

 Vol. 40 (Number 21) Year 2019. Page 17
Vol. 40 (Number 21) Year 2019. Page 17
IGNATOVA, Tatiana V. 1; OVCHARENKO, Georgy V. 2; LARKINA, Nataliya G. 3 & FILIMONTSEVA, Elena M. 4
Received: 01/04/2019 • Approved: 06/06/2019 • Published 24/06/2019
ABSTRACT: The article reveals the need and importance of innovative higher education for the creation of a new Russian economy with accent to development of innovative training for self-improvement of each manager on the basis of innovative culture, contributing to the creation of innovative managers-organizers with innovative thinking and personal responsibility for their activities in the modern production and community. |
RESUMEN: El articulo revela la necesidad y la importancia de la educacion innovadora para la formacion de una nueva economia Ruso con un enfoque en el desarollo de apprendizaje innovador para el autodesarollo de cada gerente basado en la cultura innovadora, lo que contribue al surgimiento de gerentes y de los organizadores con mentalidad innovadora y responsabilidad personal por sus actividades en la production moderna y en general. |
The structure of this paper includes a brief description of the innovative characteristics of higher education in Russia and the methodology used, the statistical results and finally conclusions and policy implications.
Education is a civil and personal value, providing the national security of the state and steady life of people. Development and flourishing of state and society depends on the health, education and work of its’ citizens, defining its future in the context of foresight.
Establishing in Russia new innovative institutes (universities) is not only necessity, but an imperative of creation of innovative professional leaders-organizers capable to supervise the innovative development of the branches of economy on the basis of self-enhancement of every person in collaboration and trust to partners, thus creating innovative intellectual environment. The innovative processes on all levels of education define the development and setting up humanitarian traditions and innovative values in educational collectives, implementing social and ecological aspects.
Innovative knowledge is created through the organization of innovative education in the context of innovative reflection of university managers based on the following principles: insight, generation of innovative ideas, synergy and cynectics, which assists not only to achieve the results of innovative thinking, but to develop civil responsibility of university managers.
From the scientific point of view the level of innovative education of a personality is created by the humane-spiritual-moral realizing and understanding of ethics, esthetics and morale of innovative thinking, defining neo-sociality of scientific-industrial performance in innovative-educational sphere, which gives birth to innovative supervisors-organizers, building innovative society.
From the theoretical point of view methodological aspects of humanity of innovative education define the realization of scientific-didactic prognosis of setting up and developing of innovative education and innovative culture for spiritual-patriotic supervisors-organizers of youth social activities.
The formation of innovative-informational-technological vector of mutually beneficial innovative competences in supervisors describes the ability of innovative thinking and managerial ethics on the basis of innovative education for the organization of innovative cycle of manufacturing and service, realizing new knowledge of personnel with use of computer modelling. There is in fact the interaction of a person, state, science, education, society, manufacture.
Socrates is considered by scientists as the first teacher-innovator, stating that human being is creator and designer. Thus, K. Marks (1955-1981) in his research marked that “… the essence of a human being is not abstract … in his activities, it is the summary of all social relations”. Also the origin of innovative educational processes lays in traditions and history of our ancestors, which now are treated as wisdom of anticipation with elements of innovative upbringing. Thus, the great Russian scholar Mikhail Lomonosov stressed and grounded his idea of national character of education in Moscow State University, according to his insistence that lectures were delivered by Russian professors in Russian language because language was possessor and expresser of all the wealth of culture of the people and country (Belyvsky, 1995).
Philosophy of education is factually goes along the vector of innovative activities in universities on the basis of creation:
The peculiarity of innovative education in the conditions of new economics is the priority of innovative teaching applicable to all citizens, allowing to provide a high degree of the competences of supervisors (Sidorova, 2012), new special knowledge of the personnel, managerial ethics and the skill to practically realize them in the innovative performance of the universities and institutes, designing Russian innovative technologies and innovations.
