

 Vol. 40 (Number 31) Year 2019. Page 7
Vol. 40 (Number 31) Year 2019. Page 7
ZHIENBAYEVA, Saira 1; KALYSH, Amanzhol 2; ZHUBANDYKOVA, Akgul 3; NABUOVA, Roza 4; ISSAYEVA, Aliya 5; ABILMAZHINOVA, Oryngul 6 & AHMULDINOVA, Aigul 7
Received: 10/05/2019 • Approved: 03/09/2019 • Published 16/09/2019
ABSTRACT: The article provides the rationale for modeling of the process of development of professional competence in a future Physical Education teacher at an entrepreneurial university; it specifies the meaning of the term “professional competence” and its structural components as applied to a Physical Education teacher in the framework of an entrepreneurial university. Professional competence of a Physical Education teacher is viewed as a set of integrated fundamental knowledge, general skills, abilities and professionally relevant personal qualities of students necessary for professional activity, reflecting the level of their expertise, willingness to perform professional functions and achieve high results. Professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher includes a whole set of competencies: personal, cognitive, activity-and-performance and reflexive. A model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university has been created and experimentally tested. A pedagogical environment that encourages the development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers during the studies at an entrepreneurial university has been identified. Methodological recommendations for the development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university have been drawn up and presented in this article. Results of this research can be used in the course of the educational process in higher education institutions in order to develop professional competence in students and improve their readiness for subsequent professional activity. |
RESUMEN: El artículo proporciona los fundamentos para modelar el proceso de desarrollo de la competencia profesional en un futuro maestro de Educación Física en una universidad emprendedora; especifica el significado del término "competencia profesional" y sus componentes estructurales aplicados a un maestro de Educación Física en el marco de una universidad emprendedora. La competencia profesional de un maestro de Educación Física se ve como un conjunto de conocimientos fundamentales integrados, habilidades generales, habilidades y cualidades personales profesionalmente relevantes de los estudiantes necesarias para la actividad profesional, lo que refleja el nivel de su experiencia, disposición para realizar funciones profesionales y lograr altos resultados. La competencia profesional de un futuro maestro de Educación Física incluye un conjunto completo de competencias: personales, cognitivas, de actividad y rendimiento y reflexivas. Se ha creado y probado experimentalmente un modelo de desarrollo de competencias profesionales en futuros profesores de educación física en una universidad emprendedora. Se ha identificado un entorno pedagógico que fomenta el desarrollo de la competencia profesional en futuros maestros de Educación Física durante los estudios en una universidad empresarial. Las recomendaciones metodológicas para el desarrollo de la competencia profesional en futuros maestros de Educación Física en una universidad empresarial se han elaborado y presentado en este artículo. Los resultados de esta investigación se pueden utilizar en el curso del proceso educativo en instituciones de educación superior para desarrollar la competencia profesional en los estudiantes y mejorar su preparación para la actividad profesional posterior. |
1. Analysis of literature has shown that similar studies focus on the traditional educational process and largely ignore the requirements of the competency-based approach to the training of future Physical Education teachers; nowadays it is necessary to reconsider the expected results of professional training provided to future Physical Education teachers at higher education institutions.
2. Analysis of literature has shown that there is a contradiction between the social need for professionally competent specialists who comply with the modern standards of physical education and sport, on the one hand, and insufficient degree of theoretical and methodological development of the issue of their training at higher education institutions, on the other hand.
3. There is a need to develop a theoretical basis and methodological support of the process of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university via the creation of a corresponding model.
1. We have created a model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university, which, by contrast to other well-known studies (Onalbek, 2013; Makhashova, 2016; Aghazadeh, 2009), is viewed as an integral whole consisting of interrelated components: target, content, organizational, processual and resultative.
2. As opposed to the previously published literature (Boardley, 2007; Rakhimbekova, 2015; Mirza, 2013), the research carried out by us has shown that all components of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers are interrelated and comprise an integral pedagogical system.
