageable and focused. When the supply meets the demand for the structure, volume and quality of training, an equilibrium of the labor market is achieved. It is necessary, as far as possible, to identify the anticipated need for specialists in the amount of prospective demand for them from entrepreneurs and administrations of all levels of management. In addition, it is necessary to take into account data on the prospects for regional development, as well as its individual economic structures, modern and local businesses, and infrastructure.
Nevertheless, forecasts for different business entities will have varying degrees of reliability. Research on future demand in this sector of the labor market makes it possible to find additional requirements for specialists and their qualifications. In the future, based on this information bank, certain agreements may be created between institutes and universities, faculties, departments and the business sphere. The system of contracts, contracts, agreements, applications will allow to form a differentiated system of preparation at the earliest stages.
The market is characterized by the variability of search directions, flexibility, functional dependence of its individual components. Appropriate flexibility in the training of specialists should be ensured by a thorough study of specific disciplines, a high level of general economic preparedness, a well-established system of interdisciplinary relations and programs of additional special courses, depending on the problems that are of interest to the administration and the business community.
The creation of a system that is most open in relation to external economic relations implies that in the process of learning there should be a bias towards the most detailed study of contradictions, trends and patterns, the conjuncture of the world and Russian economies. Along with these data, one should develop and improve economic intuition, create a common high economic culture among specialists, develop and improve the ability to ensure stable work in conditions of economic risk and competitive struggle.
Firstly, the theory of competitiveness should be applied to the region. Due to this, it is possible to conduct a competent assessment of a region by its level of competitiveness, which will allow determining its strengths and weaknesses, external and internal threats, as well as the influence of individual economic, social, managerial and other factors on its economy. In the future, such an analysis will allow the region to assess its competitive potential, as well as use its competitive advantages in relation to other regions.
Secondly, evaluation of regional competitiveness is a complex multifactorial task, which consists not only in the economically sound choice of economic and social factors for the analysis and calculation of their significance, but also in the practical use of the results obtained in regional planning and strategic development of the region.
CHAYNIKOVA, L.N. (2008) Methodological and practical aspects of assessing the competitiveness of a region: a monograph. Tambov: Publishing House of Tambov State Technical University.
COHEN, Stephen S. and DELONG, J. Bradford (2016). Concrete Economics: The Hamilton Approach to Economic Growth and Policy. Harvard Business Review Press
REBROWA, N.P. (2018) Territorial marketing: a tutorial. Moscow: Prometheus.
REBROWA, N.P., SEDELNIKOV, V.M. (2014) Conceptual aspects of strategic territorial marketing: a monograph. Omsk: Publishing house of Omsk State Technical University.
SACHS, Jeffrey (March 3, 2015). The Age of Sustainable Development. Columbia University Press
SPERO, Joan Edelman; HART, Jeffrey A. (2010) The Politics of International Economic Relations. Boston: Cengage, 2010
1. Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, Department of Economics and Management, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation; Omsk Branch; Russian Federation, E-mail: n.rebrowa2013@yandex.ru
2. Candidate of Philosophical Sciences, Associate Professor, Department of Social Sciences, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation; Omsk Branch; Russian Federation, E-mail: OVFrik@fa.ru
3. Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, Department of Economics and Management, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation; Omsk Branch; Russian Federation, E-mail: AIKovalev@fa.ru