But it is necessary to emphasize, that for the efficient innovative activities of the subjects of innovative education special actuality belongs to the task of creating innovative managers in all spheres of new economics, capable to realize functioning of innovative models of the education development in all the regions.
From the theoretical point of view the peculiarity of innovative economics applying to the innovative education is in solving the following tasks by the state and universities:
- defining the innovative-strategical way of development on the basis of the Russian innovative potential;
- creation of the innovative level of the organization in all the regions of innovative education in the universities;
- training of specialists–supervisors with innovative thinking and competences;
- functioning of the three-level innovative system of education: pre-school, school and university;
- establishing innovative infrastructure of state and regional universities;
- world level of quality of higher innovative education;
- reconstruction of industrial science, i.e. the departments are built into the organizational structure of the corporations for creation of innovations and managers with innovative reflection;
-restoration of the institutes of improvement of the professional skills in the structure of universities.
In the context of practical logics the accelerated development of prior and high-technological branches of industry on the basis of mutual strategic partnership of the state, science, education, industry and society, will allow to implement innovative projects and to maintain the formation and development of a new national model of economy – innovative, and also to support national innovative-educational net with innovative management and under control of Russian Academy of Science and regional innovative centers.
In our view, the innovative system of education is constructed only when managers of all levels realize and understand the state-social significance of upgrading the intellectual-creative personality (Archipova, Minaev, 2012). It has been noted above, that innovative education on all levels of pedagogics and psychology of management of organizations determine the formation the innovative thinking of all managers, capable to generate the ideas of novelty values and of social-moral values in order to “see and know one’s future development accounting its peculiarity on the basis of the past and present state of the situation” (Klarin, 1994).
The strategic approach to such a model defines the possession of own national innovation capital, flexible transformation of the current economic system into innovative, necessity of innovative education (Ovcharenko, Larkina, 2015). Such strategy will allow to adapt to global challenges of XXI century and, especially, to cyclic development of society according to the innovative economic theory of “Big Waves” of the Russian scientist N.D. Kondratyev.
In the conditions of formation of innovative economy the investigations testify the fact that innovative higher education is in prospect developing in listeners innovative thinking, civil activity and patriotism, competence to apply internal and external expertise.
The examples.
The company with limited responsibility “Combine-machinery plant Rostselmash” produces not only innovative models of tractors and harvesters, but creates the network of dissemination of innovative knowledge for personnel, having organized “Academy of Education”, where the personnel renewed knowledge and the managers got competences of using of principles on innovative culture.
We consider that professors of universities must be pioneers for establishing innovative education in neosociety. As the great scientist Dmitry Mendeleev noted, “…the professor must go ahead and infect with his drives a mass of off-springs”, i.e. the innovative education develops the principles of humanity, spirituality, morality, national character and hard work in the minds of students, taking into account the peculiarity of mentality, as a human being by his nature is an active constructor of his/her personality, and the architect is the society.
The events of the last 30 years of the Russia development show that in their performance professors as personalities, according to the latest research of the Russian philosophers, should be key figures in the generation of formation and development of the innovative process of education on all its levels.
In 2017 a study - monitoring the satisfaction of graduates of specialists, bachelors and masters of the Southern Federal University of the Academy of Psychology and Pedagogy – was conducted. The purpose of the study was to determine the quality of the innovative educational services provided by the university. Total of 120 students took part in the study. Based on the results of the questioning of students, 85.5% of respondents were satisfied with the quality of the educational services provided, 4.5% were not satisfied with the quality of the educational services provided and 10% were at a loss to answer.
Satisfaction of students with the quality of the educational services provided is due to many factors. Let us single out some of them: sufficiency of innovative knowledge for future effective professional activity, satisfaction with the innovative university as a whole (the prestige of the university itself), the main factor in choosing a university / direction of preparation. It is these factors that are considered to study the formation of innovative human capital in higher professional education (Kotova, Kotov et al., 2017).