3. Results of experimental work have proved the effectiveness of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers, while scientific conclusions determine the perspectives of their training with due regard to the current trends in sports development.
The following research methods have been used: firstly, analysis of literature on the examined issue of development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university. Diagnostic methods were used at the ascertaining stage of the experiment to determine the level of individual competencies. The main method employed at the formative stage of the experimental work was pedagogical experiment. Base for a pedagogical experiment: Pavlodar State University. Students doing a degree in Physical Education and Sport took part in the research: 16 people as an experimental group and 16 people as a control group. According to the results of the first measurement, the number of students with high, medium and low levels of professional competence development towards the skills of a future Physical Education teacher were the same in terms of average summarized results in the experimental and control groups with very insignificant differences in the components of professional competence: personal, cognitive, activity-and-performance and reflexive competencies. Results of the second measurement (after the experimental exposure) show insignificant dynamics of professional competence development in students from the control group, while the experimental group demonstrates the substantial improvement of parameters in this sphere. A significant change of the estimated indicator in the experimental group serves as clear proof of the accuracy of the chosen theoretical and empirical methods. The conducted experimental research has shown that after application of the pedagogical environment suggested by the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers, the number of students with a high level of personal competency rose by 16% in the experimental group, which is 12% more than in the control group; the number of students with a medium level of personal competency rose by 11% in the experimental group, and the number of students with a low level of personal competency went down by 18% in the experimental group versus 12% in the control group. The number of students with a high level of cognitive competency rose by 6% in the experimental group, while in the control group the number of such students increased only by 3%. The number of students with a high level of activity-and-performance competency rose by 34% in the experimental group, while in the control group the number of such students increased only by 5%. The number of students with a high level of reflexive competency rose by 3% in the experimental group, while in the control group the number of such students remained virtually at the same level as before.
The quoted results of experimental work show that the set of criteria for the assessment of the level of professional competence development suggested by the model of the process of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers allows handling pedagogical tasks successfully. The average summarized results showing a high level of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers rose by 16% in the experimental group, which proves the assumption that use of the model, whose components comprise a certain methodology of supporting the development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers in the course of studies, allows to increase the efficiency of teaching students and, correspondingly, the level of professional competence possessed by future Physical Education teachers.
Modernization of the higher education system is one of the main factors providing sustainable development of national economy and society. In connection with the integration of Russia into the global educational context, change of the educational paradigm and formation of a new national model, it has become necessary to change the targets set for education and develop the professional training process at higher education institutions based on the constructive educational model. It should be mentioned that the competency-based approach can be definitely called the cornerstone of modernization of higher professional education and is viewed as a specific conceptual target basis for designing and management of educational process at a higher education institution. In modern society, physical training and sports are among the most important factors in the harmonious development of personality. In view of this, the standards of training of specialists working in the area of physical training and sports have risen as well as the level of necessary professional competence, which has to be oriented not only at creation of a learning environment encouraging active acquisition of knowledge and practical skills of independent effective management of the physical education process, but also at development of professionally important qualities that affect the result of the activity conducted by a Physical Education teacher. Considering the process of gradual development of a competent specialist in physical training and sports, some researchers, such as Onalbek et al. (2013), Makhashova et al. (2016), Aghazadeh & Kyei (2009), point out that the necessary level of professionalism can be achieved after many years of independent pedagogical work. Therefore, the main drawback of the traditional educational paradigm is lengthy adaptation of graduates to professional activity, which increases the importance of their training in the course of studies at higher education institution and creates the necessity for theoretical and methodological comprehension of this process through development of professional competencies in students and searching for innovative approaches to teaching students at an entrepreneurial university.
The scientific problem of professionalism and professional competence has become the focus of attention of researchers and practical experts in the last decade. The general theoretical foundations of professional competence are outlined in the scientific research papers by Hoffmann (1999), Gifford (1994), Zhumabaeva et al. (2016), Berkimbaev et al. (2012), Fernandez et al. (2012). The issue of improvement of professional training of specialists in physical education and sports was explored by Eys et al. (2009), Sakenov et al. (2012), Omarov et al. (2016).
