

Vol. 41 (Issue 12) Year 2020. Page 12
Kraev Vyacheslav M. 1; Tikhonov Alexey I. 2
Received: 05/12/2019 • Approved: 22/03/2020 • Published 09/04/2020
ABSTRACT: Personnel selection, as well as any business process, should meet modern requirements for minimal personnel risks, appropriate value and high efficiency. The introduction of modern innovative technologies allows meeting these requirements. In the first stages of staff selection, low-cost methods should be actively used without personal contact with the applicant. Information from social networks can be used as data for this stage of selection. The article suggests new mechanisms for using information from social networks on applicants to improve the efficiency of staff selection. The proposed approach allows the selection of applicants segmenting them into "red", "yellow" and "green" groups. “Red” group candidates are expected to be rejected at an early stage. Applicants from the “green" group should be transferred to the final stages of selection, even skipping the intermediate ones. This approach significantly simplifies and speeds up the initial stages of staff selection. |
RESUMEN: La selección de personal, así como cualquier proceso de negocio, debe cumplir con los requisitos modernos de mínimos riesgos para el personal, valor apropiado y alta eficiencia. La introducción de tecnologías contemporáneas e innovadoras permite cumplir con estos requisitos. En las primeras etapas de la selección del personal, métodos de bajo costo sin contacto personal con el solicitante deben utilizarse activamente. La información de las redes sociales puede utilizarse como datos para esta etapa de la selección. En el artículo se sugieren nuevos mecanismos para utilizar la información de las redes sociales sobre los solicitantes a fin de mejorar la eficiencia de la selección de personal. El enfoque propuesto permite seleccionar a los solicitantes segmentando a éstos en grupos "rojos", "amarillos" y "verdes". Se prevé que los candidatos del grupo ”rojo” sean rechazados en una etapa temprana. Los candidatos del grupo "verde" deberían ser trasladados a las etapas finales de la selección, incluso saltándose las intermedias. Este enfoque simplifica y acelera considerablemente las etapas iniciales de la selección del personal. |
Personnel safety and personnel risk management are becoming crucial factors in the construction of business processes at enterprises (Kraev & Tikhonov, 2017). Risk management has become a topical subject in a purely financial sphere at industrial enterprises over the past 40-50 years. The basis of quantitative risk assessment is proposed to be the methodology that is used during audits, namely, risk assessment through the control points of financial and economic activity. The use of this method, as well as the results of a qualitative analysis, allows conducting a comprehensive risk assessment of the financial and economic activity of enterprises. This is one of the simplest and most barrier-free methods for risk assessment, both for the enterprise itself and its partner companies.
Enterprises should not avoid risk, but be able to manage it. One of the main rules of the financial and economic activity says: «One should not avoid risk, but anticipate it and try to reduce it to the lowest possible level» (Bagieva, 2001). In another sense, risk management consists of a systematic process, in which risks are assessed and analysis is conducted to eliminate or minimize their consequences, as well as to achieve goals. Personnel risk is one of the most complex and dangerous risks, therefore, it is necessary to classify these risks by their types. We propose dividing them into separate groups and subgroups according to one or another characteristic to achieve the goals. Each separate risk must have its own method of risk management.
According to the way of occurrence, personnel risks can be divided into quantitative and qualitative. Personnel quantitative risks relate to a shortage, and conversely, an excess of human resources in the enterprise. They may occur in the form of various losses due to the current needs of the enterprise in personnel, that do not correspond to the claimed ones. Personnel qualitative risks result from discrepancy between the actual characteristics of the available personnel of the organization and the requirements for it. They include:
According to the reasons of occurrence, personnel risks can be divided into individual and organizational.
Individual personnel risks include the following types:
Organizational personnel risks are caused, above all, by ineffective work in the sphere of personnel management, namely, ineffective systems of personnel selection and recruitment, personnel motivation and stimulation, career management, etc.
According to the form of possible damage, personnel risks are divided into material risks, the damage from which can be accurately determined in monetary terms, and non-material ones, related to the damage done, for instance, to the image of the enterprise.
