

 Vol. 40 (Number 8) Year 2019. Page 14
Vol. 40 (Number 8) Year 2019. Page 14
OLGARENKO, Gennady V. 1; UGRYUMOVA Alexandra A. 2; PAUTOVA Ludmila E. 3; EZHIKOVA Tatyana S. 4
Received: 24/10/2018 • Approved: 30/01/2019 • Published 06/03/2019
ABSTRACT: The purpose of this publication was to identified the most important problems of supplementary education of specialists of the Reclamation’s Department of the Russian Federation. At the article the authors used such methods as logical, economic and situational analysis. The role of supplementary education is justified. The dynamics of specialists who have received this kind of educational training is analysed. A register of supplementary education’s modern types for specialists of the Reclamation’s Department was compiled. The authors proposed a mechanism for managing the professional development of industry specialists. The results of the analysis can be used in the development of state and regional programs on the different levels. The article reflects the systematisation of the supplementary education’s types which can be applied to the meliorative industry. The mechanism of the professional development’s management for the specialists of the Reclamation’s Department of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation is presented. The work concretises the interrelation of competences and differences on the skill levels with programs of advanced training and retraining. The necessity of the built-in legislative mechanisms which are stimulated the specialists to the constant professional growth is revealed. A prescriptive method for recruiting of trained specialists is proposed. The necessity of fixing mandatory certification of educational programs is proved. The integration of specialists certification of the federal state budget institutions of the Reclamation’s Department into the system of professional development and retraining of specialists is substantiated. |
RESUMEN: El propósito de esta publicación fue identificar los problemas más importantes de la educación complementaria de los especialistas del Departamento de Reclamación de la Federación Rusa. En el artículo los autores utilizaron métodos como el análisis lógico, económico y situacional. El papel de la educación complementaria está justificado. Se analiza la dinámica de los especialistas que han recibido este tipo de formación educativa. Se compiló un registro de los tipos modernos de educación suplementaria para especialistas del Departamento de Reclamación. Los autores propusieron un mecanismo para gestionar el desarrollo profesional de los especialistas de la industria. Los resultados del análisis se pueden utilizar en el desarrollo de programas estatales y regionales en los diferentes niveles. El artículo refleja la sistematización de los tipos de educación complementaria que se pueden aplicar a la industria de mejora. Se presenta el mecanismo de gestión de desarrollo profesional para los especialistas del Departamento de Reclamación del Ministerio de Agricultura de la Federación de Rusia. El trabajo concreta la interrelación de competencias y diferencias en los niveles de habilidad con programas de capacitación avanzada y reciclaje. Se revela la necesidad de los mecanismos legislativos incorporados que estimulan a los especialistas para el crecimiento profesional constante. Se propone un método prescriptivo para el reclutamiento de especialistas capacitados. Se prueba la necesidad de fijar la certificación obligatoria de los programas educativos. La integración de la certificación de especialistas de las instituciones presupuestarias del estado federal del Departamento de Reclamación en el sistema de desarrollo profesional y capacitación de especialistas está justificada. |
Modern supplementary education is an important factor in the management of human resources of the organization. The change in technology, the rapid emergence of new demands on the employee, objectively cause the need to improve existing competencies and professional activities continuously or to develop new types of them fundamentally. The importance of the continuing supplementary education or "lifelong education" was emphasized in the "Report of the Working Group at the Presidium of the State Council of the Russian Federation on Education Reform", published on August 29, 2001.
In this document they say about the need to "create conditions for continuous professional growth of specialists, ensure the continuity of various levels of supplementary education and create an effective system of additional vocational education."
Strengthening the influence of supplementary education on human capital is also associated with global changes in the world and national labor markets.
All of the above fully applies to so the supplementary education system as a whole as its functioning in the sectoral context. Well-founded predictions have already been that in the nearest future all routine occupations will disappear because artificial intelligence (AI) will successfully replace a person at these jobs.