In recent years a few research papers have been published that look at the development of professional competence in specialists in the sphere of physical training and sports: Boardley & Kavussanu (2007), Rakhimbekova et al. (2015), Mirza (2013), Bowker (2006).
All in all, even given the great variety of scientific and methodological papers devoted to the issues of training specialists in the sphere of physical education and sports, these works mainly focus on the traditional educational process and take into consideration hardly any requirements of the competency-based approach to professional training. Therefore, the issue of professional competence development in a future Physical Education teacher in course of studies at a higher education institution calls for adjustments to the content of educational programs, implementation of innovative technologies and teaching methods and review of the expected result of the professional training of a future Physical Education teacher provided at a higher education institution.
Thus, there is a contradiction between the social need for professionally competent specialists who comply with the modern standards of physical education and sports, on the one hand, and insufficient degree of theoretical and methodological development of the issue of their training at higher education institutions, on the other hand. This contradiction has defined the focus of this research, which consists in the identification of effective techniques of training future Physical Education teachers that possess all necessary professional competencies at a higher education institution. In accordance with this scientific problem, we set forth the objective of this research — theoretical justification and methodological support of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university. An entrepreneurial university is a higher education institution that makes consistent efforts to overcome the limitations on generation of knowledge, teaching and transformation of theoretical knowledge into practice by initiating new types of activities, the transformation of the internal environment and modification of the interaction with the external environment.
In our opinion, the necessity for improvement of the quality of professional training provided to Physical Education students within the framework of key priority areas of modernization of the system of higher education can be fulfilled by helping such students to develop professional competencies and by looking for innovative approaches to teaching them at an entrepreneurial university. We started the exploration of this problem by a detailed analysis of the concept “professional competence”, which showed its wide use in the pedagogical literature, on the one hand, and lack of a unified approach to its definition, on the other hand. The concept of professional competence is multi-faceted and multi-dimensional, it changes alongside the transformations taking place in society and education and is viewed from different angles. Researchers suggest different variants of its interpretation; it should be noted that some researchers use the terms “competence” and “competency” as synonyms, while others define professional competence (in general understanding) as a set of personal qualities that ensure effective professional activity, but in the majority of works (Gifford, 1994); Berkimbaev et al., 2012; Hoffmann, 1999), authors stick to the established perception of competence as possession of certain knowledge, skills and experience that enable a person to make judgments about something, take certain actions and make decisions.
In the framework of our research synonymic use of the terms “competence” and “competency” is not quite reasonable from the content-related perspective of modern science. Relying on the definitions of these terms given by Omarov et al. (2016) and Fernandez et al. (2012), we are going to separate these notions and be guided by the following definitions:
- competency is a variety of skills, knowledge, personal qualities, abilities, etc. that should be present in a person according to their place in the social and professional life, i.e. competencies can be described in terms of knowledge, skills, experience, abilities, etc.
– competence is represented by integrated developed personal qualities promoting reasonable and effective activity that meets modern requirements and bringing such activity to perfection. Therefore, competence shows the correlation between the real and necessary components in the personality of a specialist and the degree to which they acquired the content of competencies, i.e. competence is mainly a qualitative indicator.
Specifying this concept with due regard to the sphere of physical training and sports, we shall view professional competence of a Physical Education teacher as a set of integrated fundamental knowledge, general skills, abilities and professionally relevant personal qualities of students necessary for professional activity, reflecting the level of their expertise, willingness to perform professional functions and achieve high results. The premises formulated by Todd, Carol (2016), Mouratidou et al. (2012), Onalbek et al. (2013) served as the theoretical basis for structuring and the content of professional competence of a Physical Education teacher.
Analysis of definitions given by researchers to the problem of professional competence shows that its essence can be revealed in two ways:
– through corresponding competencies the content of which should be structurally and content fully presented as a set of skills, knowledge, abilities, experience, etc. (this is the way we are going to use to describe professional competence of a Physical Education teacher);
– directly – through the description of corresponding skills, knowledge, abilities, etc. without using the term “competency”.