According to the possible extent of damage, personnel risks are most often referred to the group of local risks, although the organization may suffer significant losses.
Depending on the degree of sensitivity to risks of the business processes of enterprises, tolerable, acceptable and unacceptable personnel risks are distinguished.
The risk of the correct personnel election should be highlighted among personnel risks.
At this stage, it is necessary to identify at least the level of education, work experience, etc. This task is quite complicated due to the limited information about the applicant. In addition to confirming the information in the questionnaire, it is important to form a view of moral and ethical qualities of the applicant and of how the applicant corresponds to the corporate culture of the company. In most cases, an interview with an applicant is the only source that gives an idea of the motivational and emotional characteristics, as well as the specifics of their social behavior (tact, manners, benevolence, etc.) Sometimes, when trying to make an informed decision during the hiring of a new employee, managers, as well as heads of personnel services, rely primarily on these characteristics (or recommendations) from the previous place of work. The question about if the applicant is honest and decent cannot be answered using the traditional approach. But these qualities are welcomed by the employer and allow reducing personnel risks significantly (Zakharov, 2015; Kudashkin, 2015).
In the era of universal digitalization, social networks are probably the only legal and inexpensive way of obtaining information about the applicant. One of the articles (Zakharov, 2018) describes the broad development of social recruitment — a phenomenon that involves interaction with potential candidates through social networks. The author suggests that social networks should be used not only by members of public relations (PR) departments, but also by personnel services.
Social networks are very useful and effective in the personnel selection (Klimentova, 2018). The main advantage of social networks is that the human resources (HR) manager can establish contact both with those candidates who actively seek employment, and with those who are not currently looking for a job, but are very interesting for the company. Using social networks allows recruiting highly qualified specialists and creating a base of candidates for the future. From the information in the social networks, it is possible to determine what is the psychological profile of the candidate whose curriculum vitae (CV) is before us and to verify the accuracy of part of the information from the CV. For instance, how active and law-abiding their life is, what their hobbies are and whether they will be able to combine these hobbies with our position (e.g. correspondence of personal qualities) (Smirnova & Tsyplakov, 2016; Zhukov & Mansurov, 2018).
Processing and analysis of social networks data allow personalizing a product or service for a specific segment of the target audience (Tikhonov, 2019a). Algorithms and software products that allow marketing assessments of social groups and their participants have already been developed. The quality of the functioning of the personnel management system depends, first of all, not only on how qualified the employees of the enterprise are, but also on the workload one specific specialist, that is, on the level of his productivity. According to the recommendations of specialists, this workload should not exceed 100-120 applicants per month for one personnel manager (Fedotova, Tikhonov & Novikov, 2018), that is, the efficiency of the personnel manager is one of the important criteria. Effective selection determines the creation of a positive image of the company for the further involvement of experienced and skilled candidates for the vacant position.
In the recruitment process, each successive stage of the personnel selection is more expensive. Consequently, it is necessary to develop a set of automatic or semi-automatic, i.e. inexpensive filters that allow «screening out» unacceptable applicants in the early stages of the selection process. When we talk about unacceptable applicants, we mainly mean not the professional level of training, but rather the potential risk of adverse events that may occur in the future. So, we are talking about the so-called «toxic» employees (Voyskunsky, 2014).
How to recognize a potentially dangerous employee for the company in an average young person at the stage of personnel selection? Moreover, according to their personal data, such person is no different from their colleagues. To make such decisions, it is necessary to analyze an applicant not only on the basis of their questionnaire. Much more information can be obtained from social networks, as most young people use them actively. Based on this information, a decision can be made about the possibility or impossibility of considering the applicant at the next stages of selection (Korshunov, Beloborodov, Buzun et. al., 2014).
Social networks already constitute a wealth of information. The amount of accounts on VKontakte is about 26 million, approximately 60% of which are women, and 40% are men. The main users are under the age of 18 years — 37% of the participants. The second group is between the ages of 18 and 24 – it accounts for 25% of users. From more than 7 million Instagram users, 77% are women. Facebook has about 2 billion users. Users of Facebook are older than the ones of VKontakte. The age group of 25-34 years accounts for about 37% of users. 24% of users are over 45 years old (Kulik, 2018).