It is multiple-valued in researches that concept of innovations in education is applied in many Russian universities and universities in Post-Soviet countries (Ignatova, 2012). So, in the resolution of the First elitology congress (October, 2013, URI RANEPA, Rostov-na-Donu) it was noted that the Congress considers it expedient to recommend to the Russian elite, including intellectual elite, to promote the innovative development of the interelite relations of the CIS countries. Considering the Euroasian priority of foreign policy of Russia, it is expedient to develop the system of elite communications in the former Soviet Union including lectures of Russian economists, exchange of students, interaction with teachers of the Russian Slavic universities (Ponedelkov, 2014). Thereby it was recommended to develop various forms of institutionalization of integration of national elite in the Euroasian space, including scientific (intellectual) elite by mutual enrichment by experience.
Scientific and production and educational clusters on the basis of classical and technical universities in the south of Russia are created as in most of subjects of the Russian Federation. The indisputable leader is the Southern federal university in Rostov-na-Donu, the strong high school systems supplemented by the innovative centers, business incubators, technological parks have developed in Krasnodar, Volgograd, Vladikavkaz, Stavropol and Pyatigorsk which are at the same time the donors of the market of employment of graduates, and recipients of entrants from mainly neighboring regions (Ignatova, Pavlyukova et al., 2018).
The authors’ vision of the innovative thinking is the ability of a person to generate ideas, create innovative knowledge, i.e. to open their sense on the basis of self-cognition and self-perfection. It is an innovative-strategic vector of humanitarian system of the innovative education, defining freedom of every person in his/her life of the ground of designing of innovative traditions with the peculiarity of mentality, that allows to construct an innovative paradigm of management forming its new content – intellectual NEO-innovative intentions at NEO-foresight – setting up of noospheric society with a spiritual world for everybody on the basis of the degree of humanism, morale morality and respect to every personality. The investigation by the scholars the specifics of innovative education shows the necessity on insight-thinking in managers and teachers, i.e. emerging self-reflection – own vision of innovative education development, adding to self-realization and self-perfection of the personality by the creating of innovative culture.
In the conditions of economic crisis it is important to realize by the people the innovative significance of educational sphere, in which innovative culture reflects the degree of self-realization of each person in the collective. We can see such an innovative approach to educational sphere in the Institute of Jores Alferov – the Nobel Prize Laureate, where there are innovative managers-organizers in the innovative structures in science, that help scientists present their scientific achievements to many branches of economy, defining the innovative-technical breakthrough, renewal of scientific production.
It is necessary to note, that effective functioning of the innovative sphere will define the formation of a highly-intellectual society consisting of well-educated people (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Logics of innovative self-education
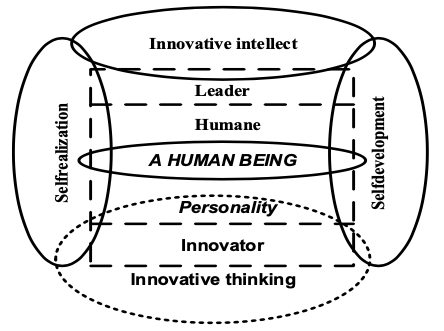
In conditions of the balance in the innovative educational sphere every human being is flexibly mold and adapted, preserving original mentality, making up for his/her creative activities not only for reproduction, but for intellectual development – this is the beginning of building social innovative environment, which lets value aspects to balance with state and civil interests.
Self-education of each human being in the new society satisfies changeable personal needs, creates the conditions of social self-determination in the process of creative vital functioning in the collective, defines the skills of universities managers to pass new special knowledge to students according their life cycle.
The analysis of tendencies in higher education in Russia shows contradictions and low level of efficiency:
- lack of understanding that there is practically no time to wait more and there is the need to respond modern challenges;
- scientific researches show, that innovative federal and regional level universities weakly use the synergy of trustworthy partnership of state, science, education and civil industry for design of new economy, implementing the novelties which have already been made up;
- lack of innovative activities and personal responsibility of managers in many regions for commercialization of the existing innovative Russian industrial technologies.