Therefore, we find it justified to identify a set of integrating competencies, such as personal, reflexive, cognitive, and activity-and-performance, in the general structure of professional competence of a Physical Education teacher. The process of professional competence development in a future Physical Education teacher can be effective if the following methodological approaches to training of such specialist are taken into account: systemic, competency-based, acmeological, and activity-based, which, as a whole, served as the basis for modeling of the system of professional competence development at higher education institutions. Thus, the principal approach used in this work is the competency-based approach, which highlights the role of competencies as essential indicators of professionalism that allow structuring knowledge, skills and abilities taught in the course of training of future Physical Education teachers in a focused manner. (Figure 1).
Figure 1
The model of professional competence development in future
Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university
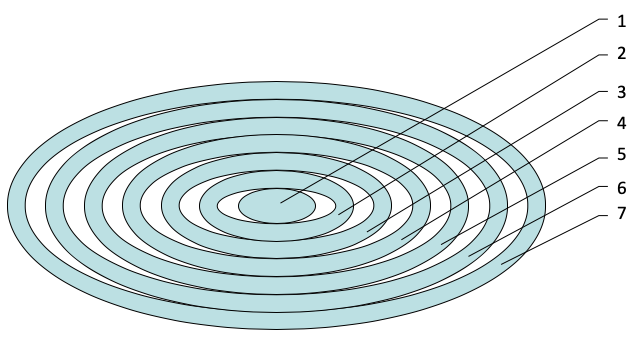
The structure of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university includes the following components:
1. The target component: The objective — development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers during their studies at an entrepreneurial university. Principles: awareness, activity, scientificity, consistency, creativity, professional focus. Methodological approaches: systemic, functional, activity-based, competency-based.
2. The content component: Professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher (personal, cognitive, activity-and-performance and reflexive competencies).
3. The organizational component: Organizational forms: lectures, seminars, practical classes, independent work, master classes, debates and discussions, trainings. Teaching methods: gamification, problem presentation of material, the method of development of personal awareness, modeling and simulation techniques, context-based learning, project work, active learning strategies. Techniques and methods: forecasting, self-analysis, self-diagnostics, analysis of pedagogical situations, interpretation of various viewpoints and behaviors, synthesis and analysis, modeling of conflicts, competitive and training activities.
4. The processual component: development of professional thinking; acquisition of skills, knowledge and abilities necessary for pedagogical and training activities; development of components that comprise professional competence; engaging students in different kinds of cognitive activities; developing the ability to analyze the best practices in training activities and use them in the professional activities; project work and modeling of training and competitive activities; possession of communicative means and methods and behavioral patterns used in the professional activity.
5. Material and technical resources of an entrepreneurial university, technologization of the educational process, the talent pool of a university.
6. Pedagogical environment: a professional selection of prospective students with identification of their pedagogical inclinations and motivation for the future activities, development of positive motivation, use of expert diagnostics and self-diagnostics, development of an individual learning plan.
7. The resultative component: levels of professional competence development (low, medium, high). The result is developed professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher.
The suggested model encourages the development of structural components comprising professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher necessary for effective and successful professional activity. It should be noted that such a model suggests a selection of the content of pedagogical practices throughout the whole educational process. Having studied a number of research papers (Onalbek et al., 2013; Mirza, 2013; Todd, Carol, 2016), we came to the conclusion that successful functioning of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university is possible if the following pedagogical requirements are met:
1. Professional selection of prospective students at the stage of entrance examinations to higher education institutions with identification of their pedagogical inclinations and motivation for the future professional activity. Nowadays potential students enter higher education institution upon passing Unified National Testing and a creative challenge that determine the level of physical fitness and basic knowledge, which is, in fact, insufficient to master the profession of a Physical Education teacher. In order to train competitive specialists, we have made an attempt to introduce psychological monitoring at this stage that determined pedagogical inclinations of future teachers, their motivation and personal psychological features. Based on the results of psychological monitoring, educational technologies were developed and differentiated learning was used in the course of professional training with further intermediate corrections.
