

Vol. 40 (Issue 37) Year 2019. Page 24
MARTYNOVA, Natalia G. 1; BUDAROVA, Valentina A. 2; MOSKVIN, Viktor N. 3; DUBROVSKIY, Alexey V. 4 & MALYGINA, OLESYA I. 5
Received: 15/07/2019 • Approved: 19/10/2019 • Published 28/10/2019
ABSTRACT: Large enterprises are interested in the use of modern technologies in the organization of production works, including the use of functional automated control systems. This technology can serve as functional GIS, which are an indispensable tool for the analysis and management of spatial data. The article presents a model of enterprise management using GIS. Also in article for the purposes of model of management of the enterprise with use of GIS the economic assessment is presented. |
RESUMEN: Las grandes empresas están interesadas en el uso de tecnologías modernas en la organización de trabajos de producción, incluido el uso de sistemas de control automatizados funcionales. Esta tecnología puede servir como SIG funcional, que es una herramienta indispensable para el análisis y la gestión de datos espaciales. El artículo presenta un modelo de gestión empresarial utilizando SIG. También en el artículo para fines de modelo de gestión de la empresa con uso de SIG se presenta la evaluación económica. |

In modern conditions, the use of technologies of geographical information systems (GIS) creates conditions for working with a large amount of information, including spatial data. Integration of the GIS technologies of the digital economy allows you to automate information flow through the creation and management of databases that provides effective activity in the sphere of management of business systems. Modern GIS has become an indispensable tool for spatial data analysis and management. Therefore, such data can be effectively managed using relational database management systems (DBMS) (Peggion M, 2008).
Today, research in the field of object management shows how important it is to implement GIS technologies in the business sphere (Berlian, Experience in the use of GIS technology in the planning system and management of the organization, 2017) (Berlian, The possibilities of using GIS technologies in planning and management of territory, 2016) (Chuprynousky V. P., 2015) (Melnikov, 2008). Therefore, at the level of legislation approved "12 target models to simplify business procedures and improve the investment attractiveness of the Russian Federation" (The Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation, 2017).
The main purpose of GIS technology is to improve economic efficiency by increasing productivity. Therefore, it is possible to quickly obtain information about all the structural units of production activities of the enterprise, including material and cash. In addition, the study of property management issues leads to the creation of models and structures for use in social institutions (Zharnikov & Epifanova, 2007).
GIS technology allows you to organize the asset management system of the enterprise with spatial reference of real estate and land and property resources. Modeling of space objects allows to establish their relationship and provide a complete information environment. GIS allows you to establish a spatial relationship that is necessary for the operational solution of administrative and economic problems. At the same time GIS technologies provide the following opportunities:
– database maintenance;
– creation of detailed space objects with different levels of representation of attribute and semantic data;
– obtaining accurate geometric parameters.
As a result, it is always possible to obtain in a visual form the actual state of objects with the establishment of their possible changes and relationships with other objects.
Layer-by-layer organization of information storage in the form of sets of layers allows structuring and forming a database, including using data from third-party systems. Therefore, it is possible to solve the production problems of various structures of the organization with the help of:
– data exchange between different stages of work
– use of these laser scanners;
– collection and cataloging of information logistics data on premises.
In connection with these organization of production work in any enterprise may include various management tasks:
– real estate and project portfolios;
– spaces and objects
– operation of movable and immovable property;
– environmental protection and environmental sustainability;
– emergency preparedness;
– visualization of other processes.
Optimization of labor productivity and achievement of the planned efficiency can be achieved with the use of GIS technologies (Dubrovsky, 2015) (Martynova, 2017). For this purpose, the management of objects is characterized by situational awareness necessary for the management of real estate. At the same time, information models are linked to reliable data, workflows, models and reports (Uvarov, 2009) (Cherdantseva, Budarova, & D, Some Issues of Retrieving Cadastral Documentation Using Land Data Management Systems, 2015) (Dremin, Kuramshin, & Mordvinov, 2018) (Ehlakov, 2018) (Sutyagin, 2015) (Bugakova, Basargin, & Kalenicki, 2018). In addition, to optimize the performance of the enterprise GIS technology makes it possible to predict the further operation of facilities and land resources.