The authors (Tikhonov & Konovalova, 2019) suppose that according to the external appearances, behavior, processes and products of another person’s activities, it is possible to draw a conclusion about his personal qualities, intentions, abilities, emotional state, social status, cultural level, etc. The accessible list of «friends» of a particular participant can be useful in this regard: it is desirable to have a common acquaintance among them — the reputation of this acquaintance is a kind of testament to the correctness of the actions on interpersonal perception. Nevertheless, one can never be sure that users who are not known are who they claim to be: a presentation may turn out to be deliberately erroneous or provocative, photo materials may not relate to the author of the presentation, biographical information may not coincide with the user's actual biography or coincide only partially. Each user of the social network may have many accounts that are registered for different reasons or differ chronologically (e.g. an abandoned and non-closed account if there is a new and actively used one) or in terms of content, that is, in essence, create different identities of the participants presenting themselves.
According to the Russian Center for the Study of Public Opinion, at least half of Russian respondents distort information about themselves on social networks: from age, marital status, appearance and income, to gender, political and religious views, musical choices, etc (Akhmetshin, Kuderova, Ryumshin et. al., 2019). Thus, on the one hand, although social networks constitute a wealth of information, one should carefully analyze it, in view of the above. Here are some of the difficulties one will encounter when analyzing social networks:
There already exists such segment of services for companies as profiling, and in particular, analysis of social networks (Tikhonov, 2019b).
Now we are going to formulate the main character traits that can be estimated using the information from social networks and may be useful for the employer:
How can these character traits be identified using social networks?
Honesty is a personality feature and the ability to tell the truth, avoid cheating, and determine the truthfulness of other people. Honesty is one of the best qualities of a strong person. Applicant’s honesty can be determined by identifying logical inconsistencies in the information presented in the social networks. After the identification of the applicant in the social network by last name, first name, location, etc., it is necessary to check whether the unique data of the applicant from the questionnaire coincide with the data in the social networks. These data includes date of birth and place of birth. In addition to unique personal data, it is necessary to check the correspondence of the level of education, the name of the educational institution, the year of graduation, the place of previous employment, etc.
Openness is a positive character trait of a strong person, whose consciousness is pure and whose intelligence, feelings and mind are not subject to egoism. Such person displays feelings and emotions sincerely, they are always ready to be self-aware, to perceive new knowledge through their mind and to share it with other people. Open people trust others, they are more sociable, effective in communication and influence, and are disposed to support and other positive forms of interaction. In the context of our study, the openness reflects the amount of personal information (including photos) that is available to other users. Some users make their social accounts unavailable for public view. In this case, we cannot speak of openness (Figure 1). It is possible that such people have something to hide or they feel psychological discomfort, giving everyone access to their personal information.
Figure 1
Example of closed profile
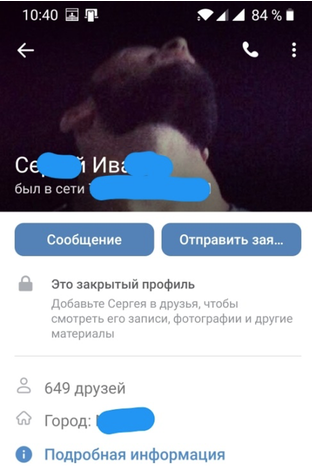
Self-restraint is usually understood as the ability of a person to control their actions, behavior, emotions, inner desires and needs. In psychological literature, self-restraint is a process, during which a person exercises control over their own mental and physiological conditions and their external appearances, as well as over their actions and behavior in general. It also should be noted that it is impossible to cultivate restraint without emotional self-regulation, which can be described as a person’s capacity for socially acceptable emotional reactions to various life situations. Emotional restraint is often considered as one of the components of a person’s self-control. In relation to the subject under discussion, self-restraint is a positive quality of an employee. As a rule, there are fewer limiting factors in Internet communication, as there is no visual contact with the interlocutor, and emotional restraint is exercised better in the form of one’s own statements and links to the emotional messages of others.