2. Development of positive motivation for professional activity in future Physical Education teachers. This requirement is connected with the fact that the process of professional competence development is of clearly expressed individual nature since it suggests active participation and personal interest of the future specialist in this process. Within our research, the educational process was built taking into account the credit system of education, which suggests that each student has their own individual plan, chooses their own educational path independently and follows them in the course of the educational process.
3. Use of such methodologies as expert diagnostics and self-diagnostics to identify the level of professional competence development in students at different learning stages at a higher education institution and the creation of an individual learning plan.
4. Studying disciplines that encourage targeted development of structural components comprising professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher throughout the whole period of studies at a higher education institution. In our research, it applies to elective courses “Improvement of professional training activity” and “Foundations of sports and pedagogical skills” accompanied by parallel training and pedagogical internship.
5. Use of innovative learning techniques (credit system, context-based learning) and active learning strategies in combination with traditional teaching methods.
Experimental testing of the effectiveness of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university was conducted on the basis of the full-time course “Physical Education and Sport”.
The structure of professional competence of a Physical Education teacher is represented by a set of integrating competencies, such as personal, reflexive, cognitive and activity-and-performance. In order to track changes in the course of development of professional competence the following levels of competence have been used: low, medium and high. Diagnostic methods were used at the ascertaining stage of the experiment to determine the level of individual competencies. For instance, the level of personal competence development was determined with the help of questionnaires aimed at identification of pedagogical orientation of a person and their motivation for learning activity as well as the questionnaire on formal-dynamic properties of individuality designed by V.M. Rusalov, the methodology by K. Zamfir modified by A. Rean and the ranking method (Onalbek et al., 2013). The level of development of cognitive competency was determined by the grade point average; the level of activity-and-performance competency — with the help of expert assessment and methods of pedagogical research: interview, observation, examination and analysis of the results of learning activity; the level of development of reflexive competency — with the help of a self-assessment test. As far as the examined components of professional competence are concerned, no statistically significant differences have been found between the control and experimental groups, which means that the chosen groups are the same in this respect and the level of their professional competence is insufficient. Therefore, it is necessary to make adjustments to professional training, i.e. the process of professional competence development in students should be carried out purposefully within the functioning of the model in compliance with the requirements for its successful implementation. The main method employed at the formative stage of the experimental work was a pedagogical experiment. The educational process in the experimental group was built according to the developed model. The model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university and justified pedagogical environment were introduced into the educational process of a higher education institution as an experimental variable. The control group studied in the framework of the traditional educational process.
Development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers through the educational process was performed within the credit system of education, oriented at the activation of self-studying and creative acquisition of knowledge based on individualization, choice of educational path and taking into account the volume of knowledge expressed in the form of credits. When the credit system of education was introduced, it became possible for students to plan the structure of their educational process individually by choosing the academic disciplines necessary for their professional activity. It is thanks to the choice of subjects that the level of professional competence of future Physical Education teachers can be improved since it is developed through the content of the discipline and organizational forms of the learning activity. The elective disciplines “Foundations of sports and pedagogical skills” and “Improvement of professional training activity” encouraged the development of professional competence in the experimental group due to the fact that they provide interrelation between other courses and help to accumulate the acquired information by focusing on gaining experience. Didactic materials for teaching these disciplines are represented by a training package that integrates the goals, content and technologies. It is based on the following approaches:
– stimulating consistent work conducted by students by the introduction of a grading and rating system;
– focusing the attention of students not only on the psychological results of the pedagogical system (knowledge, skills and abilities) but also deliberately drawing their attention to the functional products — activity and communication methods used by a teacher in order to transform latent forms of learning and teaching into outright and conscious;
– using different diagnostic techniques (to measure the level of training, acquisition of knowledge, skills and abilities, psychological readiness for a particular activity, etc.);
– modeling of activity, phenomena and pedagogical situations that arise in course of practical activity of a Physical Education teacher, which helps students to develop their creative skills and the ability to solve typical issues connected with professional activity in the sphere of sports;
– development of basic research skills (while writing comprehensive course papers).