The model of spatial information management can be presented taking into account the production processes of the enterprise (figure 1).
Figure 1
Enterprise management model using GIS
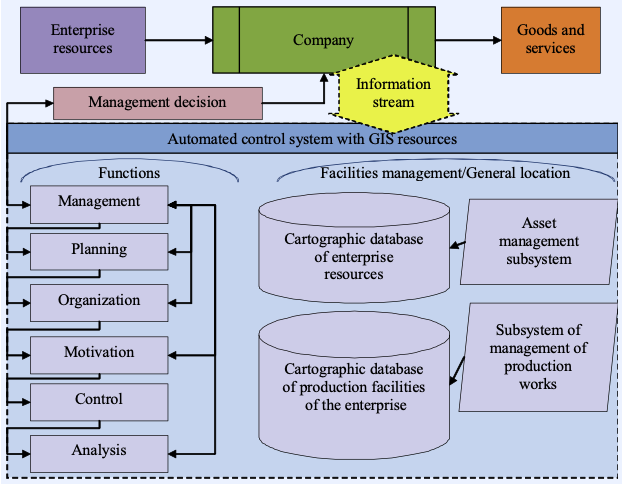
Enterprise management efficiency, provided that GIS capabilities are used, can be achieved through the correct organization of data, including visualization using thematic maps. At the same time, such a goal can be achieved taking into account the use of modern technological tools and equipment, including an organized local network; functional differentiation of personnel activities, management structure.
An important role is played by the specialization of the enterprise when using GIS technologies, for example, when developing a software architecture, it is necessary to take into account (Panskov & Stepanov, 2012) "the type of application, the type of tasks to be solved and the software solutions used". In addition, a special role can be played by the use of modern technologies, namely "cloud technologies" and mobile applications (Voronkin & Kasyanova, 2017) (Pisarev & Kikin, 2012) (Frowning, Popova, & Kramer, 2016) (Miroshnichenko & Trenevska, 2017) (Sukhanov & Lukyanov, 2011) (Kopytov, Shulgin, & Fedorov, 2015), allowing online tracking of data changes.
Therefore, we simulate the scheme of application of the above mentioned technologies for production management (figure 2).
Figure 2
The scheme of SFC with the help of modern technology
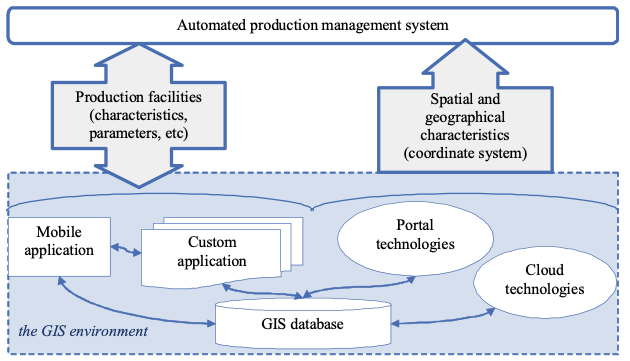
Such a management model can be implemented at any enterprise and with different production goals, as it is important to ensure a continuous flow of information about production facilities, land resources and any changes in space about their location (Mei, Bhatti, & Silva, 2018) (Cherdantseva & Budarova, Land information model cadastral works for example technical inventory of real estate objects , 2015).
In addition, the use of mobile applications makes it possible to monitor production facilities in real time (Ashkezari, Hosseinzadeh, Chebli, & Albadi, 2018) (Albrecht, 2018) (Raper, 2009). Also, the use of various "smart technologies" in production enables the rational management of business processes (Shajmardanova & Shajmardanov, 2017) (Sirazetdinov, 2017).
Today it is worth noting that many large corporations are interested in the use of modern technologies in the organization of production work and the expansion of the functionality of automated control systems.