Politeness is a moral and behavioral category, a character trait. Politeness is usually understood as the ability to communicate with people respectfully and tactfully, the readiness to find a compromise and listen to opposing views. This character trait is also exercised better in social networks, as the absence of visual contact gives no information about interlocutor and people often overstep the bounds of politeness, which they would not have overstepped in face-to-face communication.
Tolerance is a social, cultural and religious term used to describe collective and individual behavior, the essence of which is non-stalking of those whose thoughts or actions do not coincide with one’s own and cause someone's disapproval. Tolerance implies a conscious decision not to harass people with alien views. This term is usually applied to non-violent behavior based on consensus. Tolerance does not require recognition of the behavior of other people as acceptable; it only means that people tolerate a person or a social group. From a sociological perspective, the concept of tolerance implies non-violence and social stability. Subject to the seeming invisibility in social networks, religious and inter-ethnic intolerance is manifested very quickly.
Dedication is the total concentration of a person on a particular idea. Dedication is the ability to fully devote oneself to some idea, occupation, feeling, it is a permanent directed effort to accomplish the task. Any employer hopes that the employee will be fully and creatively dedicated to the job. If a difficult problem needs to be solved, the employee should think about its solution not only during working hours, but also after hours (Figure 2).
Figure 2
Example of a dedicative person's profile
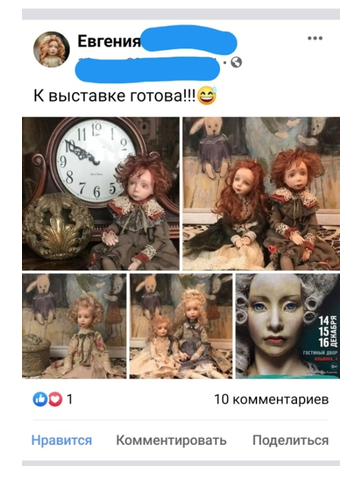
The sad part is that it is very difficult to identify the applicant’s dedication at the selection stage. The applicants can easily pretend they have a hobby, etc.
As a rule, any real hobby is a point of pride and the results of this hobby are usually published in social networks as a subject of the evaluation for friends and acquaintances.
It is possible to get information about all the considered character traits of the applicants from their pages on social networks. After researching this information, a particular profile of an applicant can be formed, which is often far from the one that is shown in the questionnaire and at the interview. If we go further in the discussion, then after revealing an outright negative profile of the applicant from social networks, their candidacy can be rejected immediately after the analysis. In this case, the company saves significant funds in the candidates’ selection by rejecting their candidacies at an earlier stage of consideration.
To formalize the proposed approach, it is necessary to develop a methodology that allows assessing the level of the above psychological qualities of the applicant in standard units, for instance, points.
We propose identifying character traits by the following information:
It is also worth paying attention to the date the profile was created or updated. If the data (text, photo or video) was recently uploaded, this may mean that the applicant has «prepare» their profile in social network for the employer. If the dates are old, this may mean that the information is irrelevant.
The suggested approach makes it possible to get relatively objective information about the applicant rather quickly. After collecting and calculating the total points, the candidates are suggested to be divided into three groups.
Applicants who fell into the «green» group by the number of points can pass the further stages of selection easier and therefore less costly for the company. If the applicant fell into the «red» group, it advisable to close consideration of their candidacy, as the «revealed negativity» will definitely outweigh the positive abilities of the applicant, or such employee will provide an opportunity to realize other personnel risks in future. Moreover, after hiring an applicant, an employer should continue monitoring the Internet activity of their employees on various web resources (social networks, forums and blogs) in order to minimize threats to the company that they may pose.