Implementation of the process of professional competence development based on reinforcement of professional content of the training is possible by the introduction of various technologies that include a combination of organizational forms, methods, teaching and diagnostic techniques providing the most effective outcome. For instance, during the experiment, the context-based learning approach was used. It is distinguished by the acquisition of intrinsically abstract pedagogical knowledge included necessary for professional pedagogical activity. Within this research, we developed and introduced into the educational process a minimum required a set of methods of context-based learning including unconventional approaches to lecturing, game- and computer-based learning combined with traditional teaching techniques.
Results of the formative stage of the experiment are represented by the following changes in key areas:
– personal competency, which includes the level of motivation, development of professionally important personal qualities and indices of dynamic personal characteristics;
– cognitive competency reflecting the grade point average;
– reflexive competency showing the student’s self-concept;
– activity-and-performance competency involving a few skills, abilities and areas of knowledge necessary to succeed in professional activity.
The summarized result was obtained using the method of expert assessment based on differentiation of competencies into three levels that allowed to produce students’ characteristics with an indication of the level of their professional competence. The role of experts was taken on by teachers who worked with these students on a regular basis, group advisers and internship managers. The results of the research are represented in Table 1.
Table 1
The level of professional competence development in students from the experimental
group (EG) and the control group (CG) before and after the experiment (%).
No. |
Components of professional competence |
before the experiment |
after the experiment |
||||||||||
high |
medium |
low |
high |
medium |
low |
||||||||
CG |
EG |
CG |
EG |
CG |
EG |
CG |
EG |
CG |
EG |
CG |
EG |
||
1 |
Personal competency |
21 |
24 |
40 |
38 |
39 |
38 |
27 |
46 |
46 |
34 |
27 |
20 |
2 |
Cognitive competency |
15 |
13 |
57 |
63 |
28 |
24 |
18 |
19 |
59 |
69 |
23 |
12 |
3 |
Activity-and-performance competency |
15 |
15 |
24 |
23 |
61 |
62 |
20 |
49 |
34 |
39 |
46 |
12 |
4 |
Reflexive competency |
39 |
36 |
22 |
25 |
39 |
39 |
38 |
39 |
30 |
45 |
32 |
16 |
Average summarized result, % |
22 |
22 |
37 |
37 |
41 |
41 |
26 |
38 |
42 |
48 |
32 |
14 |
|
The changes that took place in the experimental group compared with the control group after the experiment are statistically significant. Comparison of the initial and final levels of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers in the two groups allows to carry out analysis of these levels before and after the experiment (Table 1). The presented data show that the level of professional competence development in students from the experimental group has risen significantly. The results of the experiment suggest that the process of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers based on the reviewed model and certain pedagogical environment is effective.
As a result of this research, we have created a model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university, which, by contrast to other well-known studies (Onalbek, 2013; Makhashova, 2016; Aghazadeh, 2009), which mainly focus on the traditional educational process and take into consideration hardly any requirements of the competency-based approach to professional training, is viewed as an integral whole consisting of interrelated components: target, content, organizational, processual and resultative.
As opposed to other well-known studies (Boardley, 2007; Rakhimbekova, 2015; Mirza, 2013), where the process of training of a Physical Education teacher is not specified by the competency-based approach and description of its essence, the research carried out by us has shown that the created model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers demonstrates the interrelation of its components that comprise an integral pedagogical system. Results of the experiment have proved the effectiveness of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers that makes provisions for the following aspects of the pedagogical environment: professional selection of prospective students at the stage of entrance examinations to higher education institutions with identification of their pedagogical inclinations and motivation for the future professional activity; development of positive motivation for professional activity in future Physical Education teachers; use of such methodologies as expert diagnostics and self-diagnostics to identify the level of professional competence development in students at different learning stages at a higher education institution and creation of an individual learning plan; studying disciplines that encourage targeted development of structural components comprising professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher throughout the whole period of studies at a higher education institution; use of innovative learning techniques (credit system, context-based learning) and active learning strategies in combination with traditional teaching methods.