The results of interaction of science and industry shows the low level of implementation of the blueprints in the system of the higher school, only 5% of the higher school novelties are put into life in the manufacture (Kotova, Kotov, 2017).
In the practical aspect the fast development of the innovative-informational-communicative technologies (ICT) in the innovative sphere of education stipulates the emerging of a new type of the innovative sciences (disciplines) in the innovative environment, increasing intellectual personnel potential for research, assisting the creation of innovative product-services under the changing needs of neosociety.
The modern transformation and globalization of the world economy define the use of digital technologies in new economics, that adapts to the innovative educational system at different stages of the life cycle. Innovative-educational system in modern Russia at a given moment is formed in the context of “Concept of long-term social-economic-ecological development of the RF for the period up to 2020”, which foresees the innovative modernization of economics, describing its development and creation of a high-level standard of living of the population.
What is written above allows to make a conclusion, that establishing of innovative economy in Russia defines the role of innovative education and innovative supervisors-organizers, who can manage intellectual and creative potential of a person for realizing innovative model of development of the country in the context of innovative-economic activities of all regions with personal moral responsibility of their organizers before society.
In connection with what was said above innovative educational system in its essence must define and create a vector of humanity, patriotism and publicity for the preparation of the future generations of society on the basis innovative education of a personality, i.e. to create future innovative development, because a human being is the highest value of society, bearer of its spirituality and it emerges as a subject of the innovative-cultural process and foresight.
Archipova N.I., Minaev V.V. (2012) Problematic aspects of the formation of investment projects and programs. Problems of Economy and Law, 4, 65-70.
Ignatova T.V. (2012) Formation of an administrative reserve of the region through development of administrative and educational clusters. Creative economy. 3: 95.
Ignatova T., Pavlyukova A., Boldyreva L., Solonina S. (2018) Management of consolidation processes in Russia: social and economic aspects. CBU International Conference on Innovations in Science and Education. Prague, Czech Republic, 21-23 March, Vol. 6, 393-398.
Klarin M.V. (1994) Innovative models of teaching in foreign pedagogical searches. M.: Arena, 223 p.
Kotova N.S., Kotov S.V., Blohin A., Ogannisyan L., Borsilov Yu. (2017) Human Capital – the prospects of development in Higher Education System. 4th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conference on Social Sciences and Arts SGEM 2017, www.sgemsocial.org, SGEM2017 Conference Proceedings, 24 - 30 August, Book 3, Vol 4, 271-276.
Marx K., Engels F. (1955-1981) Collection of works, 2d edition. Volume 2. – M.: Politizdat. 651 p. P.31.
Mendeleev D.I. (1995) Private thoughts. M.: Mysl’. 415 p.
Ovcharenko G.V., Larkina N.G. (2015) The intention of scholars to the modern problems of theory and practice of management. Monography. Rostov-na-Donu: URIU RANEPA. 118 p.
Sidorova N.A. (2012) Higher education as an element of innovative socially oriented knowledge. Problems of Economy, 4, 58-62.
Ponedelkov A.V. (2014) Political elite of Russia: current state and prospects of modernization. Public and municipal administration. Scientific notes of SKAGS, 1, 29-34.
1. Doctor of Economic Science, Professor, Head of Department of Economic Theory and Entrepreneurship, South-Russia Institute of Management – branch, Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration. (Rostov-on-Don, Russia). Connecting author: E-mail: tignatova@aaanet.ru
2. Doctor of Economic Science, Professor, Department of Management, South-Russia Institute of Management – branch, Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration. (Rostov-on-Don, Russia). E-mail: menedjment@uriu.ranepa.ru
3. Candidate of Economic Science, Docent. Department of Management, Southern Federal University. (Rostov-on-Don, Russia). E-mail: nat1-la@yandex.ru
4. Candidate of Economic Science, Docent, Department of Management, South-Russia Institute of Management – branch, Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration. (Rostov-on-Don, Russia). E-mail: rustle44@mail.ru