To sum up, it can be noted that even such apparently simple procedure as hiring a suitable candidate is one of the most important and responsible tasks of the management of any enterprise. At present, when the economy has gradually moved on a market development path, it is necessary not only to fill the staffing table, but to select it in such a way that the employee who was recently hired would fit into the team and work most efficiently for the enterprise, as income depends on it. This is only possible with the objective assessment of the candidate’s level, their qualification, and also their psychological aspect, in order to identify their individual characteristics. In this regard, the most important factor is the competence of the personnel service, which consists in inexpensive and effective methods of personnel selection.
Akhmetshin, E. M., Kuderova, I. G., Ryumshin, A. V., Gayazova, S. R., Romanova, E. V., & Erzinkyan, E. A. (2019). Entrepreneurial skills development through distance learning. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22, 1-12.
Bagieva, M. N. (2001). Conceptual basis for the analysis and estimation of enterprise risks. St. Petersburg: Publishing House Saint-Petersburg State University of Economics.
Fedotova, M. A., Tikhonov, A. I., & Novikov, S. V. (2018). Estimating the effectiveness of personnel management at aviation enterprises. Russian Engineering Research, 38(6), 466-468.
Klimentova, T. A. (2018). Recruitment in Social Networks. HR-tv.ru. Available at: https://hr-tv.ru/articles/podbor-personala-v-sotssetjah.html.
Korshunov, A., Beloborodov, I., Buzun, N., Avanesov, V., Pastukhov, R., Chikhradze, K., Kozlov, I., Gomzin, A., Andrianov, I., Sysoev, A., Ipatov, S., Filonenko, I., Chuprina, K., Turdakov, D., & Kuznetsov S. (2014). Social network analysis: methods and applications. Available at: https://www.ispras.ru/proceedings/docs/2014/26/1/isp_26_2014_1_439.pdf
Kraev, V. M., & Tikhonov, A. I. (2017). Countering deception in personnel work. Stavropol: LOGOS.
Kudashkin, I. V. (2015). Peculiarities of bailiffs’ working with social networks. Actual Problems of Jurisprudence in Modern Russia, 5, 257-261.
Kulik, A. V. (2018). Personality analysis using social networks as an effective method of personnel selection. Available at: http://www.4dk.ru/news/d/20181005135017-analiz-lichnosti-po-sotsialnym-setyam-kak-effektivnyy-metod-podbora-kadrov
Smirnova, P. V., & Tsyplakov, A. A. (2016). The self-presentation and the formation of social capital in business social networks. Naukovedenie, 8(6), 66-75.
Tikhonov, A. I. (2019a). Applying of employer branding system in the IT-companies´ human resource management. Espacios, 40(38), 23-27.
Tikhonov, A. I. (2019b). The use of networking in staff recruitment: recommendations and referral programs. Amazonia Investiga, 8(19), 521-528.
Tikhonov, A. I., & Konovalova, V. G. (2019). The Relation of the Russian Employers to Automation in the Sphere of Human Resource Management: Technologies of Artificial Intelligence and Staff Recruitment. Human Resources and Intellectual Resources Management in Russia, 8(2), 79 -84.
Voyskunsky, A. E. (2014). Social perception while social networking. Bulletin of Moscow University, 2, 90-104.
Zakharov, D. K. (2018). Recruitment Using Social Networks. Control, 6(1), 25-30.
Zakharov, D. N. (2015). Social estimation of images presented in social networks. Journal of Legal and Economic Studies, 3, 200-202.
Zhukov, D. V., & Mansurov, A. V. (2018). Methodology for the identification of socially dangerous links in computer social networks. Measuring, Checking and Automation, 2, 170-173.
1. Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor of Department «Human Resource Management», Moscow Aviation Institute (MAI), 125993, Volokolamskoe highway 4, Moscow, Russia, mai512hr@mail.ru
2. PhD, Head of Department «Human Resource Management», Moscow Aviation Institute (MAI), 125993, Volokolamskoe highway 4, Moscow, Russia, mai512hr@mail.ru
[Index]
revistaespacios.com

This work is under a Creative Commons Attribution-
NonCommercial 4.0 International License