Economic evaluation of the introduction of geoinformation technologies in the enterprise management system is an important step in the process of implementing such a model. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the financial well-being of the enterprise to identify weaknesses in the management of production.
In the course of practical implementation of GIS technologies it is necessary to compare the economic performance of financial activities in the present and past periods in order to predict business development. The main economic indicators will be to determine the liquidity, profitability, stability of the financial condition of the enterprise and business activity. On the basis of the "model of economic efficiency assessment of the enterprise management system" proposed by O. A. Mamonova (Mamonova, 2011) (figure 3) it is possible to determine the financial importance of the enterprise and the possibility of its modernization with the use of GIS technologies, including to predict the rationality of GIS application.
Figure 3
"The model of evaluating the economic efficiency of the
management system of the enterprise" Mamonova O. A.
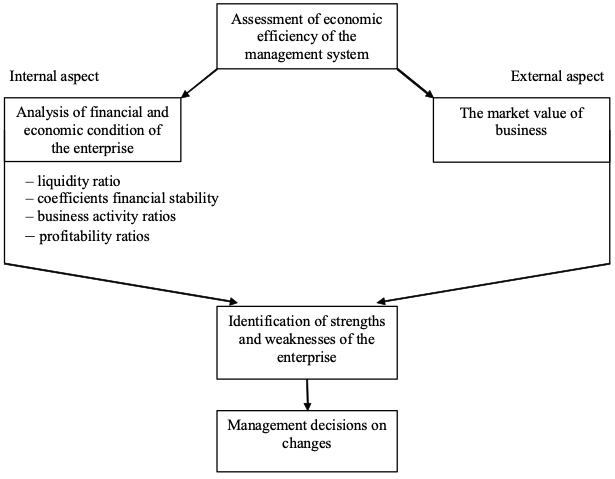
This evaluation model allows determining the value of the business before the introduction of GIS technologies and after, which gives the most objective assessment of the overall modernization of business processes. The author of the model emphasizes that "the application of a comparative approach to determining the market value of the business will reflect the position of the enterprise in the market, the change in its value in the direction of increasing or decreasing, will show fluctuations relative to competitor enterprises, which are most often taken as analogues and more identify the effectiveness of the enterprise management system in a competitive environment" (Mamonova, 2011).
In addition, for the most reliable assessment of the implementation of GIS technologies, traditional analysis should be applied. As a traditional analysis, it is necessary to determine the indicators of costs, benefits and overall economic efficiency. Therefore, the economic effect can be determined by the formula proposed by G. M. Shamarova (Shamarova, 2013), as:
Et = RT – ZT,
where: Et – the economic effect of the implemented solution for the calculation period; RT – the cost estimate of the results of the solution for the calculation period; ZT – the cost estimate of the cost of the solution for the calculation period.
The above methods of economic assessment give the most complete idea of the need to implement a management model of the enterprise using GIS.
In the course of practical implementation of GIS technologies management tasks are achieved:
- improve the quality of management tools and methods (planning, organization, motivation, control);
- to achieve effective use of the enterprise potential;
- use non-standard, original ideas in the management of the enterprise.
Enterprise management model using GIS serves to improve the competitiveness of the company, based on the maximum use of its own business assets and resources.
In the course of the analytical part of the study for the management of enterprises with GIS technologies practical recommendations can be made for the implementation of management processes:
-it is necessary to identify the main problems in the enterprise in the implementation of management processes;
-to establish not effective processes and their degree of influence on production activity;
-to create an information computer network of the enterprise using modern technologies, including geoinformation.
The economic efficiency of the implementation of the enterprise management model using GIS in the short term will be at least 40% in the first year of implementation, in the future the figure will increase.
Modernization of digital production is a new round of development of integrated geoinformation technologies, which "are an effective tool for the analysis of economic information" (Cvetkov, 2006).