Thus, the World Economic Forum predicts that the developed world will lose 5 million jobs due to robots by 2020. Scientific American experts have found that 40% of the 500 largest companies will disappear within ten years. Former Microsoft and Google CEO Kai Fu Lee, the chief investor of Chinese AI startups, believes that artificial intelligence "will replace 50% of human professions."
In such conditions, professions and competences which are directly targeted to the client acquire special significance. The World Economic Forum singled out top 10 skills which will be in demand by 2020, such as creativity, flexibility of thinking, tolerance in relationships, adaptability, management skills, punctuality, service orientation, etc. Almost all of these qualities relate to Soft skills.
Categories of Soft skills and hard skills are the subject of discussions and employers have to use such technologies during the selection of employees, which allows them to identify candidates the ability of using soft skills.
For a significantly grown-up able-bodied population of the Russian Federation, after the retirement age will increase from January 1, 2019, it becomes quite important to identify the areas, professions, specialties and competencies which are demanded in this century.
Today, the Russian educational field demonstrates a wide variety types of supplementary education, due to different approaches and views on the implementation of this level of education. This idea is confirmed by the data (Table 1).
Table 1
Distribution of the Russian Federation’s specialists who have been
trained at supplementary education for 2013-2015, thousand people
Types of training |
Years |
Growth, % |
||
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
||
The number of specialists who have been trained at supplementary education, total including: |
2 000 |
3 824 |
4 298 |
115 |
|
1 268 |
3 473 |
3 871 |
205 |
Professional retraining, total, including: |
126 |
351 |
428 |
239 |
|
28 |
162 |
215 |
667 |
|
98 |
189 |
213 |
117 |
Source: http://www.gks.ru/ and authors' calculations.
It can be seen from [Table 1] the dynamics of the distribution of specialists who have completed training by various programs of supplementary education has been positive for the 3 years. At the same time, the maximum increase is provided by specialists trained by the retraining programs from 250 to 500 hours. This indicates the demand for new specialties by the labor market and characterizes the tendency for employees to acquire additional specialties during their working life. Nevertheless, the maximum number of specialists choose to upgrade their qualification as an option that is less expensive (often the training is carried out at the expense of the student's extrabudgetary resources) and less labor-intensive (the possibility of learning without interruption from a permanent place of work). The total number which coveres the upgrading of qualifications of the Russian Federation’s specialists has increased for the period 2013 - 2015 from 2.7% to 5.6% (almost in 3 times), which indicates the high relevance of this type of training.
With the development of market relations, there has been a polarization of the supplementary education’s programs which realised within the framework of the state task and on the order of legal entities and individuals in the country. However, the source of funding for the supplementary education’s programs hasn’t generally a regulatory impact on the quality of the educational program.
Moreover, voluntary certification of educational programs, which without having an official legislative base, is in fact an experimental one on the educational market of the country, is another important direction of the modern development of supplementary education.
However, the importance of supplementary education’s certification increases invariably, it is connected with a number of such objective reasons, such as:
-availability of professions and specialties, where international certification (IT, foreign language, etc.) is widespread;
-appearance and dissemination of professional standards in the Russian Federation;
-creation of centers for the assessment of qualifications (CSCs) that carry out and certify specialists according with professional standards;
-increasing of the requirements' volatility for the competencies of employees;
-increase in the working-age period.
The variety of supplementary education’s types implemented in the modern educational space of the Russian Federation can be reflected [Fig. 1].