To sum up, we have specified the concept “professional competence of a Physical Education teacher”, which, by contrast to the views expressed in the research papers by Omarov et al. (2016), Fernandez et al. (2012) and Bowker (2006), we interpret as a set of integrated fundamental knowledge, general skills, abilities and professionally relevant personal qualities of students necessary for professional activity, reflecting the level of their expertise, willingness to perform professional functions and achieve high results. A set of integrating competencies, such as personal, reflexive, cognitive and activity-and-performance, has been identified within the general structure of professional competence of a Physical Education teacher.
We have designed and experimentally tested a model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university, which, as opposed to well-known research papers (Boardley, 2007; Rakhimbekova, 2015; Mirza, 2013), is viewed as an integral whole that consists of interrelated components: target, content, organizational, processual and resultative. The research has shown that all components of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers, their content and processual background are interrelated and comprise an integral pedagogical system. Aspects of a pedagogical environment that provide effective functioning of the model of professional competence development of future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university have been determined. They include the following: professional selection of prospective students at the stage of entrance examinations to higher education institutions with identification of their pedagogical inclinations and motivation for the future professional activity; development of positive motivation for professional activity in future Physical Education teachers; use of such methodologies as expert diagnostics and self-diagnostics to identify the level of professional competence development in students at different learning stages at a higher education institution and creation of an individual learning plan; studying disciplines that encourage targeted development of structural components comprising professional competence of a future Physical Education teacher throughout the whole period of studies at a higher education institution (“Foundations of sports and pedagogical skills” and “Improvement of professional training activity”); use of innovative learning techniques (credit system, context-based learning) and active learning strategies in combination with traditional teaching methods. Results of the research are in perfect agreement with its objective: we have provided theoretical justification and methodological support for the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university.
The following scientific and methodological recommendations can be suggested:
– development of professional competence in future Physical Education teachers can be encouraged by the high-quality professional selection of prospective students at the stage of entrance examinations to higher education institutions with identification of their pedagogical orientation towards sports and pedagogical activity;
– throughout the whole learning process it is necessary to conduct psychological and pedagogical monitoring, the results of which will allow to determine and adjust the further pedagogical activity aimed at the development of necessary competencies and structural design of an individual learning plan;
– the elective disciplines “Foundations of sports and pedagogical skills” and “Improvement of professional training activity” developed by us are recommended to be introduced into the list of elective disciplines within the Physical Education and Sport curriculum at higher education institutions.
Results of theoretical analysis and experimental work presented in this research have proved the effectiveness of the model of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university. Our scientific conclusions offer a solution to the issue of professional competence development in future Physical Education teachers and determine the perspectives of their training with due regard to the current trends in sports development. In particular, we suggest updating the content of educational programs taught at the Physical Education and Sport department by means of integrating disciplines, creation of didactic and methodological materials for their support and differentiation of educational programs used for training of Physical Education teachers specialized in different sports as a prospective direction of further scientific development of this issue.
Materials of this research can be used in the course of the educational process to teach students in the humanities classes and to develop individual and group programs and strategies for students’ personal growth. Results of this research are oriented towards further enhancement of the educational process in higher education institutions in order to improve the readiness of students for subsequent professional activity. The scientific prospects of this research consist in updating of the content and ways of development of professional competence of future Physical Education teachers at an entrepreneurial university.
Aghazadeh, S.M., & Kyei, K. (2009). A Quantitative Assessment of Factors Affecting College Sports’ Team Unity. College Student Journal, 43(2), 294–302.
Berkimbaev, K.M., Nyshanova, S.T., Kerimbaeva, B.T., Meyrbekova, G.P. (2012). The Formation of Professional Competencies of Future Specialists. New Educational Review, 30, 271–281.