Political support, experience with GIS technologies, joint use of the system and other factors have a positive impact on the development of the national economy of any state. Therefore, the role of GIS technologies in the development of business enterprises, taking into account the peculiarities of planning or management decisions. GIS experience is becoming the most important factor in achieving operational benefits. Therefore, the use of GIS technologies to solve analytical problems has a positive impact on the decision-making system in enterprise management.
Albrecht, J. (2018). GIS Project Management. Comprehensive Geographic Information Systems, (1), 446-477.
Ashkezari, A. D., Hosseinzadeh, N., Chebli, A., & Albadi, M. (2018). Development of an enterprise Geographic Information System (GIS) integrated with smart grid Sustainable Energy. Grids and Networks, (14), 25-34.
Barliani, I. J. (2017). Experience in the use of GIS technology in the planning system and management of the organization. Proceedings of Interexpo GEO-Siberia-2017: International Scientific Conference: Vol.2. Geospace in social and humanitarian discourse. (2), pp. 20-23. Novosibirsk: SSGA.
Barliani, I. J. (2016). The possibilities of using GIS technologies in planning and management of territory. Proceedings of Interexpo GEO-Siberia-2017: International Scientific Conference: Vol.1. Global processes in the regional dimension: experience of history and modernity. (1), pp. 247-250. Novosibirsk: SSGA.
Bugakova, T. Y., Basargin, A. A., & Kalenicki, A. I. (2018). Application of GIS-technologies and methods of mathematical modeling for definition of plate roll is the Foundation of engineering structures. Bulletin of SSGA, 23(2), 70-80.
Cherdantseva, N. G., & Budarova, V. A. (2015). Land information model cadastral works for example technical inventory of real estate objects. In this Edition: actual problems of architecture, construction, environment and energy conservation in the face of Western Siberia collection of materials of the international scientifically-practical Conference: in 2 vols. (2), pp. 94-99. Tyumen: FEDERAL VPO "Tyumen State University of architecture and civil engineering" .
Cherdantseva, N. G., Budarova, V. A., & D, M. Y. (2015). Some Issues of Retrieving Cadastral Documentation Using Land Data Management Systems. The prospects of science, 11(74), 173-177.
Chuprynousky, V. P., Tishchenko, P. A., Sinyakov, S. A., Raevsky, A. M., & Valiullina, L. R. (2015). Capabilities of GIS technology to manage specified business properties assets. Retrieved 11 02, 2018, from Esri CIS:
https://www.esri-cis.ru/news/arcreview/detail.php?ID=21947&SECTION_ID=1078.html
Cvetkov, V. J. (2006). Informatization, innovative processes and geoinformation technologies. Izvestia vuzov geodesy and aerophotosurveying, (4), 112-118.
Dremin, V. V., Kuramshin, A. F., & Mordvinov, S. V. (2018). Information models in management decisions. The Alley of science, 2(3(19)), 28-31.
Dubrovsky, A. V. (2015). Possibilities of application of geoinformation analysis in solving problems of monitoring and modeling of spatial structures. Proceedings of the Higher Educational Institutions. Izvestia vuzov "Geodesy and aerophotosurveying", 5, 236-243.
Ehlakov, M. A. (2018). Main principles of formation and perception of information models. Modern education: contents, technologies, quality, (2), 214-217.
Frowning, Y. A., Popova, E. V., & Kramer, A. S. (2016). Architecture of a control system of interaction of enterprises and customers on the basis of cloud technologies. Scientific journal of Kubsau, 119(05), 1-11.
Kopytov, V. V., Shulgin, A. O., & Fedorov, S. A. (2015). Development of architecture of integration environment of cross-platform mobile applications with corporate information system. Modern Information Technology and IT-education, 11(2), 71-77.
Mamonova, O. A. (2011). The model of the economic efficiency estimation of the enterpriseґs management system. Izv. penz. gos. pedagog. univ. im.i V. G. Belinskogo, 24, 352-356.
Martynova, N. G. (2017). Development of a model of electronic documents circulation while performing cadastral works. Tyumen, Russian.