Fig. 1
Classification of modern types of supplementary education
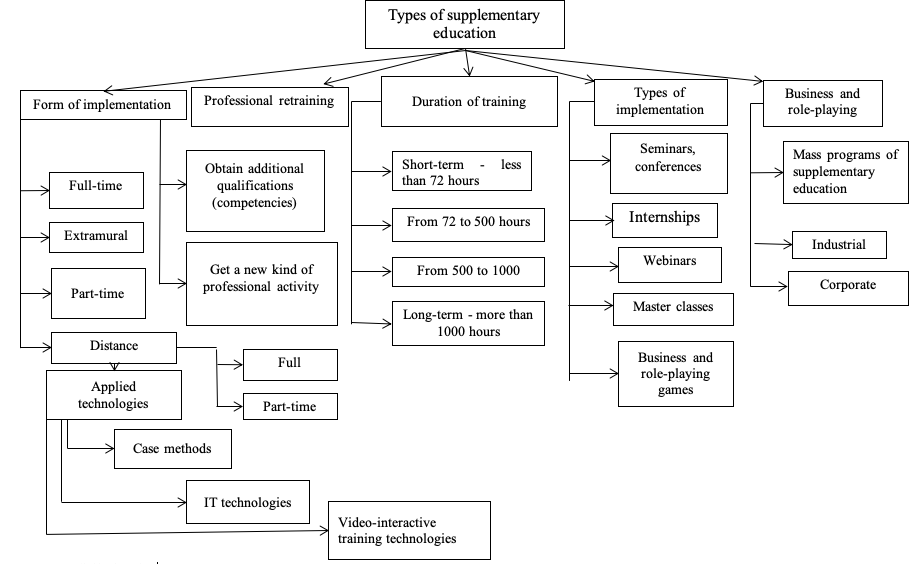
Source: compiled by the authors
Consider the specifics of implementing this structure of supplementary education in the conditions of training and retraining specialists of the Department of Reclamation.
The need to systematize the demanded programs of supplementary education calls for the formation of a register of best practices for the implementation of land reclamation's supplementary education.
Recent years are characterized by a sharp aging of engineering, management and working specialists: the average age is about 55-60 years. Meanwhile, no more than 1000 engineers graduate reclamation institutes (that is, in terms of operation, no more than 200-300 people).
Practically the training of special technical specialists and working specialties is stopped. If this trend continues, then there will be no one to exploit the reclamation systems after 5-10 years.
A complex of measures is needed to attract young specialists to the industry, the renewal of targeted training, retraining and upgrading of engineering and technical specialists and highly skilled workers.
It is also important to establish training and production centers on the basis of state agrarian higher educational institutions of the Ministry of Agriculture for the training and retraining of engineers for the design, operation and repair of melioration and irrigation systems, and specialists with secondary specialized education in the operation and maintenance of meliorative equipment.
Attraction of graduates from rural areas with financing of training from the Federal budget in the direction of the Department of Reclamation with the granting of benefits upon admission. Organize the construction of housing for young reclamation specialists working in operational organizations, allocating at least 500 million rubles in centralized funds, with connection to the Federal target programs "Social Development of the Village" and "Housing for Young Professionals".
According to modern standards, the following personnel support is provided for the operation of reclamation systems: the chief engineer is 1 person on 2000 hectares; senior engineer - 1 person for 2000 hectares, engineer - 1 person on 500 hectares, technician - 1 person on 200 hectares, working specialists - 10 people on 2000 hectares from the calculation of training specialists with higher education for 5 years, medium-technical - 3 years, working specialties - 1 year. Not all services for the exploitation of reclamation systems are manned in accordance with these standards.
The cost of training specialists with higher education is about 50 thousand rubles per year, medium-technical - 25 thousand rubles, and working specialties - 20 thousand rubles. Financing the upgrading of the qualifications of sectoral specialists is not sufficient at the expense of the state task, and off-budget sources are also limited and regulated by their structure.
Today it is possible to single out a number of enlarged directions of supplementary education in the industry, which provide the highest level of professional development of specialists taking into account changing requirements to their competencies. This group is presented in [Table 2].