Boardley, I.D., & Kavussanu, M. (2007). Development and Validation of the Moral Disengagement in Sport Scale. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 29, 608–628.
Bowker, A. (2006). The Relationship between Sports Participation and Self-Esteem during Early Adolescence. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science, 38(3), 214–229. doi: 10.1037/cjbs2006009.
Eys, M., Lougheed, T., Bray, S.R., & Carron, A.V. (2009). Perceptions of Cohesion by Youth Sport Participants. The Sport Psychologist, 23, 330–345.
Fernandez, N., Dory, V., Ste-Marie, L.-G., Chaput, M., Charlin, B., Boucher, A. (2012). Varying Conceptions of Competence: An Analysis of How Health Sciences Educators Define Competence. Medical Education, 46(4), 357–365.
Gifford, S. (1994). Evaluating the Surrey New Teacher Competency Profile. British journal of in-service education, 20(3), 313–326.
Hoffmann, T. (1999). The meanings of competency. Journal of European Industrial Training, 23(6), 275–285.
Makhashova, P., Meirmanov, A., Zhunusbekov, Zh., Makasheva, O., Mirzaliyeva, E., Ermuratova, A., Sakenov, J. (2016). On the Development of Professional Competence in Students of Creative Pedagogical Specialties. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education, 11(11), 4660–4668.
Mirza N.V. (2013). Creative component of professional competence of a teacher. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research. 2. Retrieved from: www.science-sd.com/455-24286.
Mouratidou, K., Barkoukis, V., & Rizos, S. (2012). Achievement Goals and Moral Competence in Sport: Examining the Moderating Role of Demographic Characteristics. European Psychologist, 17(1), 34–43. doi: 10.1027/1016- 9040/a000043.
Omarov Y.B., Toktarbayev, D. G.-S., Rybin, I.V., Saliyeva, A.Zh., Zhumabekova, F.N., Hamzina, Sh., Baitlessova, N., Sakenov, J. (2016). Methods of Forming Professional Competence of Students as Future Teachers. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education, 11(11), 6651–6662.
Onalbek, Zh.K., Grinshkun, V.V., Omarov, B.S., Abuseytov, B.Z., Makhanbet, E.T., Kendzhaeva, B.B. (2013). The main Systems and Types of Forming of Future Teacher-Trainers’ Professional Competence. Life Sci J, 10(4), 2397–2400.
Rakhimbekova, G.O., Baigozhina, Z.M., Abdrakhmanova, A.Y., Samatanova, A.R., Orazakova, R.K., Nurtayeva, Z.Z., Sakenov, J.Z. (2015). Development of professional competence in students of creative pedagogical specialties (professionally-oriented aspect). Life Sci J, 12(1s), 24–28.
Sakenov, D.Zh., Kushnir. Y.V., Shnaider, Y., Abdulkhamidova, D.Zh. (2012). Preparation of Students of Higher Education Institution for Professional Activity in the Course of Studying of Pedagogical Disciplines. World Applied Sciences Journal, 19(10), 1431–1436.
Todd E., Carol C. I. (2016). An evaluation of teachers’ knowledge and use of physical education instructional models. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 16(4), 1310–1315.
Zhumabaeva, Z., Zhumasheva, A., Kenzhebayeva, T., Sakenov, J., Tleulesova, A., Kenenbaeva, M., Hamzina, Sh. (2016). On the Role of Elective Disciplines in the Formation of Professional Competence of Students as Future Teachers. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education, 11(15), 6671–6686.
1. Kazakh National Women`s Teacher Training University, Kazakhstan. E-mail: zhienbayeva-saira@mail.ru
2. Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, Kazakhstan
3. Kazakh National Women`s Teacher Training University, Kazakhstan
4. Kazakh National Women`s Teacher Training University, Kazakhstan
5. Kazakh National Women`s Teacher Training University, Kazakhstan
6. Kazakhskiy Gumanitarno-Yuridicheskiy Innovatsionnyy University, Kazakhstan
7. Pavlodar State Pedagogical University, Kazakhstan