Mei, L. Y., Bhatti, S. S., & Silva, E. A. (2018). GIS-Based Approach to Analyze the Spatial Opportunities for Knowledge-Intensive Businesses. Comprehensive Geographic Information Systems, (1), 83-100.
Melnikov, V. O., & Maksimov, O. A. (2008). Geographic Information systems and possible spheres of their practical application in the modern information society. Scientific and technical information series 2: information processes and systems, (11), 9-19.
Miroshnichenko, M. A., & Trenevska, K. A. (2017). Cloud computing in agro-industrial sector of economy: tendencies of development and advantages of implementation. Scientific Journal of KubSAU, (128), 376-385.
Panskov, V. S., & Stepanov, Y. A. (2012). Architecture Development of specialized software on the basis of GIS-technologies. Scientific-technical Vestnik of the Volga region, (4), 207-210.
Peggion, M., Bernardini, A., & Masera, M. (2008). Geographic information systems and risk assessment. Italy: European Communities.
Pisarev, V. S., & Kikin, P. M. (2012). Mobile devices as a means of decision-making in case of crisis situations. Proceedings of Interexpo GEO-Siberia-2012: Vol.3. International Scientific Conference: Geodesy, Geoinformatics, cartography, surveying, (3), pp. 211–214. Novosibirsk: SGUGiT.
Raper, J. (2009). GIS, Mobile and Locational Based Services. International Encyclopedia of Human Geography , 513-519.
Shajmardanova, Z. A., & Shajmardanov, S. A. (2017). Modern methods of enterprise management in the concept of «Digital enterprise». Conference proceedings. All-Russian scientific-practical conference with international participation: Science in motion: from reflection to reality creation, pp. 373–378. Moscow: Pero.
Shamarova, G. M. (2013). Bases of the state and municipal management: the textbook. Moscow: Moscow. fin.-prom. Uni t Synergy.
Sirazetdinov, R. T. (2017). Modeling of sustainable development of the enterprise. Proceedings of Analytical mechanics, stability and management: International Chetaevskoj Conference: Vol. 4 Section 4. Computer technologies in science, education, production management, pp. 192–200. Kazan: KNRTU-KAI.
Sukhanov, V. I., & Lukyanov, D. S. (2011). Cloud computing for small and medium-sized businesses. Scientific Journal of KubSAU, (73), 145-160.
Sutyagin, M. V. (2015). Standardization of requirements to information models of competences and related objects. Open education, 1(108), 19-25.
The Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. (2017, 01 31). On the trust models, the facilitation of doing business and increase investment attractiveness of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation : decree of the RF Government dated 31 January 2017 No. 147-R. Retrieved 11 www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_212324/, 2018, from ConsultantPlus: www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_212324/
Uvarov, B. C. (2009). Managing the business guiding by its information model information model used for the enterprise management. Russian Journal of Entrepreneurship, 8(2), 52-58.
Voronkin, E. Y., & Kasyanova, E. L. (2017). Application of "Cloud technologies" for work with thematic maps. Proceedings of Interexpo GEO-Siberia-2017: International Scientific Conference: Youth. Science. Technology, pp. 30-34. Novosibirsk: SSGA.
Zharnikov, V. B., & Epifanova, E. V. (2007). The Problem of property and its effective management in modern conditions. Proceedings of Interexpo GEO-Siberia-2017: International Scientific Congress: Vol.2. 2, 2(2), pp. 15-19. Novosibirsk: SSGA.
1. Ph. D., Tyumen Industrial University, Russia. e-mail: natali.cherdanceva@mail.ru
2. Ph. D., Tyumen Industrial University, Russia. e-mail: budarova@bk.ru
3. D. Sc., Siberia State University of geosystems and technologies, Russia. e-mail: mosk_46@mail.ru
4. Ph. D., Siberia State University of geosystems and technologies, Russia. e-mail: avd5@mail.ru
5. Ph. D., Siberia State University of geosystems and technologies, Russia. e-mail: 131379@mail.ru