Table 2
Register of supplementary education's modern types for specialists
of the Reclamation's Department of the Russian Federation
Directions of supplementary education |
The name of the supplementary education's program |
The categories of specialists and positions which are focused on training under the program |
Management |
Competences of an effective leader |
Directors, industrial builders, economists, deputy directors, irrigation engineers, managers, zootechnicians, electrical engineers, lawyers, agronomists |
Psychological features of managerial activity in budget organizations |
Directors, economists, deputy directors, managers, lawyers |
|
Features of management of budgetary organizations on the example of Federal State Research Institution All-Russia Scientific and Research Institute |
Directors, economists, deputy directors, managers, lawyers |
|
Contract system in the sphere of procurement of goods, services for provision of state and municipal needs |
Legal advisors, economists, financiers, software engineers, deputy directors, marketers, engineers for the exploitation of land reclamation systems, agronomists, engineers, ameliorators, bookkeepers, builders, hydrotechnicians, livestock specialists, land reclamation specialists, managers, procurement department chiefs, directors, project engineers -metrical work, electrical engineering, labor protection and safety specialists, environmental engineers, inventory engineers of buildings and structures |
|
Career management and professional professional quality |
Managers, directors, economists, deputy directors, managers, lawyers |
|
Management - the personnel reserve of managers |
Managers, directors, economists, deputy directors, managers, lawyers |
|
Economics and organization of land improvement |
Insurance of civil liability of the owner of a dangerous object for causing damage as a result of an accident at a hazardous facility. Compulsory types of insurance |
Directors, economists, deputy directors, managers, lawyers |
Remuneration of labor in budget organizations. An effective contract. |
Economists, accountants, human resources specialists |
|
The procedure for adjusting the list of particularly valuable movable property. Disposal of state property |
Economists, accountants, directors, deputy directors, managers, lawyers |
|
Audit of personnel |
Economists, human resources specialist, managers |
|
Taxation of a budgetary organization. Tax and accounting reporting |
Chief accountants, economists, accountants, marketers, lawyers, engineers, managers |
|
Fundamentals of business planning of activities (peasant) farms |
|
|
Technique and technology of land reclamation |
Preparation of engineering and technical specialists for the operation of sprinklers and irrigation equipment |
Directors, engineers, chiefs of the department of material and technical supply, mechanics of the service of meliorative systems, agricultural mechanics |
Melioration of soils: drainage and irrigation |
Hydraulic engineers, engineers, ameliorators, deputy directors, specialists in information technology, meliorators of the exploitation service of reclamation systems, meliorators |
|
Monitoring of agricultural lands |
Hydraulic engineers, engineers, ameliorators, deputy directors, specialists in information technology, meliorators of the exploitation service of reclamation systems, meliorators |
|
Effective using of irrigated land |
Hydraulic engineers, engineers, ameliorators, deputy directors, specialists in information technology, meliorators of the exploitation service of reclamation systems, meliorators |
|
Environmental management and water using |
Hydraulic engineers, engineers, ameliorators, deputy directors, specialists in information technology, meliorators of the exploitation service of reclamation systems, meliorators |
|
Energy efficiency, using of material and technical resources and water using. Certification of land reclamation systems |
Hydraulic engineers, engineers, ameliorators, deputy directors, specialists in information technology, meliorators of the exploitation service of reclamation systems, meliorators |
|
Development of safety declarations for hydraulic structures |
Hydraulic engineers, engineers, ameliorators, deputy directors, specialists in information technology, meliorators of the exploitation service of reclamation systems, meliorators |
|
Innovative technologies of crops' cultivation on irrigated lands |
Agronomists, heads of the department for the development of the agro-industrial complex, chiefs of reclamation departments, specialists of the reclamation department, environmentalists |
|
Modern technologies of crop management |
Agronomists, heads of the department for the development of the agro-industrial complex, chiefs of departments of land improvement, specialists of the department of land reclamation |
|
Hydrometeorology of agrolandscapes |
Builders, deputy directors for budget and contract work, economists, meliorators |
|
Labor protection at agricultural enterprises |
Engineers, ameliorators, agricultural builders, warehouse managers, primary school teachers, deputy directors, ground radio equipment operators, mechanics of the operation of reclamation systems, agricultural machinery operators, economists, chiefs of planning and production departments, chief mechanics, electricians, maintenance of land reclamation systems, leading labor safety engineers, builders, major meliorators, chief engineers, agronomists, radio engineer |
|
Development of projects for environmental protection for various types of agro landscapes |
Builders, deputy directors for budget and contract work, economists, meliorators |
|
Pre-certification training of specialists of organizations in the field of safety of hydraulic structures (with breakdown by professional training modules) |
Engineers-ameliorators, technicians, deputy directors, hydraulic engineers, engineers for wheeled and caterpillar machines, engineers, biologists, meliorators of the service of reclamation systems operation, heads of irrigation systems operation service, civil engineers, agronomists |
|
Design, construction and operation of hydromeliorative systems and hydraulic structures |
Deputy directors, specialists in the departments of capital construction, heads of departments for operation and monitoring of land reclamation systems, electrical engineers, agronomists, environmentalists, meliorators, economists, hydraulic engineers, mechanics, directors, scientists, agronomists, engineers, specialists of water use and cadastre department, , engineers for technical supervision, geodesists, junior staff, lawyers |
All of the above supplementary education's programs can be adapted to the requirements of specialists in terms of duration and the form of their implementation. The presented list is constantly expanding in accordance with sectoral changes and socio-economic trends in the national economy of the Russian Federation.
Thus, there is a need to coordinate the ongoing process of professional development of industry specialists in accordance with the most important tasks facing the organizations of the Reclamation's Department. The authors proposed a mechanism for managing the professional development of industry specialists in the form [Fig. 2].
Fig. 2
Mechanism of management of specialists' advanced training of the Reclamation's
Department of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation
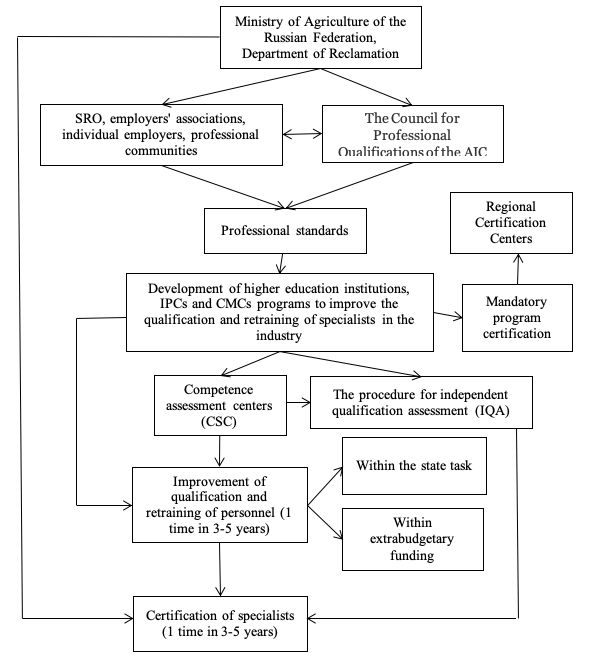
As you can see from [Fig. 2], the development of professional standards should be placed in the basis of continuing (once every 3-5 years) professional development of staff and their subsequent certification. At the same time, representatives of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation as the Council for Professional Qualifications of the AIC, as well as representatives of employers, SROs, associations of employers, individual professional communities take an active part in the development of professional standards.
The immediate process of developing packages for programs to improve the skills and retraining of personnel is largely a reflection of the creativity of specific educational organizations that specialize in this educational field. Therefore, the register of modern types of supplementary education for specialists of the Reclamation's Department of the Russian Federation will constantly change according to changes in the requirements of the modern economy and the development of scientific and technological progress.
At the same time, basic training programs (PCs) and retraining should undergo mandatory certification, not voluntarily, as certification provides a number of benefits for the employee and for the employer.
Thus, it is possible to systematize the most significant contemporary problems of implementing supplementary education in training specialists of the Department of Reclamation:
At first, in the conditions of the transition from the Unified tariff-qualification reference book of works and occupations of the workers and the Qualification Reference Book for the positions of managers, specialists and employees to professional standards, it is necessary to specify the competencies and differences in skill levels, which must be reflected in the programs of professional development and retraining.
Secondly, in the face of ever-changing demands on modern workers, there is a need for built-in legislative mechanisms that encourage staff to receive regular training, either as a part of improving their existing qualifications or as a part of retraining.
Thirdly, the continuity of educational and professional standards should be ensured, taking into account the interests of all characters who are involved in the training of employees.
Fourthly, the personnel training of the Reclamation's Department within the state task should envisage the application of the normative approach in the acquisition of trainees by local Federal State Research Institutions.
Fifthly, it is necessary to fix mandatory certification of educational programs, which will allow implementing such principles of education as unification, continuity, competitiveness and quality of educational and methodological support of programs.
Sixthly, the certification of the specialists of the Federal State Research Institutions of Reclamation's Department should be integrated into the system of professional development and retraining of personnel and has a result of the final evaluation of the success of the specialists' activity.
Today in the Russian Federation, the shortage of highly skilled workers is 27 percent, the heads of local departments - from 23 to 32 percent. And first of all it refers to large enterprises . In addition, there is a tendency of emigration of highly qualified specialists abroad, which aggravates the situation with the preparation of such specialists for local enterprises and organizations.
In these conditions, all the measures listed and proposed by the authors can help to reduce tensions in the labor market in terms of providing highly qualified specialists.
Press service of the President of the Russian Federation. 2001. "Report of the Working Group at the Presidium of the State Council of the Russian Federation on Education Reform". http://president.kremlin.ru/text/docs/2001/08/30255.shtml.
Boboshko, E.V. 2016. "Problems and prospects of supplementary education's development". Pedagogical sciences 54-2. https://novainfo.ru/article/8477.
Dram, K. 2017. "Not millions people will lose their jobs - tens of millions." https://vc.ru/29737-ne-milliony-lyudey-poteryayut-rabotu-desyatki-millionov.
Ibragimova, O.V, and N.V. Kuznetsova. "Distance educational technologies in additional vocational education": 421-435. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/distantsionnye-obrazovatelnye-tehnologii-v-dopolnitelnom-professionalnom-obrazovanii
Kalugina, T G.2013. Why we need certification of qualifications. http://www.akvobr.ru/sertifikacia_kvalifikacii.html.
Kovalyov, V.A. 2014. "The system of additional professional education: main problems and development prospects". Professional education in Russia and abroad 4 (16): 8-13.
Medyannikova, E.V. "Supplementary professional education: problems and prospects".http://mospolytech.ru/science/autotr2009/methodical/articles/m03/m03_08.pdf.
Olgarenko, G.V., and A.A. Ugryumova. 2016. " Assessment of competencies and skills development managers of federal state research institutions in the field of land improvement". Irrigation and water management: problems and solutions: 302-304.
Ugryumova, A.A., and G.V. Olgarenko. 2016. "Competence approach in raising the qualifications of the leaders of the federal state research institutions in the field of land reclamation". International scientific publication Modern fundamental and applied researches 2(21): 271-277.
Ugryumova, A.A., ed. 2017. Modern trends in socio-economic development of regions. Kolomna: State Educational Institution of Higher Education of Moscow Region State University of Humanities and Social Studies.
1. Doctor of Agricultural Sciences, Professor. Federal State Research Institution All-Russia Scientific and Research Institute for Irrigation and Farming Water Supply Systems “Raduga”, Russia
2. Doctor of Economics, Professor. Federal State Research Institution All-Russia Scientific and Research Institute for Irrigation and Farming Water Supply Systems “Raduga”, Russia *corresponding author: feminaa@mail.ru
3. Candidate of Psychology, Associate Professor. Federal State Research Institution All-Russia Scientific and Research Institute for Irrigation and Farming Water Supply Systems “Raduga”, Russia
4. Specialist in Teaching and Methodological Work. Federal State Research Institution All-Russia Scientific and Research Institute for Irrigation and Farming Water Supply Systems “Raduga”, Russia
5. Press service of the President of Russia. 2001. "Report of the Working Group at the Presidium of the State Council of the Russian Federation on Education Reform". Accessed August 29, 2001. http://president.kremlin.ru/text/docs/2001/08/30255.shtml
6. Dram, K. 2017. Not millions people will lose their jobs - tens of millions. https://vc.ru/29737-ne-milliony-lyudey-poteryayut-rabotu-desyatki-millionov
7. Kalugina, T G.2013. Why we need certification of qualifications. http://www.akvobr.ru/sertifikacia_kvalifikacii.html